In a new study, people who believed negative stereotypes about old age had higher risk of Alzheimer’s.
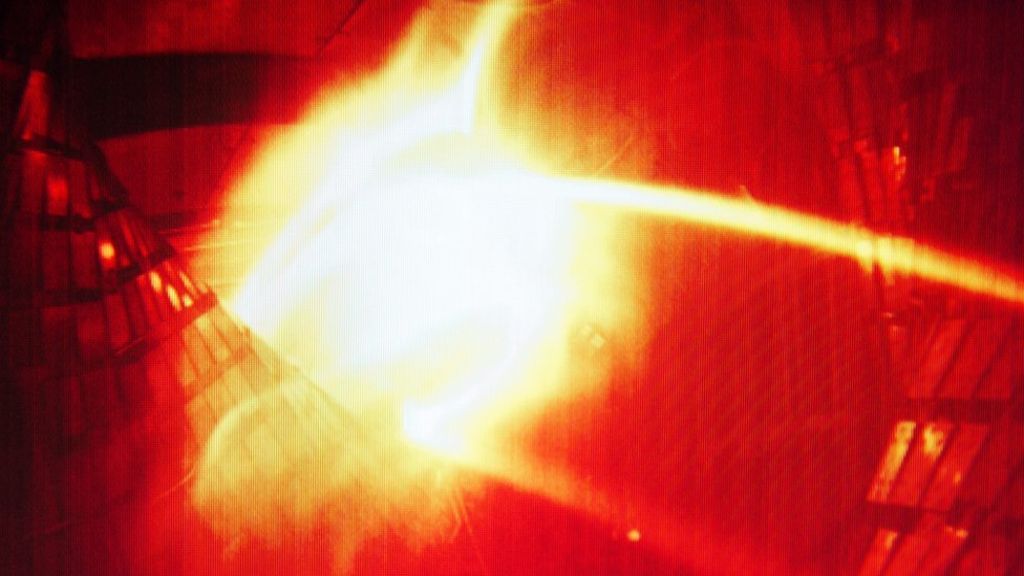
A German nuclear fusion experiment has produced a special super-hot gas which scientists hope will eventually lead to clean, cheap energy.
The helium plasma — a cloud of loose, charged particles — lasted just a tenth of a second and was about one million degrees Celsius.
It was hailed as a breakthrough for the Max Planck Institute’s stellarator — a chamber whose design differs from the tokamak fusion devices used elsewhere.
This article is based on my skype conversation with Elizabeth Parrish, founder and CEO of BioViva. BioViva is a biotech company in the Seattle area focused on developing gene therapies to mitigate the diseases of aging. Liz is currently experimenting these therapies on herself. Her research was recently covered in a MIT Technology Review article and she did an AMA on Reddit you may want to check out.
