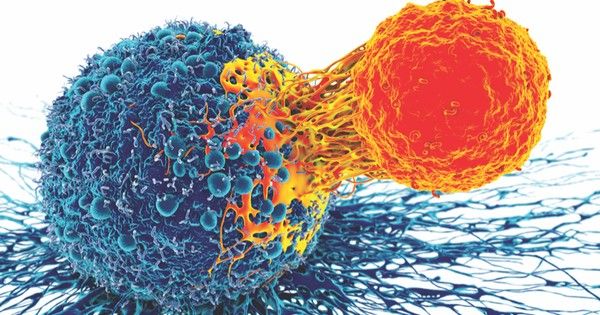
For years immunotherapy has held huge promise. Finally, it seems to be coming to fruition with hopes for a cancer vaccine in the near future…
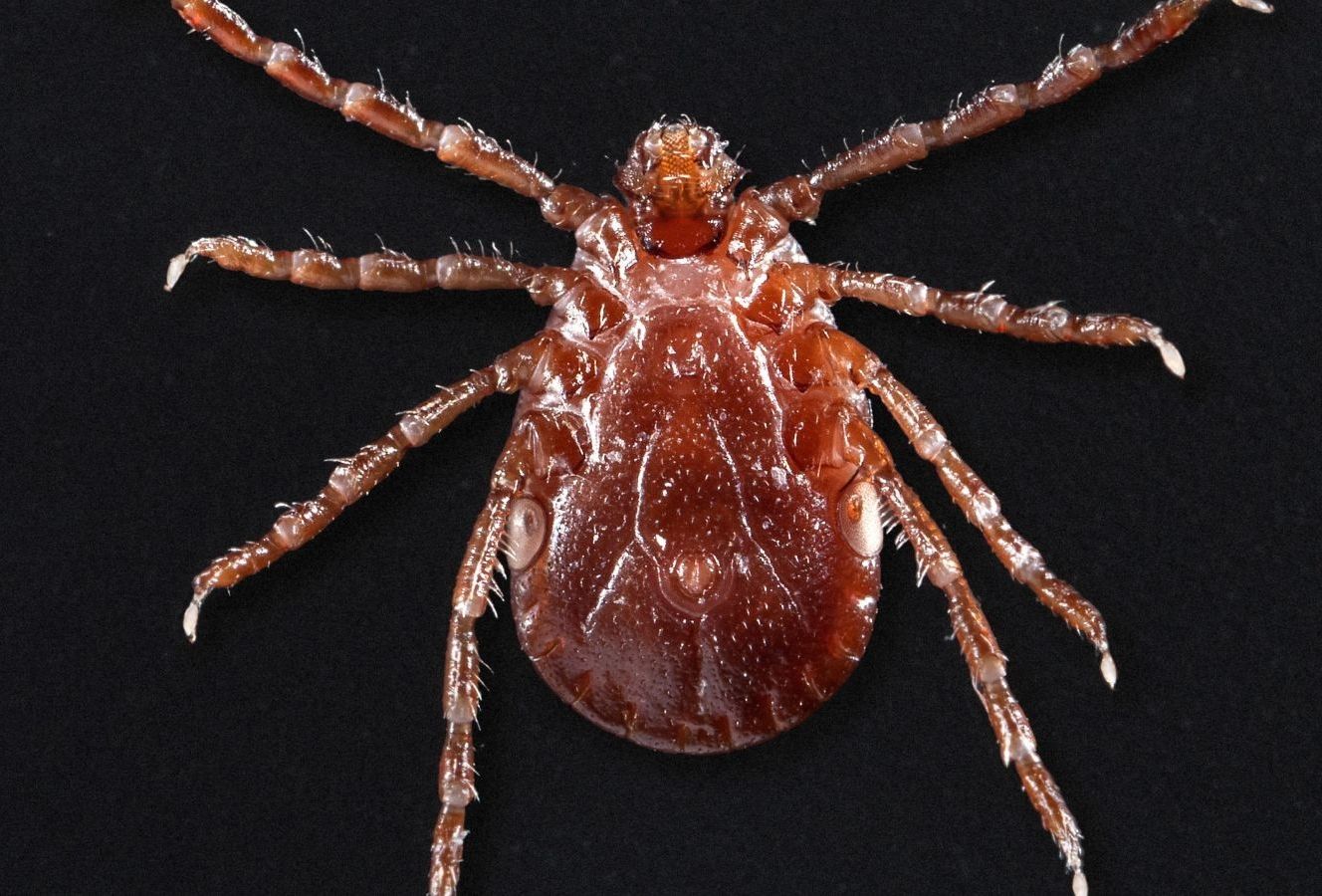


A disease-carrying, newly invasive tick to the United States, the Asian longhorned tick, is poised to spread across much of North America, suggests a new study published Thursday in the Journal of Medical Entomology. According to the study, the tick might be able to live anywhere from Southeastern Canada to most of the eastern half of the U.S. and even parts of the West Coast.
