W/ Neel Guha & Mayee F. Chen of Stanford university.
Speakers: Mayee Chen, Neel Guha, Cecile Tamura

In a groundbreaking study published in the journal Optica, this innovative instrument emerges from the collaborative genius of the National Quantum Science and Technology Institute (NQSTI), incorporating expertise from several esteemed institutions. The device serves as a window into a dual universe, allowing the simultaneous examination of phenomena governed by both classical laws and the bizarre rules of quantum mechanics.
At the heart of this discovery lies the technique of optical trapping, a method that harnesses the power of light to manipulate microscopic particles. Now, empowered by the insights of physicist Francesco Marin and his team, the dual laser setup dramatically enhances our understanding of how these nano-objects interact. As they oscillate in their laser confines, the spheres reveal a dance of behaviors—some that align with our everyday experiences, and others that defy our intuition.

What would you think if I told you that traveling faster than light is no longer pure science fiction? Scientists have found a way to do it 10 times faster.
Science surprises us once again! Scientists have reached a revolutionary milestone by discovering a new theoretical way to travel faster than light. This breakthrough, based on innovative concepts in physics, opens the door to incredible possibilities in the realm of space exploration and the conquest of the cosmos. In this article, we will explore in detail this exciting development and the implications it could have for the future of humanity.

When it comes to AI research, the company leading the way is undoubtedly OpenAI. Having successfully launched ChatGPT, the San Fransisco-based organisation has bigger targets in mind now.
In December 2024, it launched its latest version, o3, which has shown significant progress when it comes to Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). In other words, it has launched an AI system that can understand, learn and apply knowledge across a wide variety of tasks just like a human being.
But now, OpenAI CEO Sam Altman has revealed in his latest blog that the focus has shifted towards Superintelligence.
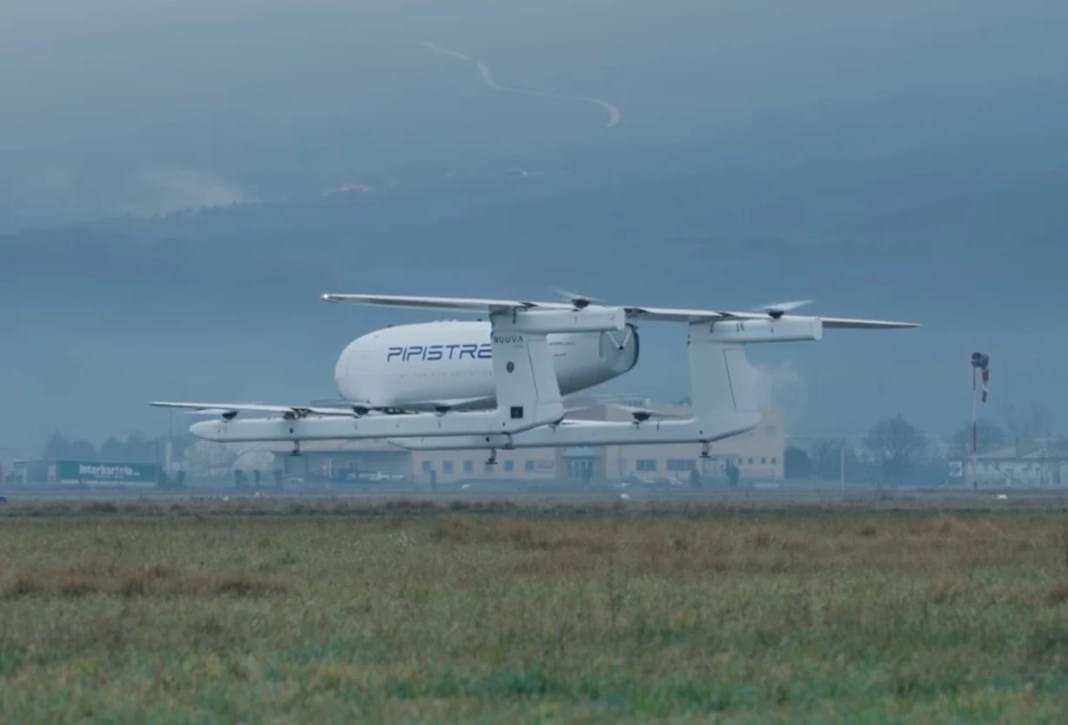

Pipistrel Aircraft has announced the successful completion of the first hover flight for its Nuuva V300, a hybrid-electric vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) unmanned aircraft designed for long-range logistics and specialized defense operations.
