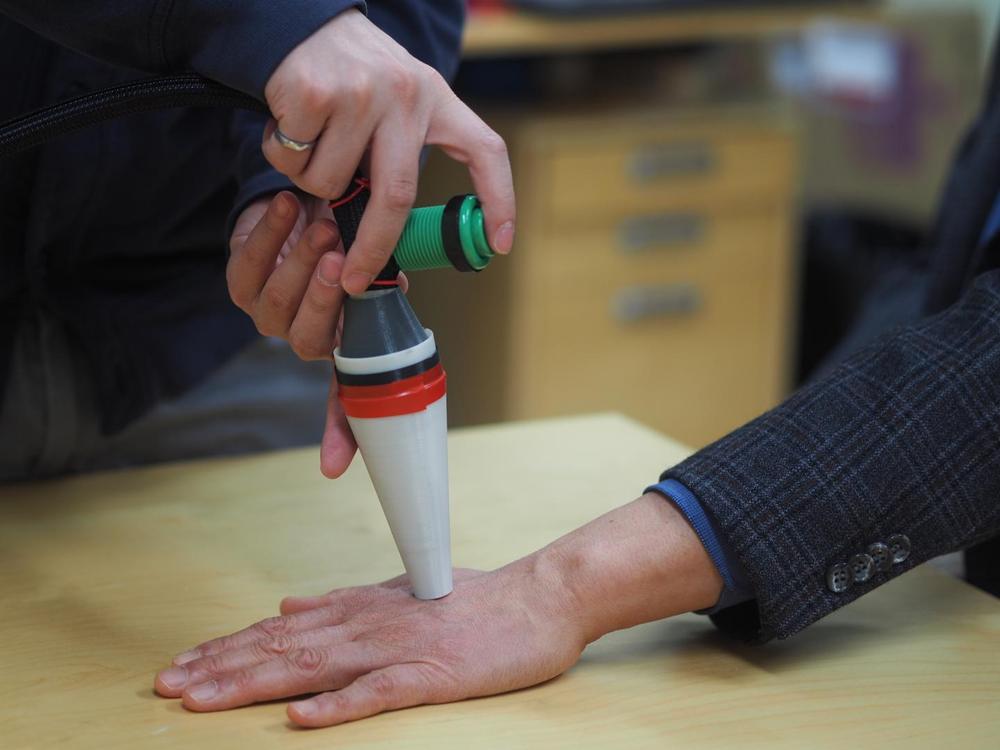
Canadian researchers have developed a laser probe that uses changes in light patterns to detect melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer.
The device works on the principle that light waves change as they pass through objects. Cancerous cells have a different physical profile to healthy cells, and the researchers designed a system that can detect these patterns instantly. By determining the optical polarisation of different skin lesions, the team was able to distinguish cancerous from non-cancerous tissues.
“With skin cancer, there’s a saying that if you can spot it you can stop it – and that’s exactly what this probe is designed to do,” said researcher Daniel Louie, a PhD student who constructed the device as part of his studies in biomedical engineering at the University of British Columbia (UBC).