The Asian longhorned tick, or Haemaphysalis longicornis, made an unwelcome splash last year, when researchers and health officials discovered it on a pet sheep in New Jersey. Any hopes that the discovery was an isolated incident faded away this year, with sightings of the tick popping up again in New Jersey and eight other states this past spring and summer (Arkansas, Connecticut, Maryland, New York, North Carolina, Pennsylvania, Virginia, and West Virginia). Since 2017, the tick has been found on pets, farm animals, and at least two people in the U.S., and it’s possible that it might have made its way here at least as early as 2010.
For decades after the discovery of DNA, researchers mostly thought of genetics in terms of genes, the pieces or sequences of DNA that encode instructions for building proteins in cells. Then scientists discovered that genes make up just 2 percent of our DNA and that most genetic complexity stems from the vast non-gene code, which influences when genes are turned on or off. Further, half of that non-gene code was found to come from insertions of viral DNA. Consequently, say the authors, genetic variation, and the potential for disease-causing mistakes, occurs in transposons as well as in genes.
New laboratory techniques can identify which of our genes are influenced by DNA snippets that are left behind in our genetic code by viruses, a new study finds.
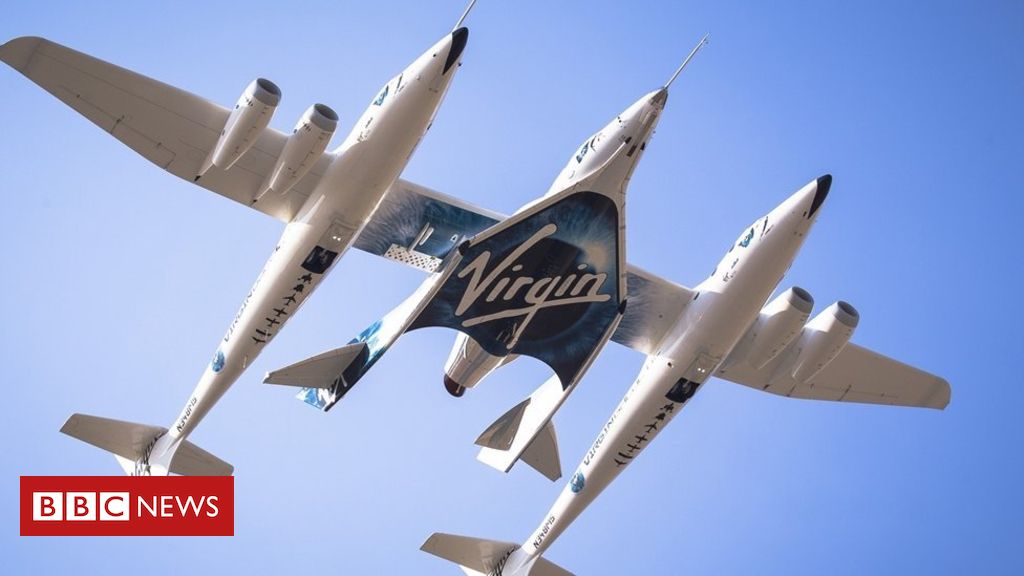

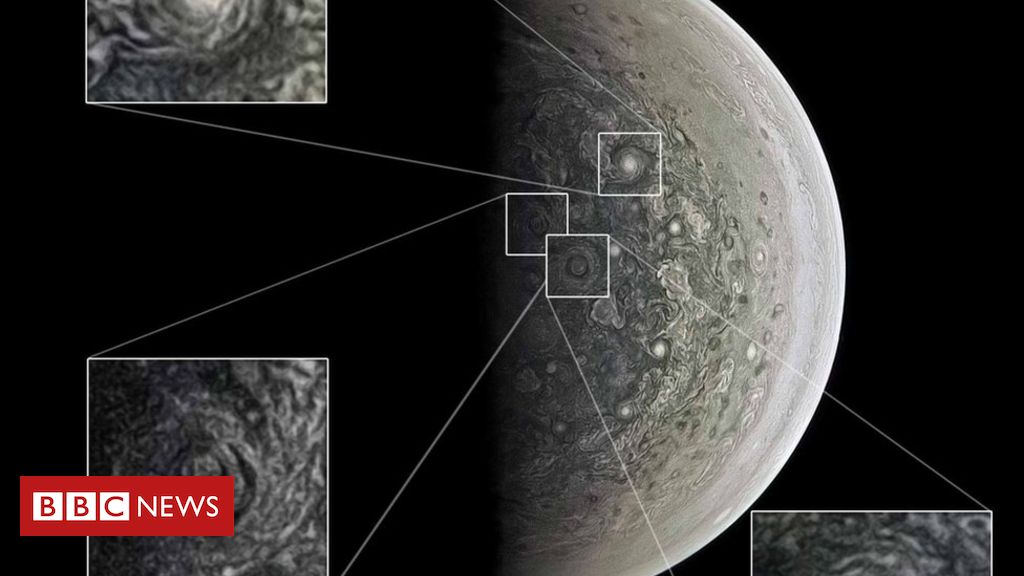
The latest test flight by Sir Richard Branson’s Virgin Galactic successfully rocketed to the edge of space and back.
