Australian miners uncovered the gem of a find—a dog-size herbivore named Weewarrasaurus pobeni.



Not only did NASA’s Insight probe make it down to the surface of Mars, but part of the support system for the mission took their first, and last, close up peek at the red planet. https://bit.ly/2UgwmHY&h=AT1M4EEI8SBcHDGIg7qDLpkauTEHcWZ6QCn…HKZoQvgkWA
As NASA’s InSight mission lands on Mars, its companions sail onward.
By 2020, China plans to assign each of its 1.4 billion citizens a “social credit score” that will determine what people are allowed to do, and where they rank in society.
It’s part of a broad effort in China to build a so-called reputation system that will measure, in theory, the credibility of government officials and businesses, in addition to citizens. The Chinese government says the system will boost “trust” nationwide and build a culture of “sincerity.”

Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), Mixed Reality (MR), Haptics and Holographics, are all in gradual market diffusion stage as of 2018, after having long been the stuff of science fiction content. Even so, even as of 2018, the misconceptions remains overwhelmingly widespread and strong, that these are for gaming, entertainment, leisure and recreation. None of these technologies or interface methods, however, were ever meant to be for just that alone.



A merican girls are now going through puberty significantly earlier than in decades prior, a trend that’s been linked to physiological and psychological risks. The various factors thought to drive early puberty include obesity, toxic stress, and environmental elements. A landmark study published Monday looks at one particular type of environmental element — the chemicals in household items.
A long-running study on mothers and children published in Human Reproduction determined that the onset of female puberty is associated with exposure to chemicals like phthalates, parabens, and the antibacterial agent triclosan. These products in personal care products, like some brands of perfumes, cosmetics, and toothpaste. The same result was not found in populations of boys, whose timing of puberty was also examined in this study.
“We have known for the past 15 to 20 years that girls are entering puberty at an earlier age than they used to in the past,” lead author and University of California, Berkeley associate professor Kim Harley, Ph.D. tells Inverse. “We certainly know that obesity plays a role in that but now we also know that the hormone-disrupting chemicals that are in our homes and in our environment could be an additional factor that’s contributing to this.”
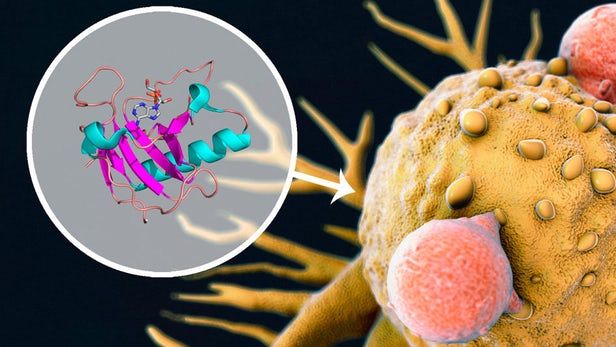
Researchers at MIT have used two experimental cancer drugs in tandem to fight melanomas. The team paired protein kinase inhibitors with ribonuclease drugs and set them loose onto tumors, and found that the combination worked better than either drug does alone. The discovery could help reduce side effects of cancer treatments and make them more effective.

Open brain surgery is about as dangerous as it sounds, but for sufferers of conditions like Parkinson’s and epilepsy it can be the only way to relieve their symptoms. Unfortunately, this means drilling a hole in the skull and stimulating the brain with electrical currents, bringing on the risk of serious side effects. Fortunately, scientists have opened a new doorway to the brain, developing the Stentrode, a promising first-of-a-kind device that can deliver the currents to targeted areas through a small keyhole incision in the neck.
Physicists at The University of Toledo are part of an international team of scientists who discovered a single material that produces white light, opening the door for a new frontier in lighting, which accounts for one-fifth of global energy consumption.
“Due to its high efficiency, this new material can potentially replace the current phosphors used in LED lights — eliminating the blue-tinged hue — and save energy,” said Dr. Yanfa Yan, professor of physics at UT. “More research needs to be done before it can be applied to consumer products, but the ability to reduce the power that bulbs consume and improve the color quality of light that the bulbs emit is a positive step to making the future more environmentally friendly.”
The renewable energy research was recently published in Nature, the world’s leading multidisciplinary science journal.