Sure but it makes more sense that there’s not a “lake” or ring of water, rather, a bubbly inferno.
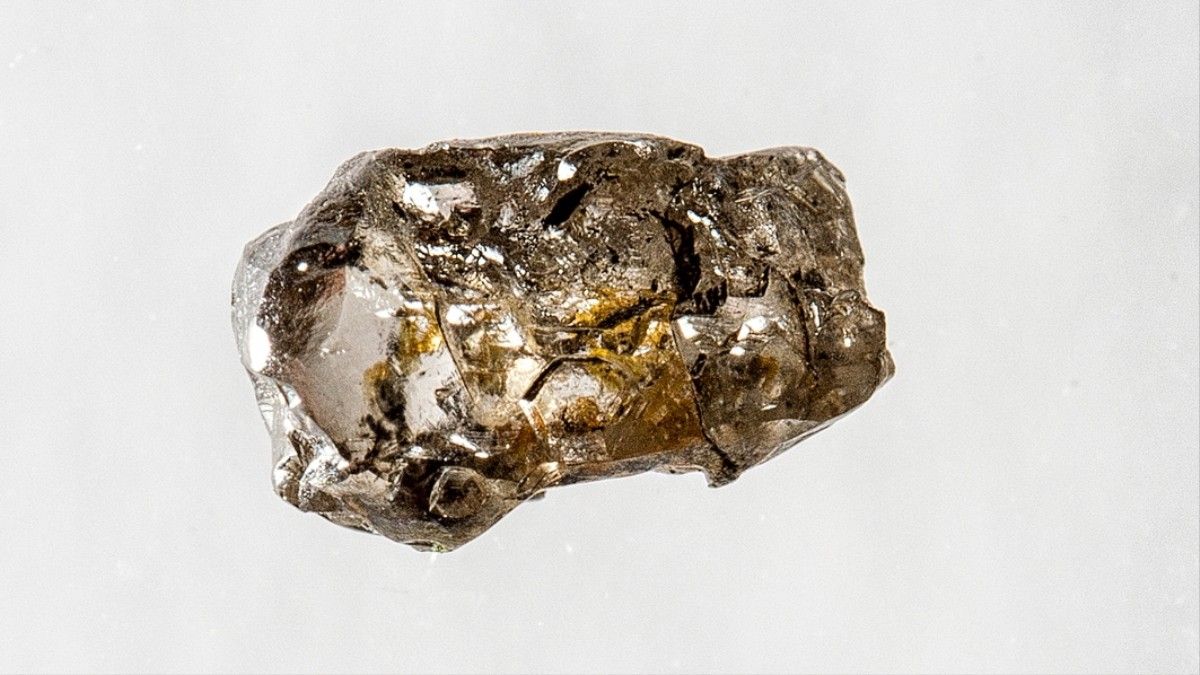
The discovery of a rare gem shows that there an enormous water reservoir in the Earth’s mantle.


Mountains and volcanoes are some of the most fascinating geological formations on Earth — and scientists and adventurers alike can’t get enough of them. Not a lot of us will get a first-hand look at what the planet’s tallest peaks and ranges look like from their summits, but thanks to the photos taken by NASA satellites in orbit and camera-wielding astronauts in space, they are visible as they never would be to the naked eye — hundreds of miles above the Earth.
Click through the slideshow to see stunning images of the Earth’s mountains and volcanoes — from Mount Everest and the Himalayas to the volcanoes of Hawaii and the snow-covered peaks of the Rocky Mountains — captured from space.