The firm’s SpaceShipTwo passenger rocket ship reached a height of 82.7km, beyond the altitude at which US agencies have awarded astronaut wings.
It marked the plane’s fourth test flight and followed earlier setbacks in the firm’s space programme.
This video is the tenth in a multi-part series discussing computing. In this video, we’ll be discussing what cloud computing is and the fundamental change it brings in how we view and think about computing.
[0:27–2:19] Starting off we’ll discuss, the revolution the cloud computing paradigm, computing as a utility, brings to the field of computing, and similar transformations seen when electricity became a utility.
[2:19–5:24] Following that we’ll discuss, what exactly cloud computing is and the types of cloud computing: Infrastructure As A Service (IaaS), Platform As A Service (PaaS) and Software As A Service (SaaS) further extending to serverless architecture, Functions As A Service (FaaS).

Join me for a quick review of the spikes & dips in the Bitcoin exchange rate. This time, it’s all about one very simple chart. [continue below graphic]…
The chart below shows a history of BTC price spikes, dips and recovery. Click to enlarge, then start at the top—and move down.
 The table at right illustrates why I do not get too worked up over the plunge in the BTC exchange rate. There are no fundamental flaws in Bitcoin math or mechanisms, the market need for benefits conveyed by Bitcoin is terrific, and popular arguments against Bitcoin are severely flawed. Skeptics and Critics typically say this:
The table at right illustrates why I do not get too worked up over the plunge in the BTC exchange rate. There are no fundamental flaws in Bitcoin math or mechanisms, the market need for benefits conveyed by Bitcoin is terrific, and popular arguments against Bitcoin are severely flawed. Skeptics and Critics typically say this:
“Even if blockchain currencies are beneficial and inevitable, Bitcoin can be displaced by another, better cryptocurrency.”
—Or—
“A viable crypto may emerge—but it will be one that is backed by a tangible asset or issued/sanctioned by government.”
These arguments are false. They are made by individuals who don’t yet fully appreciate a distributed, consensus mechanism and, especially, its relationship with trust, value, government and free markets.
What Bitcoin currently lacks is education, familiarity, standards, simple commercial tools (built upon clear analogies), definitive best practices, a widespread understanding of multisig & security, and limited recourse for certain commercial & retail transactions. But Bitcoin is still an infant, just like the early TV or the early telephone. All of these are under development—without a hint of significant obstacles. Even the messy process of democracy among the various stakeholders is heading toward harmony (miners, developers, vendors, exchanges and consumers).
Of course, I am bullish on Bitcoin, and this may color my analysis. But, I try hard to keep an open mind. There have been moments in its history where I have questioned the market need or the potential for a setback in politics, legislation, or the mechanism itself. Those doubts are in the past. Bitcoin has demonstrated the elegance and value of the blockchain—and the ability to evolve beyond the blockchain with SegWit and Lightning Network. It has achieved a fluid, robust and growing two-sided market.
No one holding assets likes to see a big price pullback. It’s natural to look at the market as if we each got in at the peak—and then tally the “losses”. But I, for one, am not glancing toward the exit. I see the future and I sleep well at night. I am comfortable participating in the Bitcoin era.
Philip Raymond co-chairs CRYPSA, hosts the Bitcoin Event and is keynote speaker at Cryptocurrency Conferences. He advises The Disruption Experience in Singapore, sits on the New Money Systems board of Lifeboat Foundation and is a top writer at Quora. Book a presentation or consulting engagement.


“When we send astronauts to the surface of the Moon in the next decade, it will be in a sustainable fashion,” says NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstinee. Learn how we’ll expand partnerships with industry and other nations to explore the Moon and advance our exploration missions to even farther destinations, such as Mars: https://go.nasa.gov/2GeqhZL
