By housing an optical tweezer array inside a cryogenic vacuum chamber, researchers have trapped rubidium Rydberg atoms for up to 50 minutes.

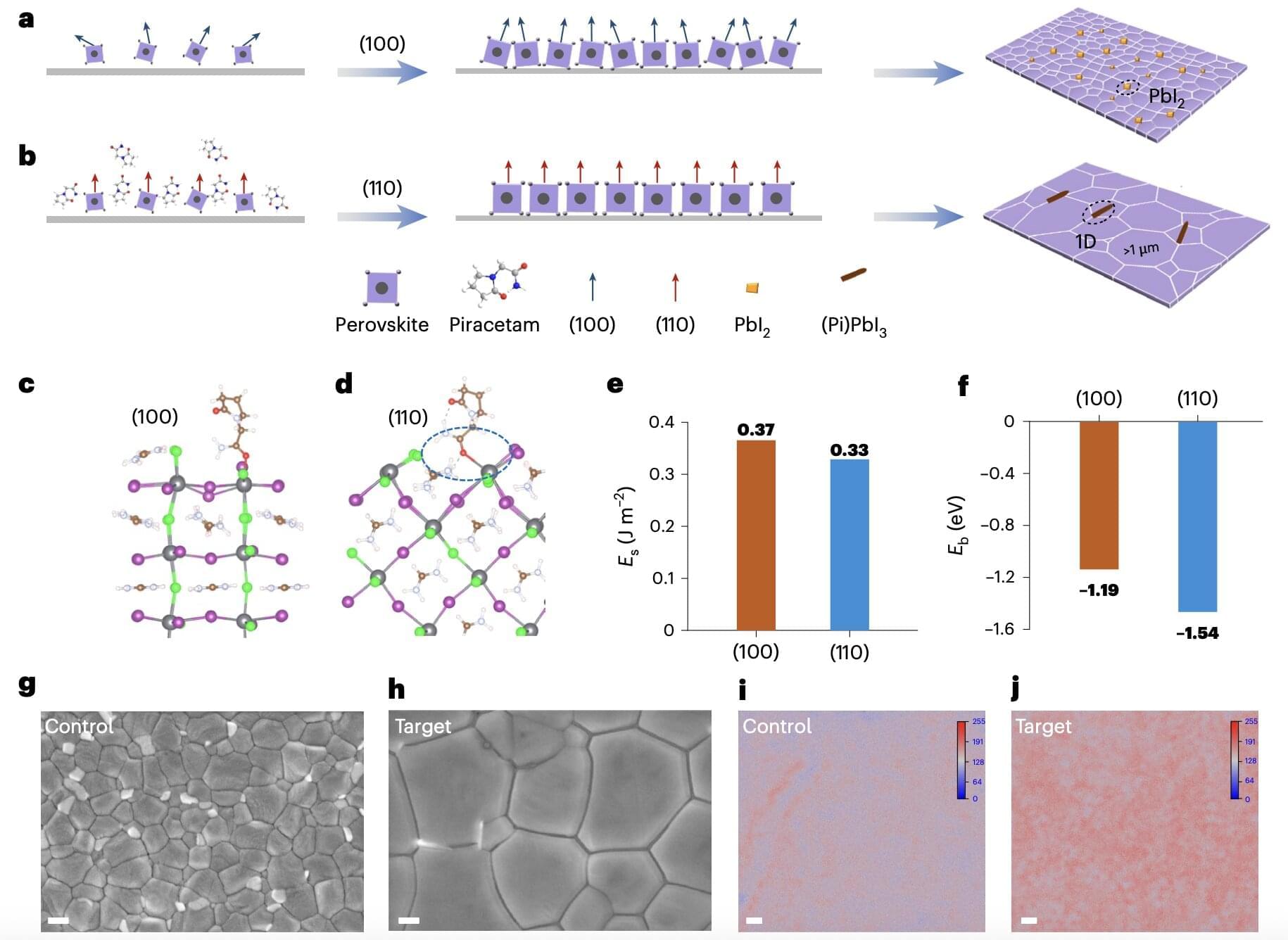
All-perovskite tandem solar cells (TSCs) are a class of solar cells comprised of two or more sub-cells that absorb light with different wavelengths, all of which are made of perovskites (i.e., materials with a characteristic crystal structure known to efficiently absorb light). These solar cells have been found to be highly promising energy solutions, as they could convert sunlight into electricity more efficiently than existing silicon-based solar cells.