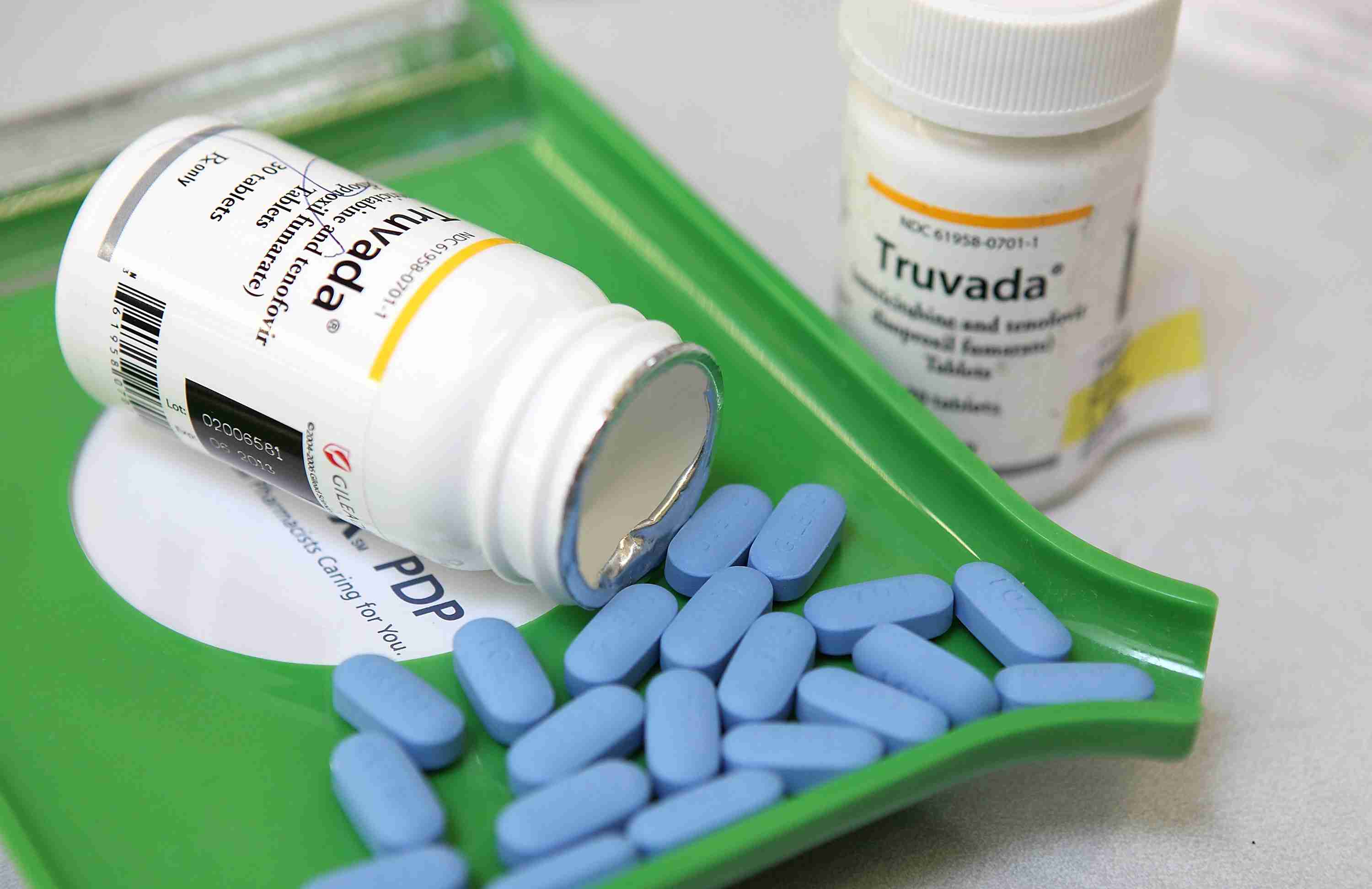
HIV treatments have come a long way in the more than 30 years since the virus was first identified.
Powerful antiretroviral drugs (ARVs) can now keep the virus controlled at levels that current tests cannot detect in the blood. Perhaps just as important, people who take these drugs diligently soon after they’re infected are unlikely to pass the virus to others. But the treatment isn’t perfect. Those with HIV need to take a pill every day for the rest of their lives, and even if they do, the virus can easily morph to become resistant to the drugs. That’s why patients on ARV treatment should faithfully monitor their virus and cycle between different combinations of drugs.
Finding new, easier ways to more effectively treat HIV and stop its spread is therefore an urgent priority, and researchers are now looking beyond daily drugs to therapies that might provide people with more lasting protection.


But while screening can be extremely helpful, it also carries some risks. Here’s what you need to know about lung cancer screenings.
How does lung cancer screening work?
