Closing the instability gap.
(Phys.org)—It might be said that the most difficult part of building a quantum computer is not figuring out how to make it compute, but rather finding a way to deal with all of the errors that it inevitably makes. Errors arise because of the constant interaction between the qubits and their environment, which can result in photon loss, which in turn causes the qubits to randomly flip to an incorrect state.
In order to flip the qubits back to their correct states, physicists have been developing an assortment of quantum error correction techniques. Most of them work by repeatedly making measurements on the system to detect errors and then correct the errors before they can proliferate. These approaches typically have a very large overhead, where a large portion of the computing power goes to correcting errors.
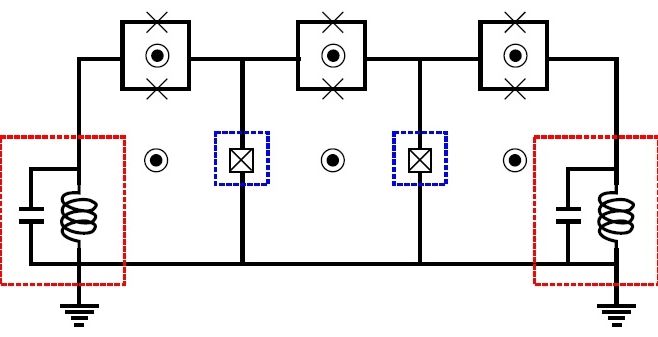
In a new paper published in Physical Review Letters, Eliot Kapit, an assistant professor of physics at Tulane University in New Orleans, has proposed a different approach to quantum error correction. His method takes advantage of a recently discovered unexpected benefit of quantum noise: when carefully tuned, quantum noise can actually protect qubits against unwanted noise. Rather than actively measuring the system, the new method passively and autonomously suppresses and corrects errors, using relatively simple devices and relatively little computing power.