Despite their potential, most all-perovskite TSCs developed to date only perform well when they are small and their performance rapidly declines as their size increases. This has ultimately prevented them from being manufactured and deployed on a large-scale.
Researchers at Wuhan University and other institutes in China recently introduced a new strategy for enhancing the performance of all-perovskite TSCs irrespective of their size, which could in turn contribute to their future commercialization. Their proposed approach for fabricating these cells, outlined in a paper published in Nature Nanotechnology, entails the use of piracetam, a chemical additive that can help to control the initial phase of crystal formation (i.e., nucleation) in wide-bandgap perovskites.
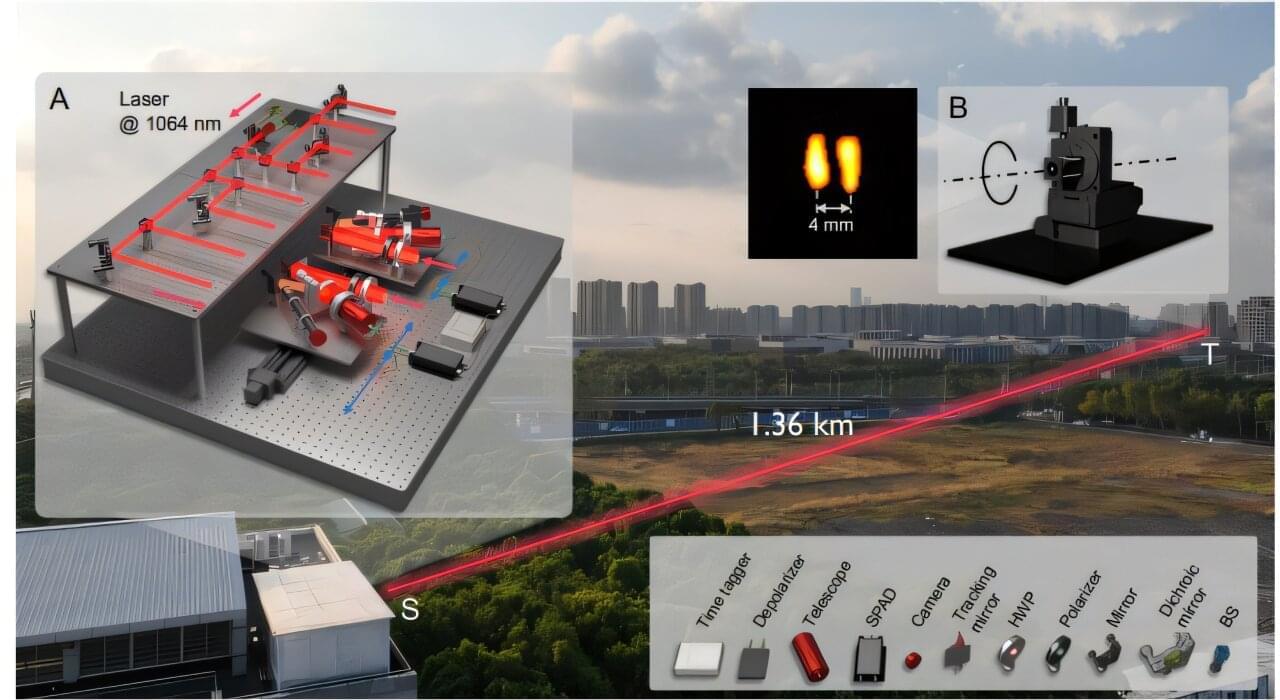
You are the protagonist in a thriller. One morning, an unknown caller with a distorted voice says, “To save your city, solve the puzzle. Go to the coordinates. X marks the clue.” You rush to the spot and see an X on a distant billboard, too far to read. Your vision is sharp, but not that sharp. So, what do you do? A new laser emitter designed by a team of researchers from China could come to the rescue.
According to the study published in Physical Review Letters, the developed setup includes multiple laser emitters that enable super-resolution imaging of targets as small as millimeters in scale from a 1.36 kilometers (0.85 miles) distance in an outdoor urban environment. The device successfully images letter-shaped physical targets measuring 8×9 mm, with letter widths of 1.5 mm, placed at the far end of its imaging range.
Interferometry is a widely used imaging technique in astronomy which works by merging light from different sources to create an interference pattern. These interference patterns are formed when light waves interact to either reinforce or cancel each other depending on their phase differences. These patterns carry detailed information about the object or phenomenon being studied.