The milestone brings the company closer to deploying its autonomous cargo drone, which promises to revolutionize aerial deliveries with a 600-pound payload capacity and a 300-nautical-mile range.
The Nuuva V300 represents a leap forward in hybrid-electric propulsion, combining eight battery-powered electric motors for vertical takeoff with an internal combustion engine for forward flight. This dual-power system enhances fuel efficiency, minimizes maintenance costs, and provides greater operational flexibility. The aircraft’s design allows it to carry up to three Euro pallets (EPAL) through a nose-loading fuselage, offering a streamlined solution for cargo logistics, humanitarian aid, and defense applications.
The future of medicine may very well lie in the personalization of health care—knowing exactly what an individual needs and then delivering just the right mix of nutrients, metabolites, and medications, if necessary, to stabilize and improve their condition. To make this possible, physicians first need a way to continuously measure and monitor certain biomarkers of health.
To that end, a team of Caltech engineers has developed a technique for inkjet printing arrays of special nanoparticles that enables the mass production of long-lasting wearable sweat sensors. These sensors could be used to monitor a variety of biomarkers, such as vitamins, hormones, metabolites, and medications, in real time, providing patients and their physicians with the ability to continually follow changes in the levels of those molecules.
Wearable biosensors that incorporate the new nanoparticles have been successfully used to monitor metabolites in patients suffering from long COVID and the levels of chemotherapy drugs in cancer patients at City of Hope in Duarte, California.
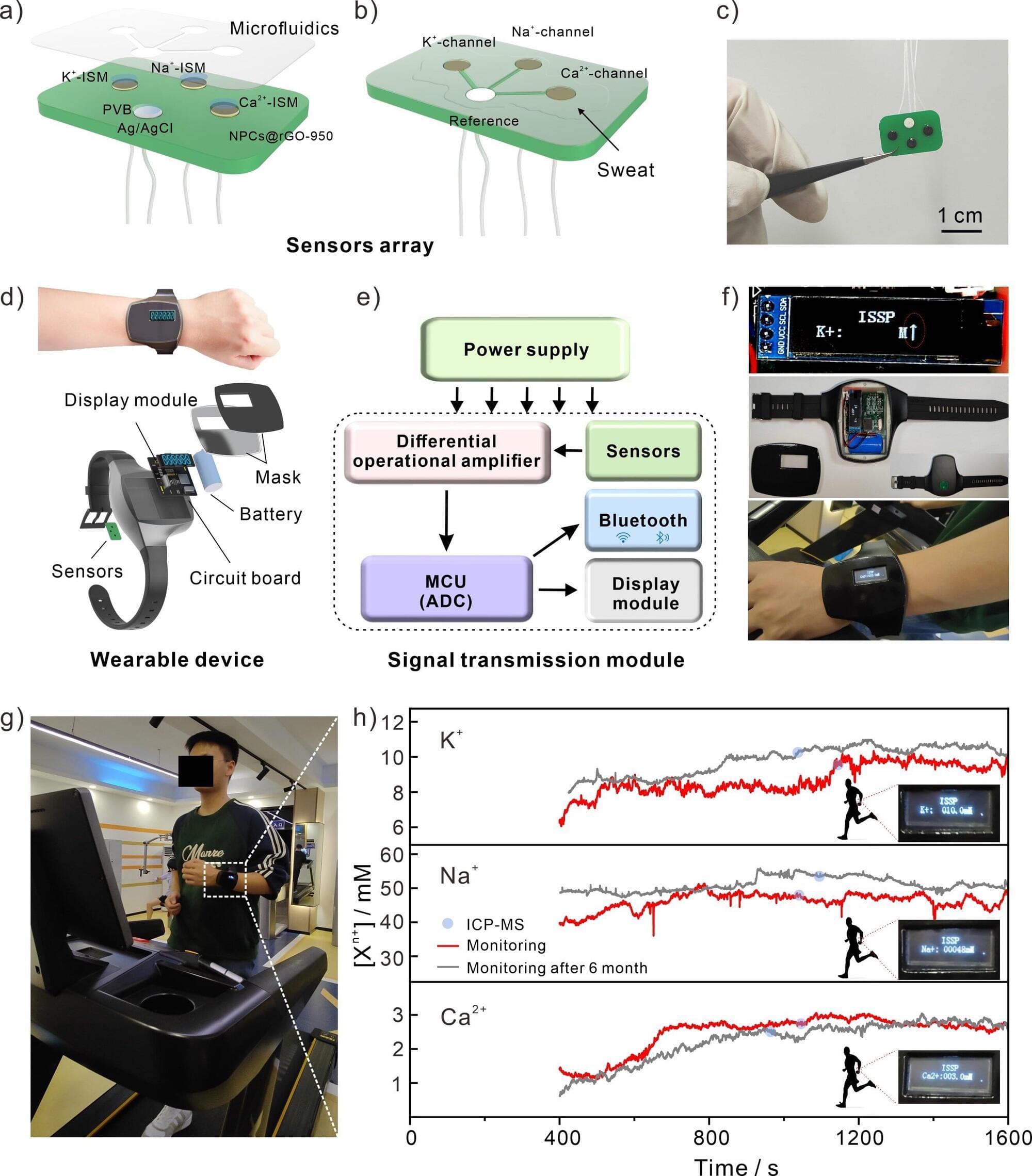
Researchers have created a unique wristwatch that contains multiple modules, including a sensor array, a microfluidic chip, signal processing, and a data display system to monitor chemicals in human sweat. Their study is published in the journal ACS Nano.
“It can continuously and accurately monitor the levels of potassium (K+), sodium (Na+), and calcium (Ca2+) ions, offering both real-time and long-term tracking capabilities,” said senior researcher Prof. Huang Xingjiu from the Institute of Solid State Physics at the Hefei Institutes of Physical Sciences of Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Tremendous progress has been made in sweat sensors based on electrochemical methods, making it easier to track body changes. The stability of the sensor chip is crucial for its application effect and service life, which is the key to ensuring the long-term reliable operation of the sensor.
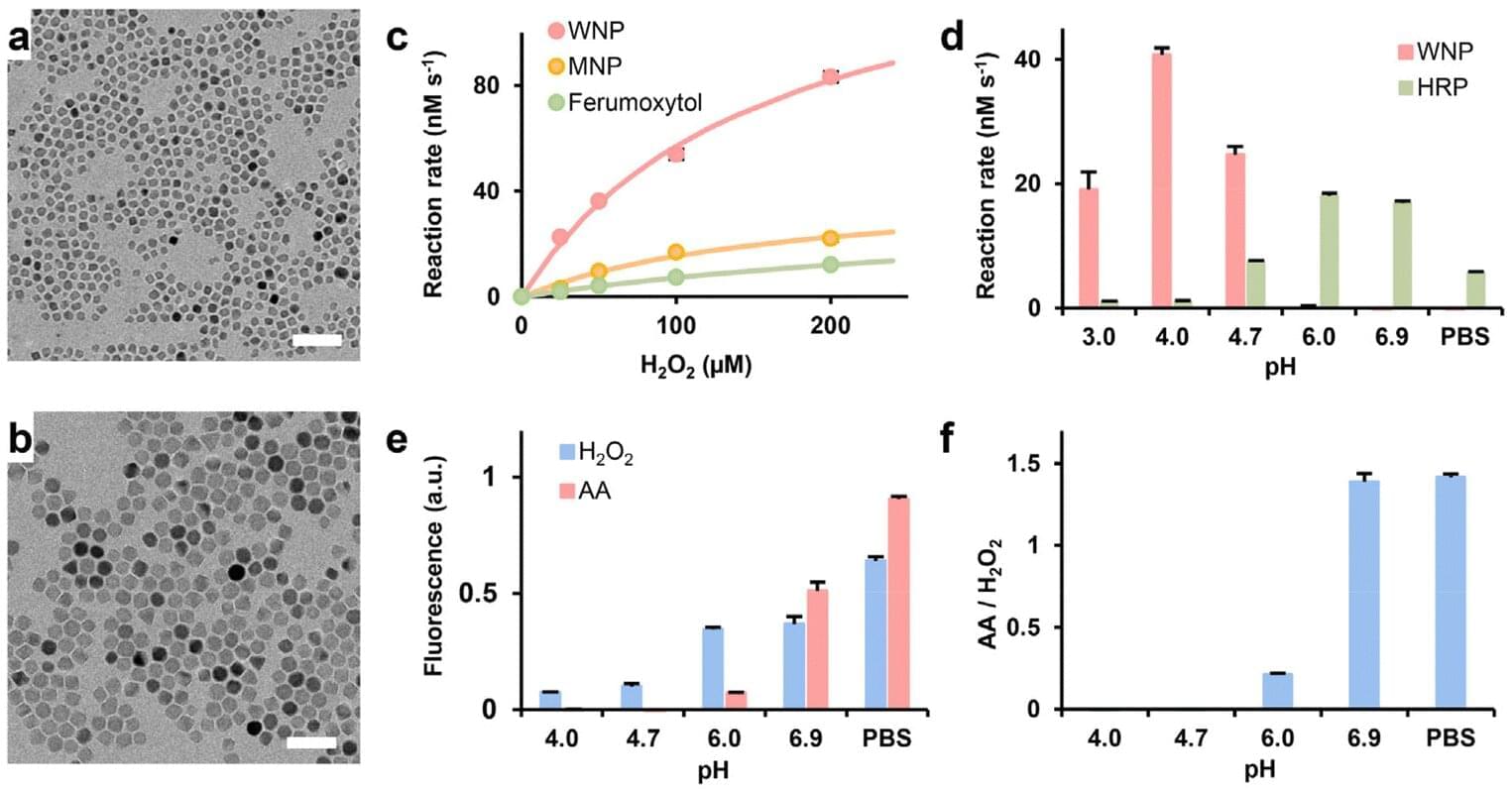