Currently, there’s only one recommended screening test for lung cancer: low-dose computer tomography (low-dose CT scan). This test creates images of the inside of the body — or in this case, the lungs — using low doses of radiation.
The OriHime-D can also be used by people involved in childcare, nursing care or other activities that prevent them from leaving home or a certain location.
A cafe with an all-robot staff controlled by paralyzed people has opened in Tokyo.
The cafe, called Dawn ver.β, held its ribbon cutting ceremony on Nov. 26.
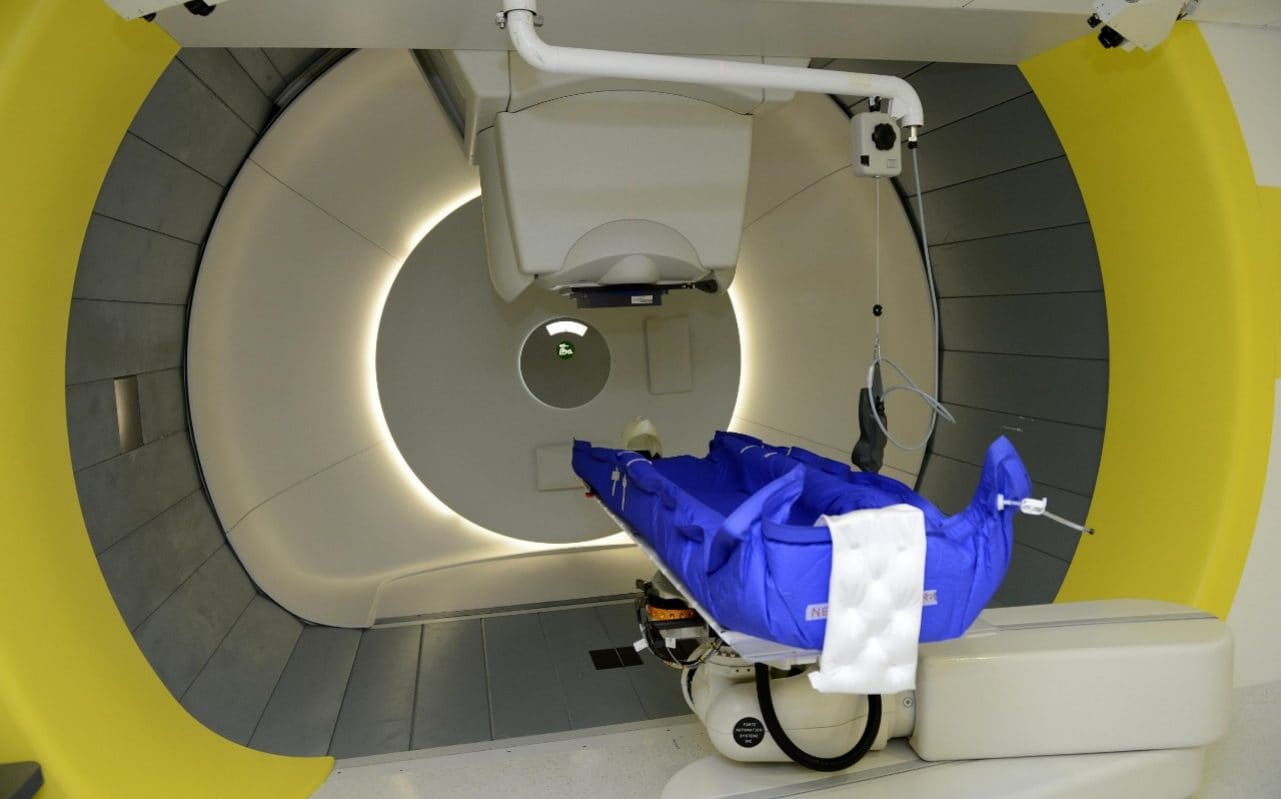
Hundreds of children with cancer are resorting to inferior treatment because of a failure to open two flagship specialist centres, experts have warned.
NHS officials have admitted that no patient has yet received state-of-the-art proton beam therapy (PBT) at either its new London or Manchester sites, despite a Government pledge to be treating 1,500 a year by 2018.
Leading oncologists have called for transparency after two promised opening dates at The Christie NHS Foundation Trust were missed this year and the deadline quietly pushed back.