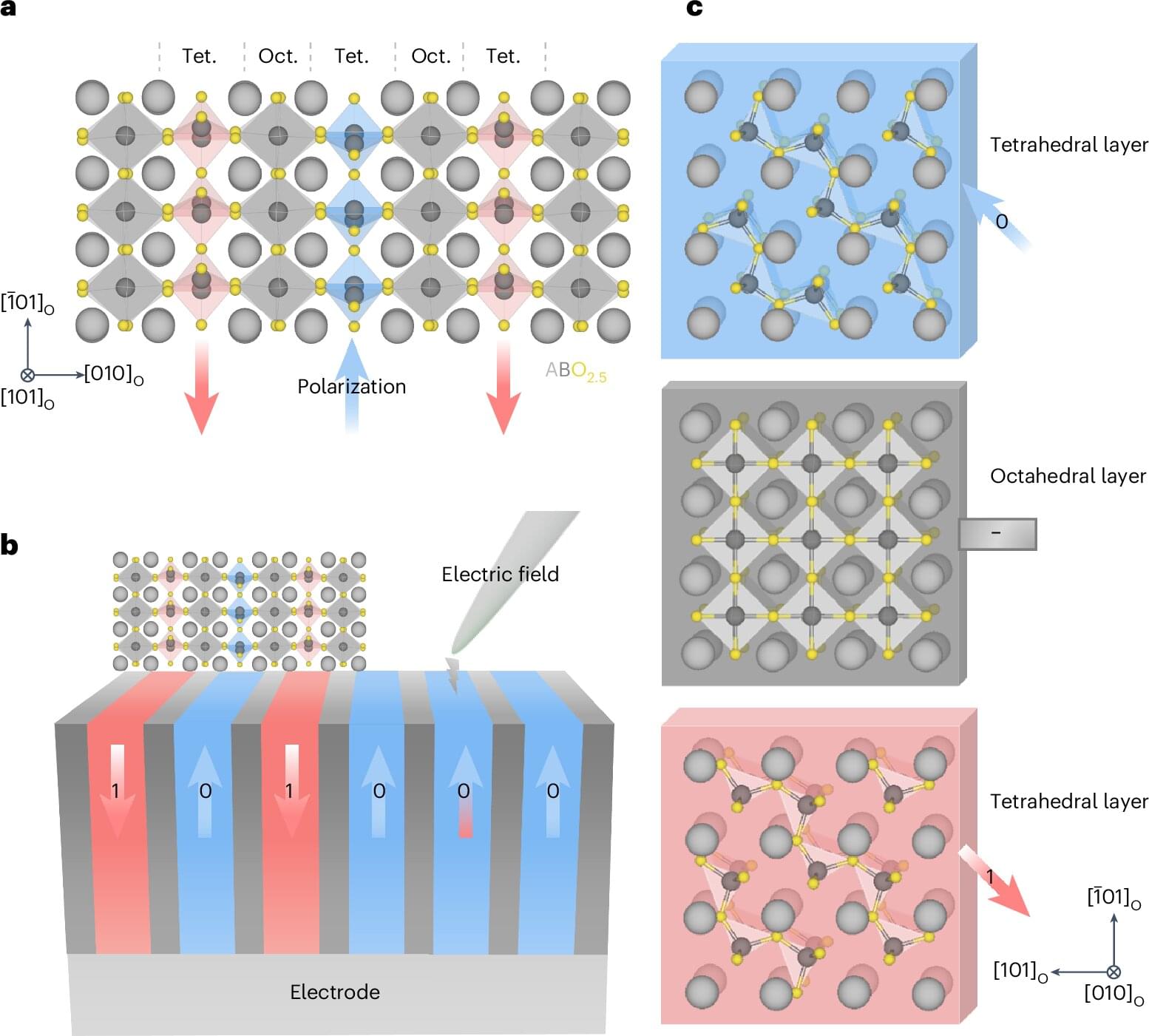
A research team has discovered ferroelectric phenomena occurring at a subatomic scale in the natural mineral brownmillerite.
The team was led by Prof. Si-Young Choi from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and the Department of Semiconductor Engineering at POSTECH (Pohang University of Science and Technology), in collaboration with Prof. Jae-Kwang Lee’s team from Pusan National University, as well as Prof. Woo-Seok Choi’s team from Sungkyunkwan University. The work appears in Nature Materials.
