Loving the progress around Quantum.
Today, a group of scientists — John A. Rogers, Eric Seabron, Scott MacLaren and Xu Xie from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign; Slava V. Rotkin from Lehigh University; and, William L. Wilson from Harvard University — are reporting on the discovery of an important method for measuring the properties of nanotube materials using a microwave probe. Their findings have been published in ACS Nano in an article called: “Scanning Probe Microwave Reflectivity of Aligned Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes: Imaging of Electronic Structure and Quantum Behavior at the Nanoscale.”
The researchers studied single-walled carbon nanotubes. These are 1-dimensional, wire-like nanomaterials that have electronic properties that make them excellent candidates for next generation electronics technologies. In fact, the first prototype of a nanotube computer has already been built by researchers at Stanford University. The IBM T.J. Watson Research Center is currently developing nanotube transistors for commercial use.
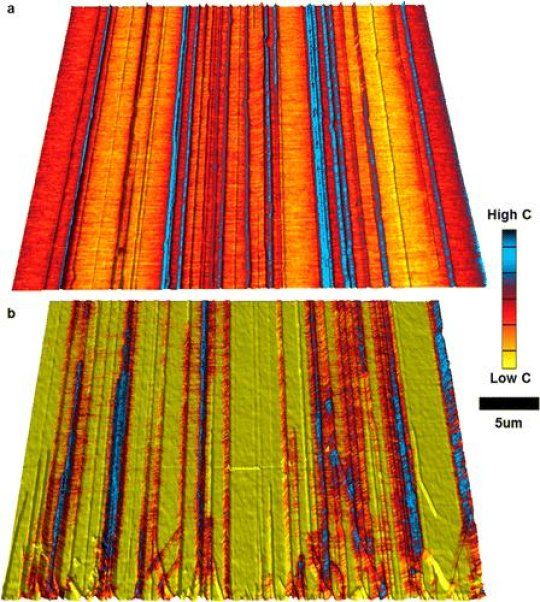
For this study, scientists grew a series of parallel nanotube lines, similar to the way nanotubes will be used in computer chips. Each nanotube was about 1 nanometer wide — ten times smaller than expected for use in the next generation of electronics. To explore the material’s properties, they then used microwave impedance microscopy (MIM) to image individual nanotubes.