Researchers at the University of Kentucky are exploring new ways to use nanoparticles in combination with other materials as an innovative approach to cancer therapy.
The paper titled “Iron Oxide Nanozymes Enhanced by Ascorbic Acid for Macrophage-Based Cancer Therapy” was published earlier this year in Nanoscale.
Sheng Tong, Ph.D., an associate professor in the F. Joseph Halcomb II, M.D., Department of Biomedical Engineering in the UK Stanley and Karen Pigman College of Engineering, led the study.
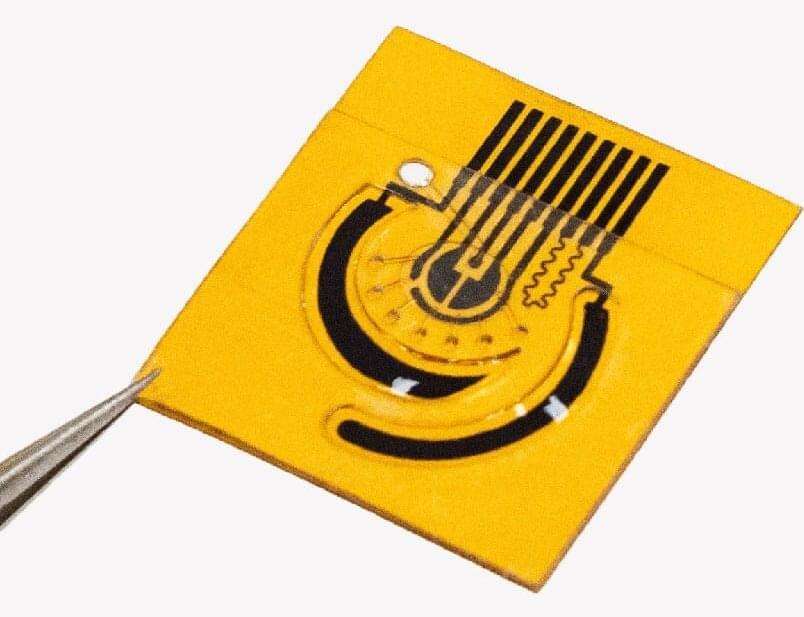

If you have ever had your blood drawn, whether to check your cholesterol, kidney function, hormone levels, blood sugar, or as part of a general checkup, you might have wondered why there is not an easier, less painful way.
Now there might be. A team of researchers from Caltech’s Cherng Department of Medical Engineering has unveiled a new wearable sensor that can detect in human sweat even minute levels of many common nutrients and biological compounds that can serve as indicators of human health.
The sensor technology was developed in the lab of Wei Gao, assistant professor of medical engineering, Heritage Medical Research Institute investigator, and Ronald and JoAnne Willens Scholar. For years, Gao’s research has focused on wearable sensors with medical applications, and this latest work represents the most precise and sensitive iteration yet.