Electronic devices store data in memory units called domains, whose minimum size limits the density of stored information. However, ferroelectric-based memory has been facing challenges in minimizing domain size due to the collective nature of atomic vibrations.
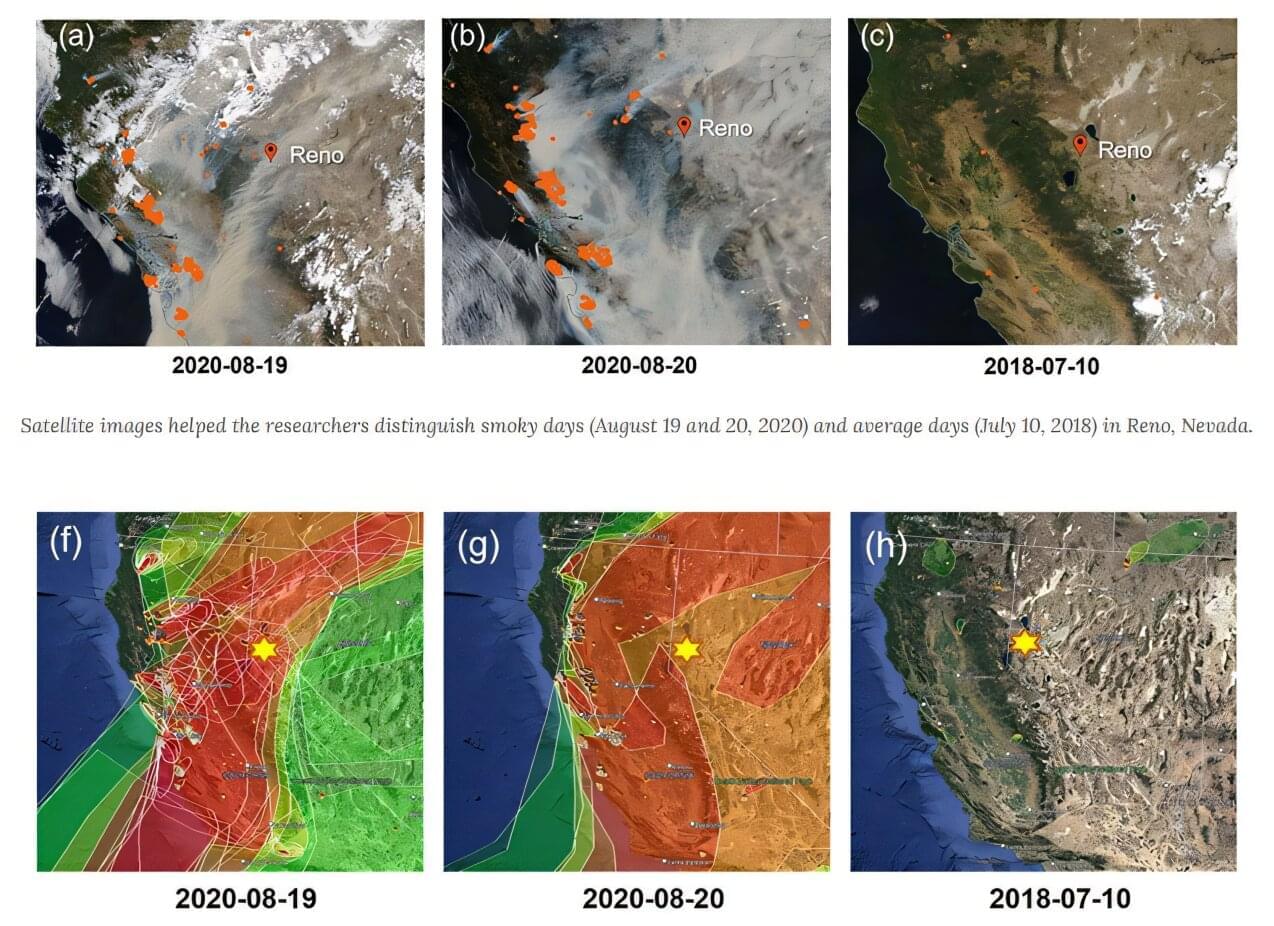
With wildfires increasing in frequency, severity, and size in the Western U.S., researchers are determined to better understand how smoke impacts air quality, public health, and even the weather.
As fires burn, they release enormous amounts of aerosols—the vaporized remains of burning trees and homes that enter the atmosphere and the air we breathe. Now, a new study dissects these aerosols and gases to pinpoint their potential effects on our health as well as the planet’s short and long-term weather.
