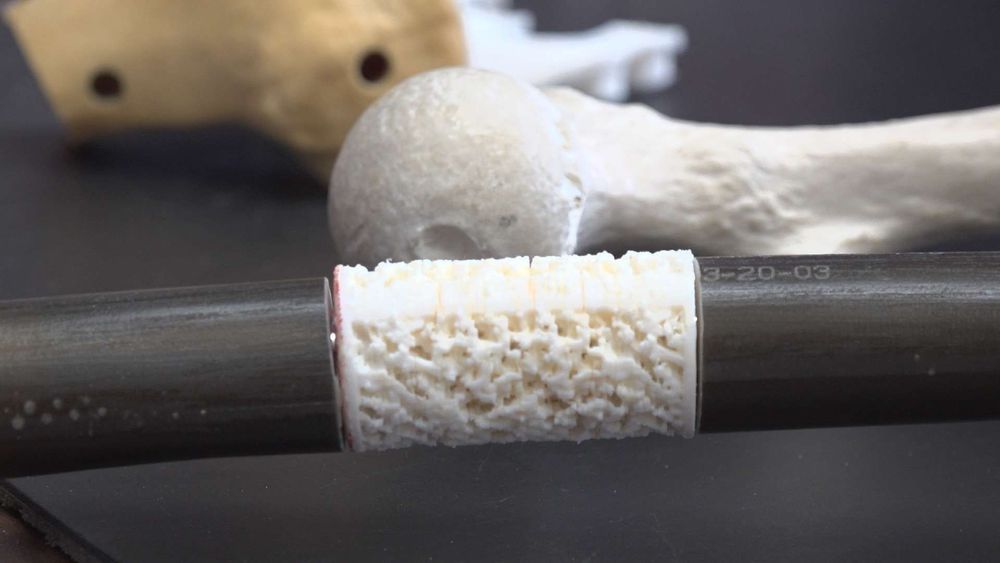
TUCSON, Ariz. – A lab in Arizona is hoping to help wounded veterans – through 3D printing.
Arizona’s Orthopedic Research Lab is hoping to use the technology to help military veterans with bone injuries.
Dr. John Szivek, who runs the University of Arizona Orthopaedic Research Lab, said the lab received a $2 million grant from the Department of Defense to create 3D bone printing to help military personnel.