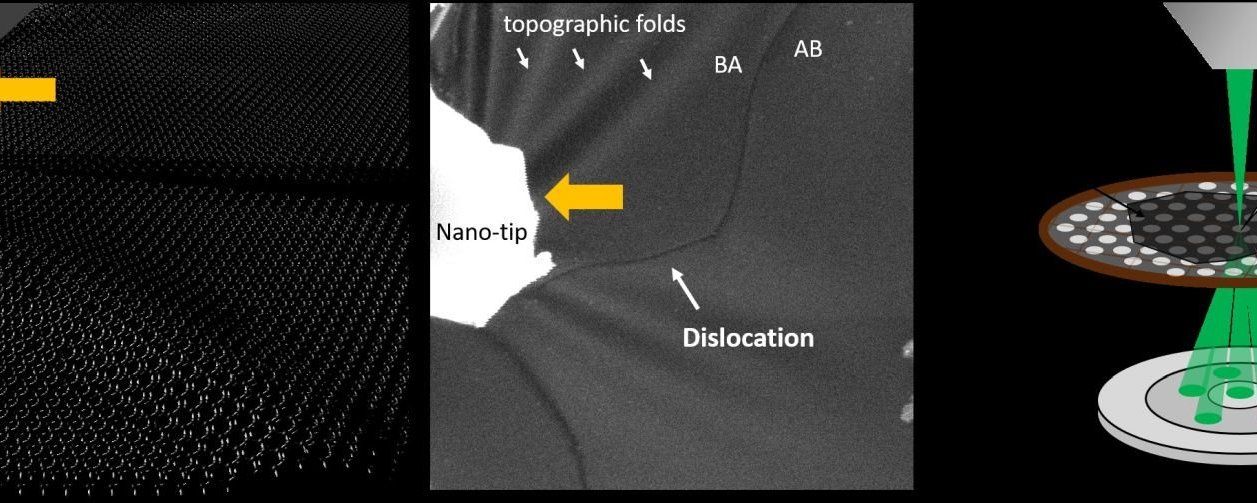
Materials can deform plastically along atomic-scale line defects called dislocations. Many technical applications such as forging are based on this fundamental process, but the power of dislocations is also exploited in the crumple zones of cars, for instance, where dislocations protect lives by transforming energy into plastic deformation. FAU researchers have now found a way of manipulating individual dislocations directly on the atomic scale.
Using advanced in situ electron microscopy, the researchers in Prof. Erdmann Spiecker’s group have opened up new ways to explore the fundamentals of plasticity. They have published their findings in Science Advances.