The research, published in Environmental Science: Atmospheres, measured air quality in Reno, Nevada over a 19-month period between 2017 and 2020 to capture both smoky and clear days. During this timeframe, smoke from more than 106 wildfires impacted the city’s air. DRI scientists Siying Lu and Andrey Khlystov led the research, which found increases in both fine aerosols (known as PM 2.5 for the size of the particulate matter) and carbon monoxide during smoky days.
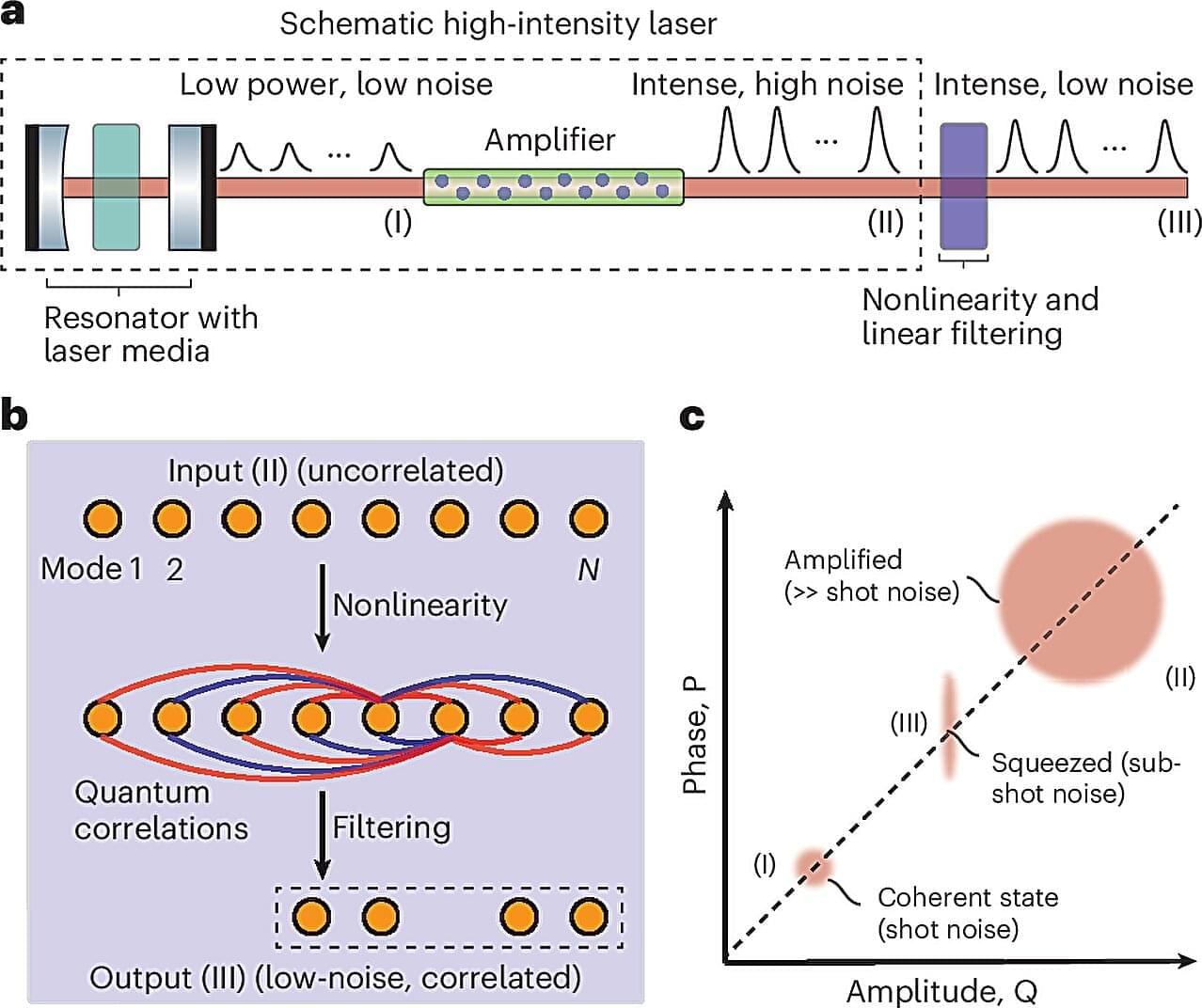
Scientists have discovered a way to convert fluctuating lasers into remarkably stable beams that defy classical physics, opening new doors for photonic technologies that rely on both high power and high precision.