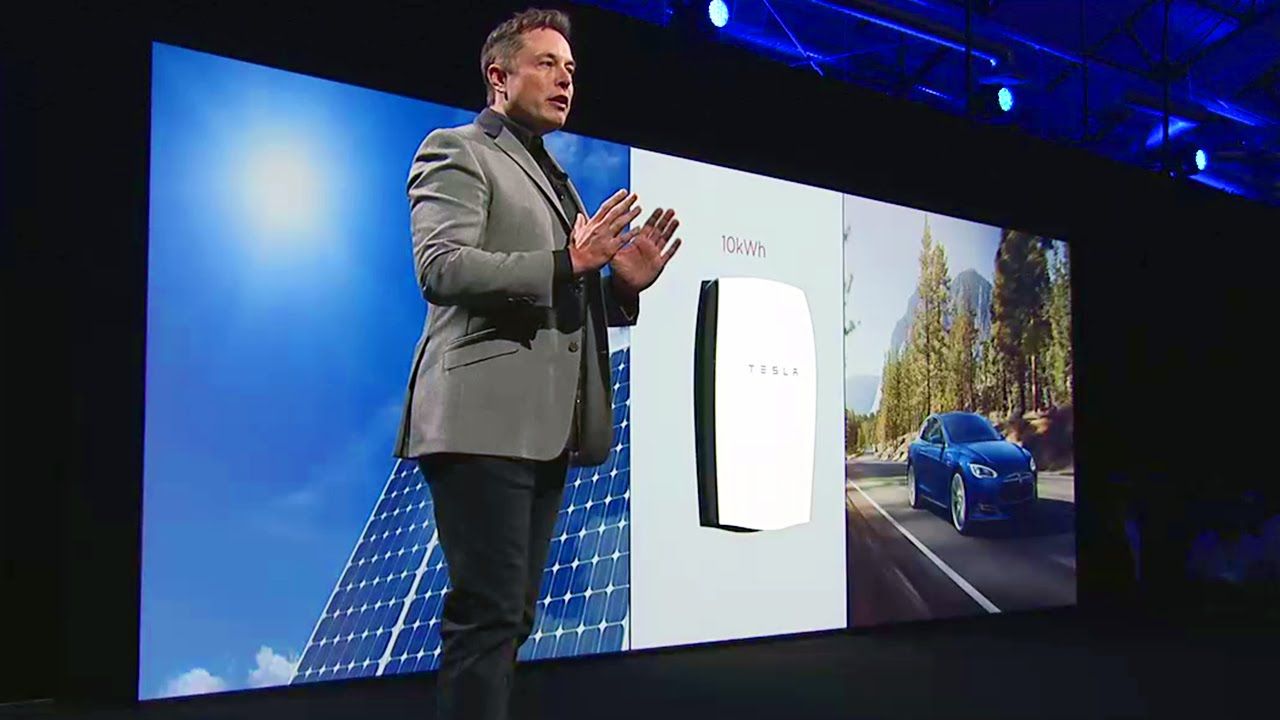
Tesla Powerwall Keynote by Elon Musk “The Missing Piece”
English and Spanish subtitles added, credit to Luis Gámez for transcribing and translating.
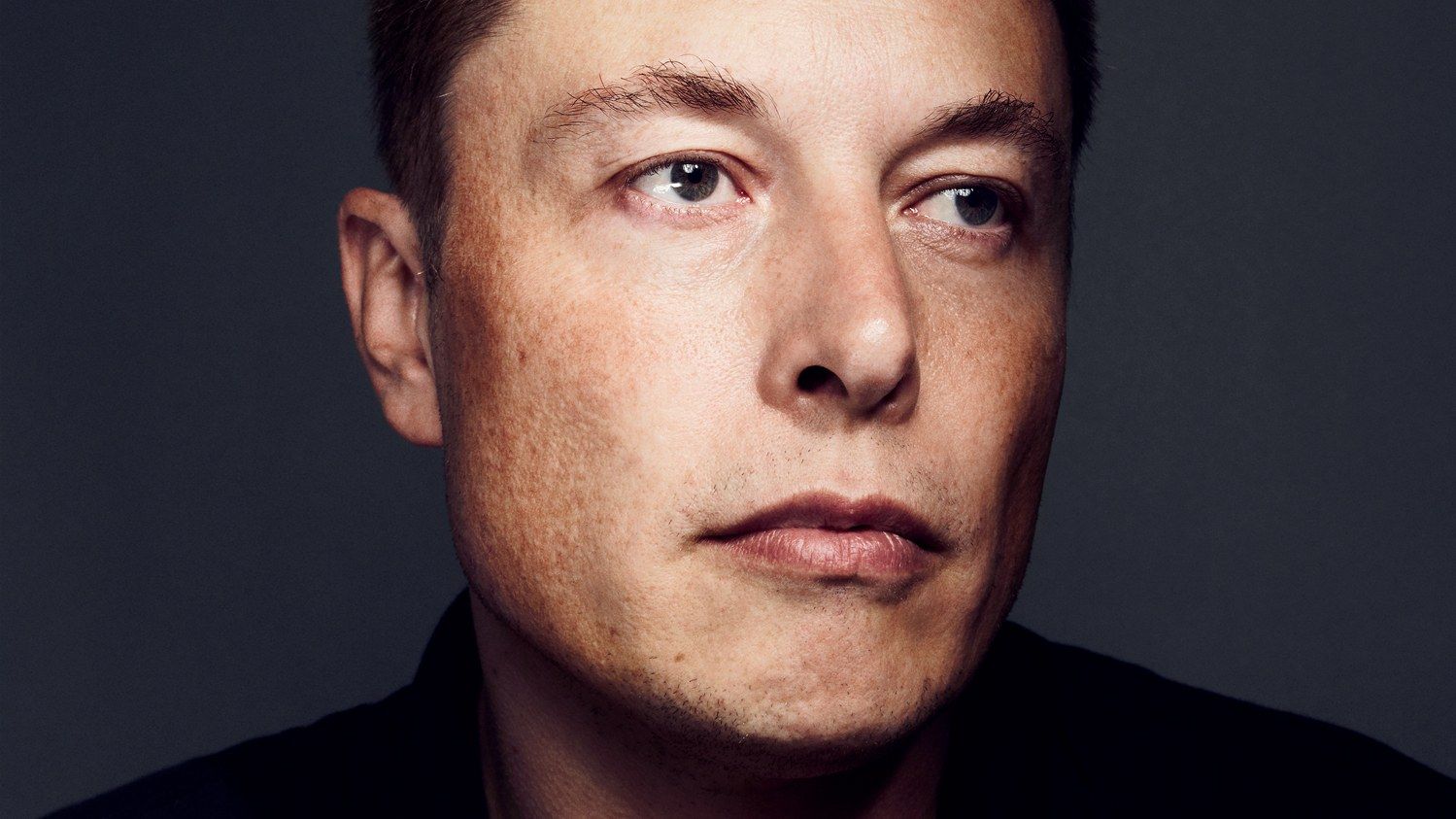
One of his companies is trying to upend the auto industry. Another of his companies is trying to put people on Mars. Yet another is trying to bring electricity to everyone who needs it. Elon Musk wants to reinvent the world in a single lifetime. But is the future ready for Elon Musk?
Following the current fashion for visionary technological geniuses to be portrayed through three critical moments in their lives, * here are three from Elon Musk’s. Except, in this case, they all come from one single day—October 12, 2015, a Monday—a day that feels like it could’ve been pretty much any day in Musk’s life right now.
