Some Parkinson’s disease patients with a specific genetic variant have widespread reduction of gray matter in dementia-related brain regions.



Thanks so much to Luanna Helena for having me on Creatively Speaking Radio to discuss Bioquark Inc. (http://www.bioquark.com) and nature’s clues for human regeneration, disease reversion, and age rejuvenation -
Also got to introduce our new mosquito / “ectocrinome” research program — (https://www.bizjournals.com/philadelphia/news/2019/01/02/bio…nefit.html) —
http://blogtalkradio.com/creativelyspeaking/2019/01/12/episode-79-ira-pastor
Technologies have often been observed to improve exponentially over time. In practice this often means identifying a constant known as the doubling time. Moore’s law is, classically, the empirical observation that the number of electronic components that can be put on a chip doubles every 18 to 24 months. Today it is frequently stated in terms of the number of computations available per unit of cost, a formulation promoted by Kurzweil. Different doubling times describe the rate of advancement in many technologies.
A frequently noted competitor to Moore’s law is known as Wright’s law, which has aeronautical roots. Wright’s law expresses the idea that performance of a technology—price or a quality metric—improves by a constant percentage for every doubling of the total number produced. Does exploration of outer space conform to behavior like Moore’s law or Wright’s law? Our results are broadly consistent with these laws. (More)



Several experiments over the past few years have reportedly violated Bell’s inequality – last year, the first Bell’s inequality experiment was completed without loopholes, but there’s still dispute over whether or not local realism actually holds up.
The new worldwide experiment aims to settle the matter once and for all, by using a huge amount of random, user-generated data to test Bell’s inequality.
Basically, the researchers are holding what’s called the ‘BIG Bell Test: worldwide quantum experiments powered by human randomness’, and they aim to conduct a range of Bell’s inequality tests around the world, controlled by human decisions made by volunteers (which they call Bellsters).


A quantum computer isn’t just a more powerful version of the computers we use today; it’s something else entirely, based on emerging scientific understanding — and more than a bit of uncertainty. Enter the quantum wonderland with TED Fellow Shohini Ghose and learn how this technology holds the potential to transform medicine, create unbreakable encryption and even teleport information.
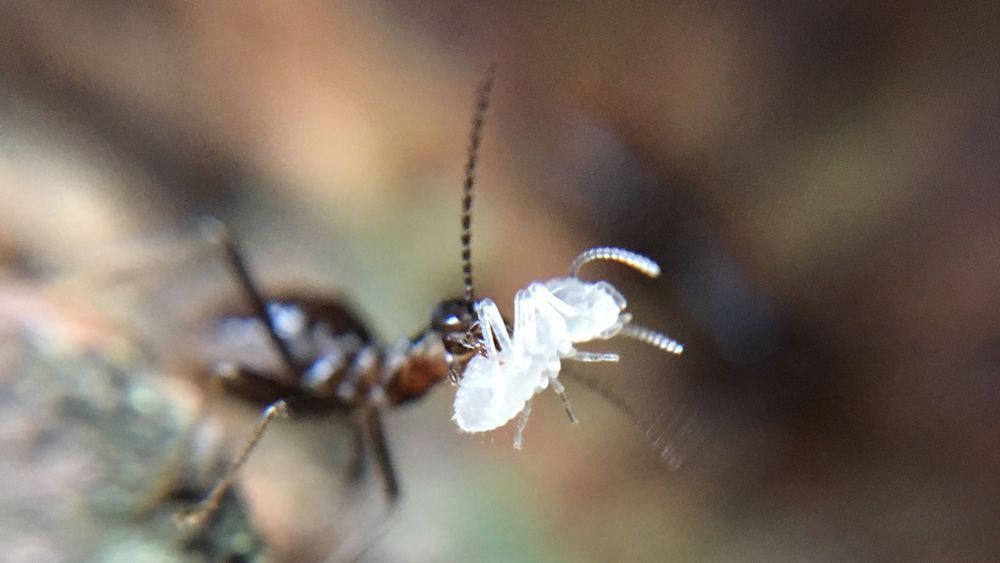

Homeowners tend to equate termites with property value apocalypse, but ecologically speaking, they’re more a force of stability than destruction. A new study points to how termites can help the rainforests they call home to weather droughts—which are expected to increase in frequency and intensity as climate change causes the tropics to heat up.
Termites are found across the tropics, where they feed on wood and dead leaves and build mounds that can sometimes be seen from space. Despite the wide-ranging influence of these ecological engineers, there’s been little research on how termites impact the ability of the forests they call home to withstand one of the biggest natural disturbances they face: drought.