Lasers are essential tools in science, industry and medicine, but increasing their power often results in “noise”—unpredictable fluctuations in intensity that disrupt applications requiring consistent, stable light.
Researchers led by Cornell and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have demonstrated how noisy, amplified lasers can be transformed into ultra-stable beams through the clever use of optical fibers and filters. The technique was detailed in Nature Photonics.
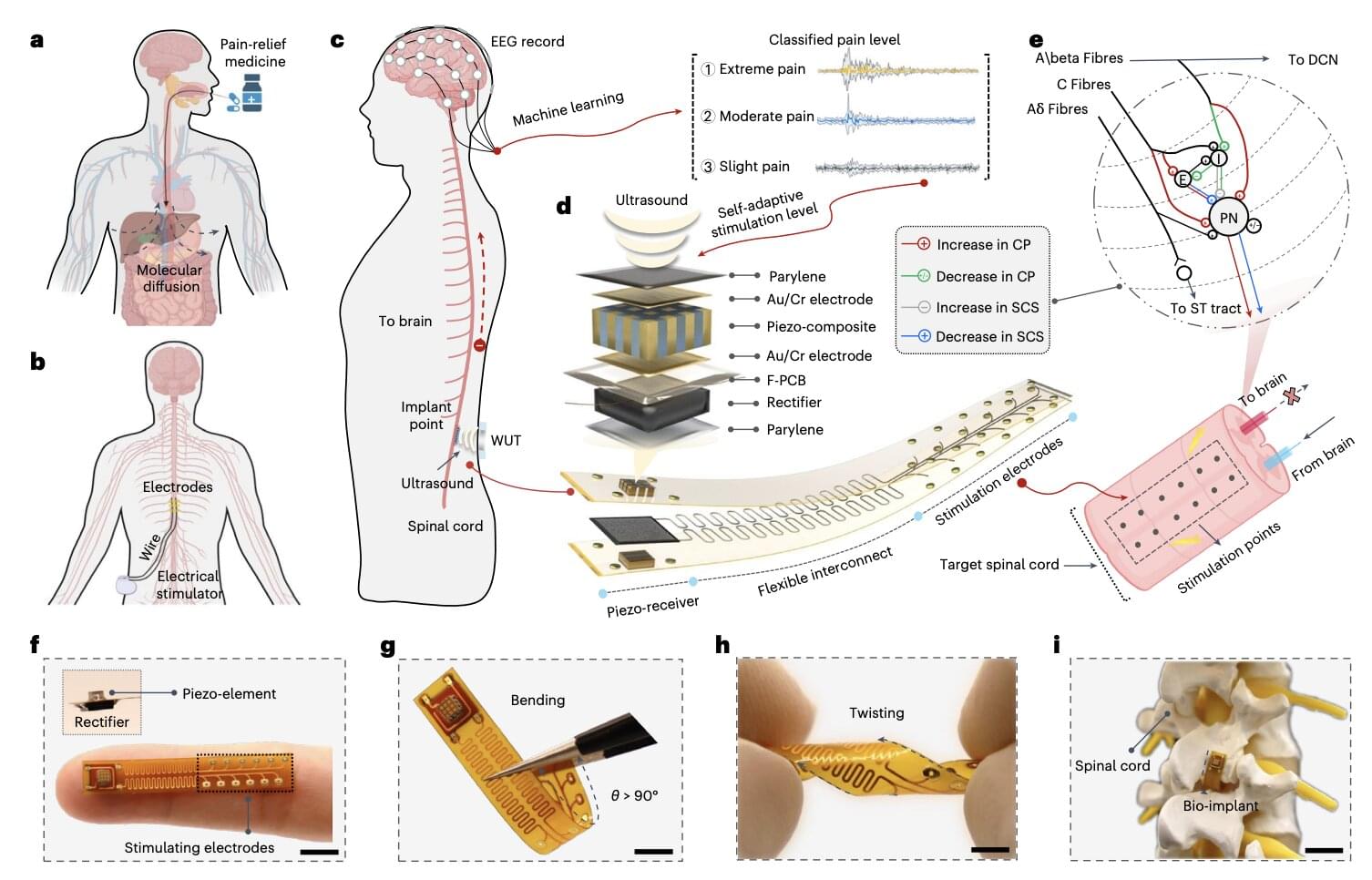
Chronic pain conditions, characterized by persistent or recurrent pain in specific parts of the body, can be highly debilitating and often significantly reduce the quality of life of the individuals experiencing them. Statistics suggest that approximately 20.9% of adults living in the United States have experienced chronic pain at some point in their lives, while 6.9% have experienced severe chronic pain that significantly impacted their daily functioning and well-being.