Musk starts most workweeks here at his rocket company, SpaceX, in an industrial suburb of Los Angeles, and each Monday, he explains to me, there is a brainstorm about “Mars colonial transport architecture.” He says these words as though most people could look through their Monday schedule and find something similar.
Recently, the study of potential risks from advanced artificial intelligence has attracted substantial new funding, prompting new job openings at e.g. Oxford University and (in the near future) at Cambridge University, Imperial College London, and UC Berkeley.
This is the dawn of a new field. It’s important to fill these roles with strong candidates. The trouble is, it’s hard to find strong candidates at the dawn of a new field, because universities haven’t yet begun to train a steady flow of new experts on the topic. There is no “long-term AI safety” program for graduate students anywhere in the world.
Right now the field is pretty small, and the people I’ve spoken to (including e.g. at Oxford) seem to agree that it will be a challenge to fill these roles with candidates they already know about. Oxford has already re-posted one position, because no suitable candidates were found via the original posting.
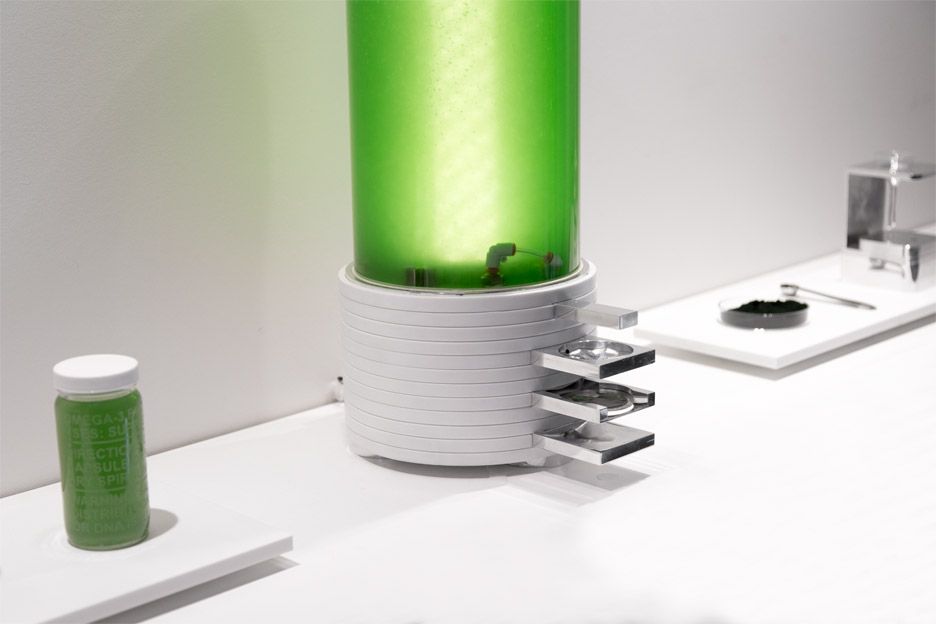
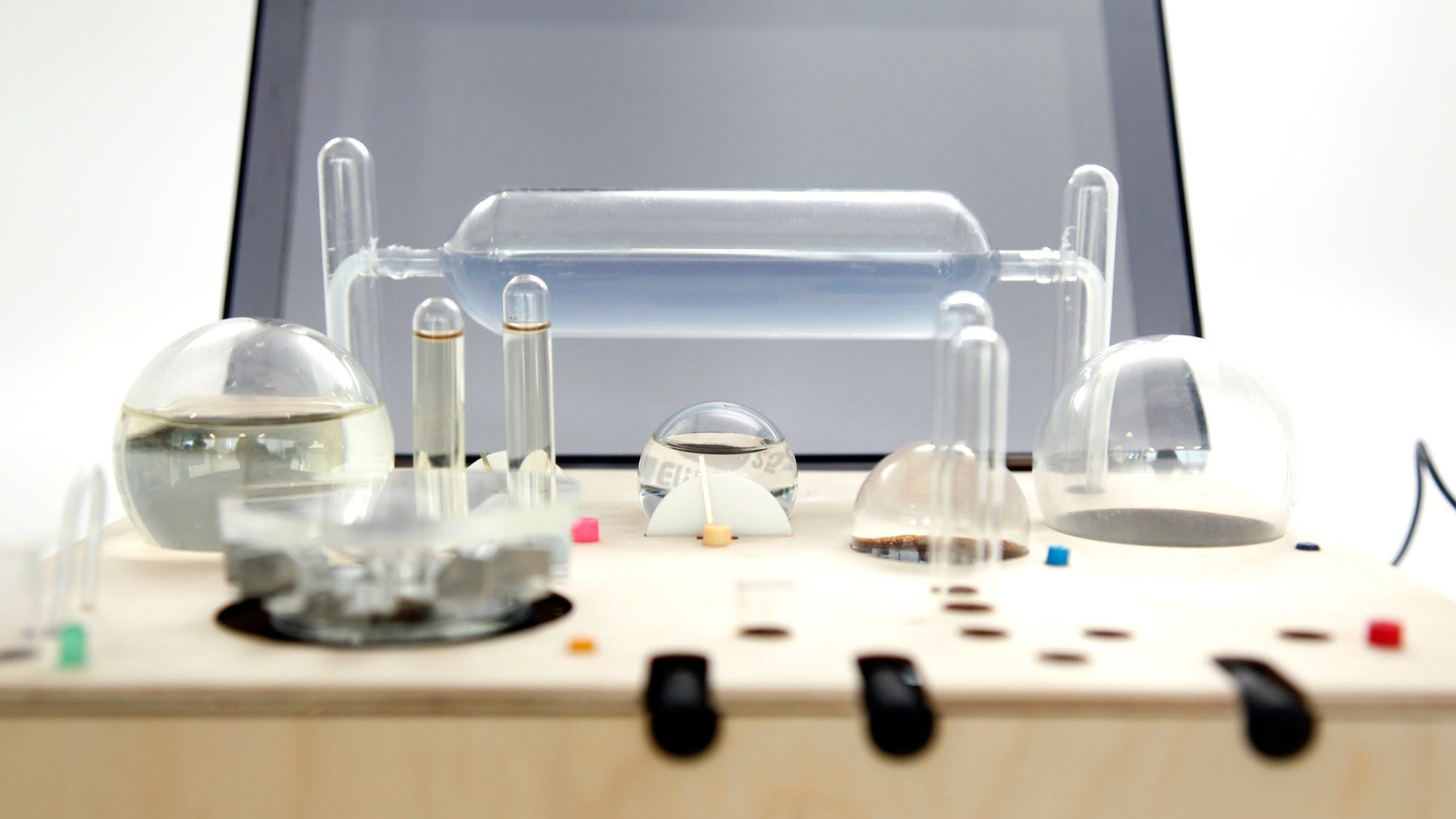
MIT Media Lab graduate Will Patrick has designed a prototype desktop bioreactor that could enable the production of pharmaceutical drugs at home.
The cylinder-shaped Farma kitchen appliance could be used to grow, measure, filter and dry synthetically designed microbes.