Currently, chronic pain is primarily treated using pain-relief medications, many of which are based on opioids. Yet many of these pharmaceutical drugs are highly addictive and have severe side effects, so they often end up causing more harm than good.
In recent years, some scientists and engineers have been trying to devise alternative pain-management strategies that do not rely on opioids and can ease the pain of patients without adversely impacting their health. One proposed solution entails the use of implantable electrical stimulators, devices that can be surgically inserted into a patient’s body, delivering electrical signals to their nerves or spinal cord to reduce the pain they are experiencing.
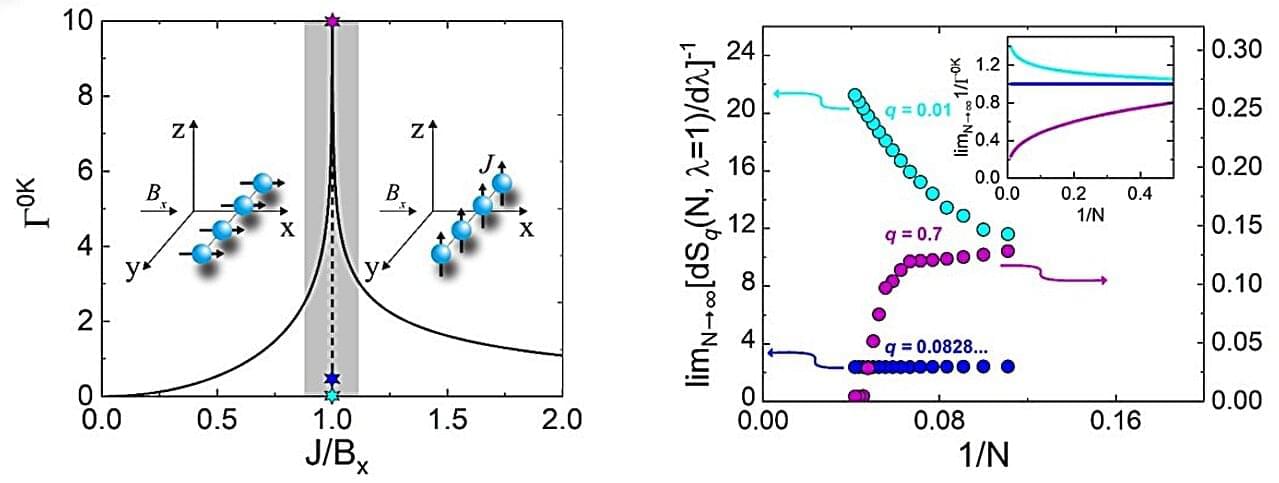
Statistical mechanics is one of the pillars of modern physics. Ludwig Boltzmann (1844–1906) and Josiah Willard Gibbs (1839–1903) were its primary formulators. They both worked to establish a bridge between macroscopic physics, which is described by thermodynamics, and microscopic physics, which is based on the behavior of atoms and molecules.
The Austrian physicist Boltzmann explained the second law of thermodynamics in statistical terms. He defined the entropy of a system based on the number of possible microstates it could assume.
Unlike Boltzmann, who focused more on the physics of gases and the distribution of particles in equilibrium, the American Gibbs developed a general mathematical formalism that could be extended to more complex systems. Together, their contributions formed the basis of a physics capable of modeling a wide variety of phenomena.
A pioneering method to simulate how nanoparticles move through the air could boost efforts to combat air pollution, suggests a study in the Journal of Computational Physics.
Tiny particles found in exhaust fumes, wildfire smoke and other forms of airborne pollution are linked with serious health conditions such as stroke, heart disease and cancer, but predicting how they move is notoriously difficult, researchers say.
Now, scientists have developed a new computer modeling approach that dramatically improves the accuracy and efficiency of simulating how nanoparticles behave in the air. In practice, this could mean simulations that can currently take weeks to run could be completed in a matter of hours, the team says.
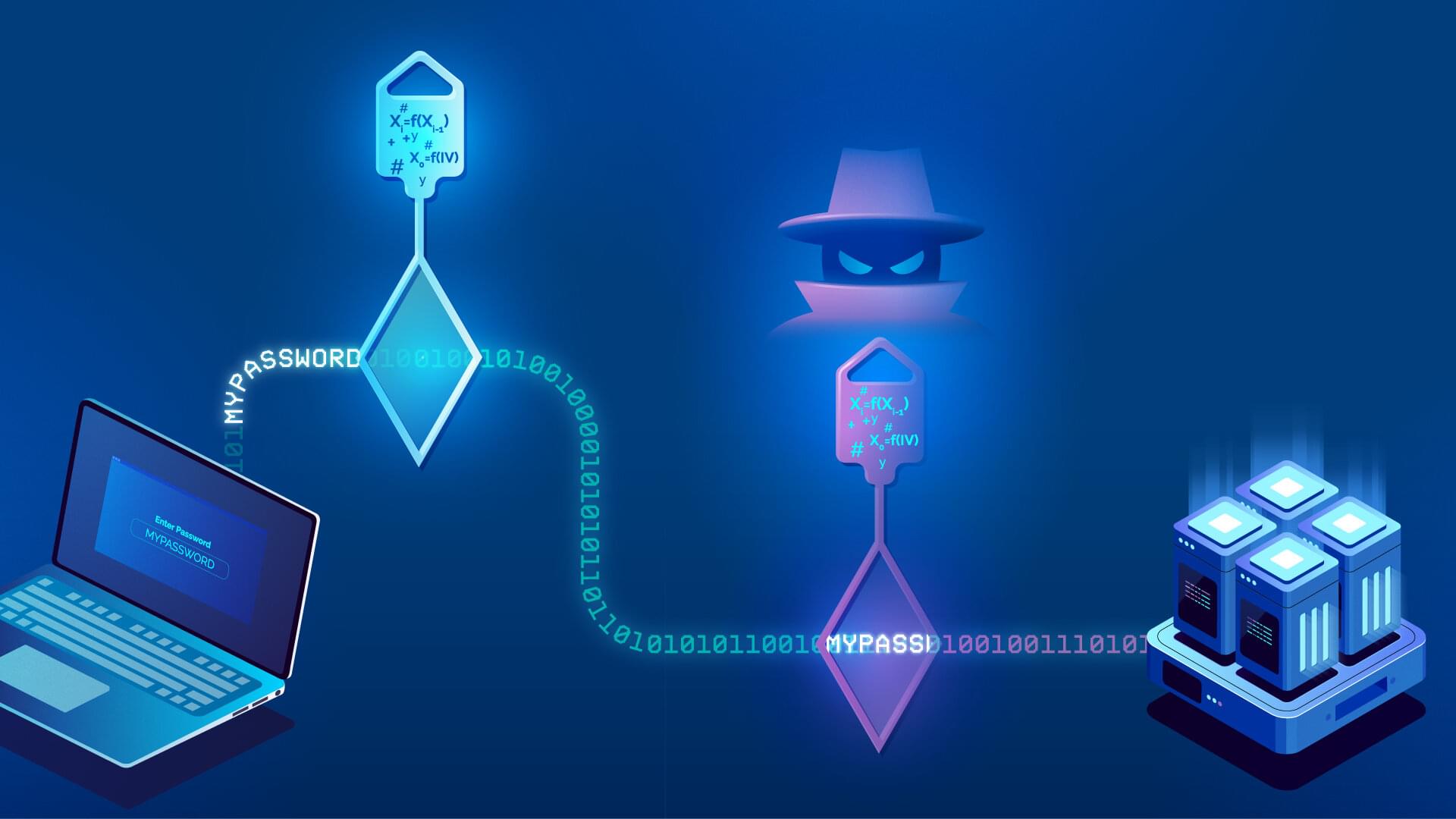
A joint team of researchers led by scientists at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) and King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology (KACST) has reported the fastest quantum random number generator (QRNG) to date based on international benchmarks. The QRNG, which passed the required randomness tests of the National Institute of Standards and Technology, could produce random numbers at a rate nearly a thousand times faster than other QRNG.
“This is a significant leap for any industry that depends on strong data security,” said KAUST Professor Boon Ooi, who led the study, which is published in Optics Express. KAUST Professor Osman Bakr also contributed to the study.
Random number generators are critical for industries that depend on security, such as health, finance, and defense. But the random number generators currently used are vulnerable because of an intrinsic flaw in their design.