Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
This Pinoy-made app was designed for fishermen with no smartphones
A smartphone app that helps people without smartphones? Read on to learn how it works: #SpaceApps #SpaceAppsPH
ISDApp is a Pinoy-designed app made especially for fishermen without smartphones. Learn how this app works—and why it won an award from NASA.

NASA Selects Experiments for Possible Lunar Flights in 2019
NASA is coming again… to the Moon!
NASA has selected 12 science and technology demonstration payloads to fly to the Moon as early as the end of this year, dependent upon the availability of commercial landers. These selections represent an early step toward the agency’s long-term scientific study and human exploration of the Moon and, later, Mars.
“The Moon has unique scientific value and the potential to yield resources, such as water and oxygen,” said NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine. “Its proximity to Earth makes it especially valuable as a proving ground for deeper space exploration.”
NASA’s Science Mission Directorate (SMD) initiated the request for proposals leading to these selections as the first step in achieving a variety of science and technology objectives that could be met by regularly sending instruments, experiments and other small payloads to the Moon.
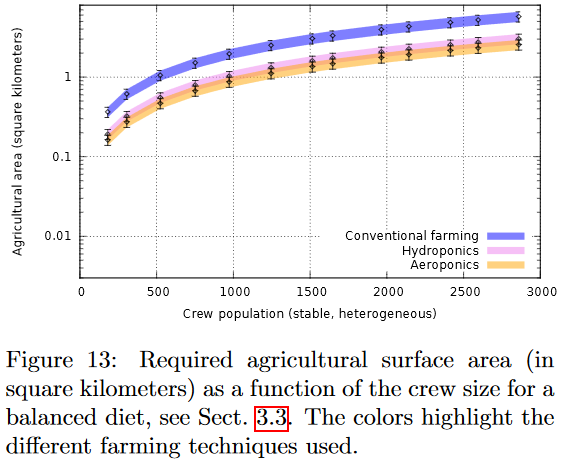
Dr. Marin’s Work on Generation Ships – Updated
Dr. Marin and his group are creating some great simulations involving generation ships. I’ve been following the work for a while and you can learn more about the three major papers they’ve produced. The first paper uses a Monte-Carlo simulation to measure viability. The second paper uses the HERITAGE program developed for the first paper to calculate the minimum crew for a generation ship. The third paper uses the same program to calculate food production for three different methods of agriculture.
Dr. Frédéric Marin at the Astronomical Observatory of Strasbourg is doing some great research on the feasibility of Generation Ships. A generation ship is “a hypothetical type of interstellar ark starship that travels at sub-light speed.” He and his team have created a wide variety of research papers and projects, which includes developing their own Monte Carlo calculation program.
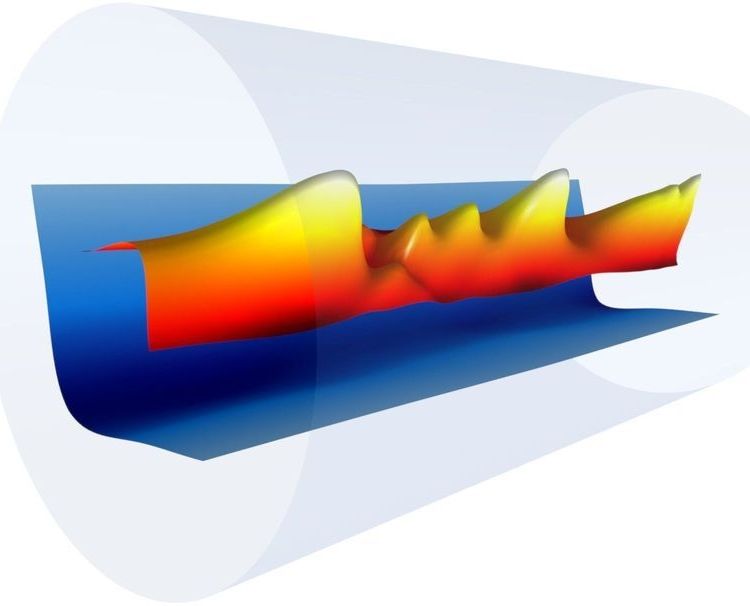
Laser ‘drill’ sets a new world record in laser-driven electron acceleration
Combining a first laser pulse to heat up and “drill” through a plasma, and another to accelerate electrons to incredibly high energies in just tens of centimeters, scientists have nearly doubled the previous record for laser-driven particle acceleration.
The laser-plasma experiments, conducted at the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab), are pushing toward more compact and affordable types of particle acceleration to power exotic, high-energy machines—like X-ray free-electron lasers and particle colliders—that could enable researchers to see more clearly at the scale of molecules, atoms, and even subatomic particles.
The new record of propelling electrons to 7.8 billion electron volts (7.8 GeV) at the Berkeley Lab Laser Accelerator (BELLA) Center surpasses a 4.25 GeV result at BELLA announced in 2014. The latest research is detailed in the Feb. 25 edition of the journal Physical Review Letters. The record result was achieved during the summer of 2018.
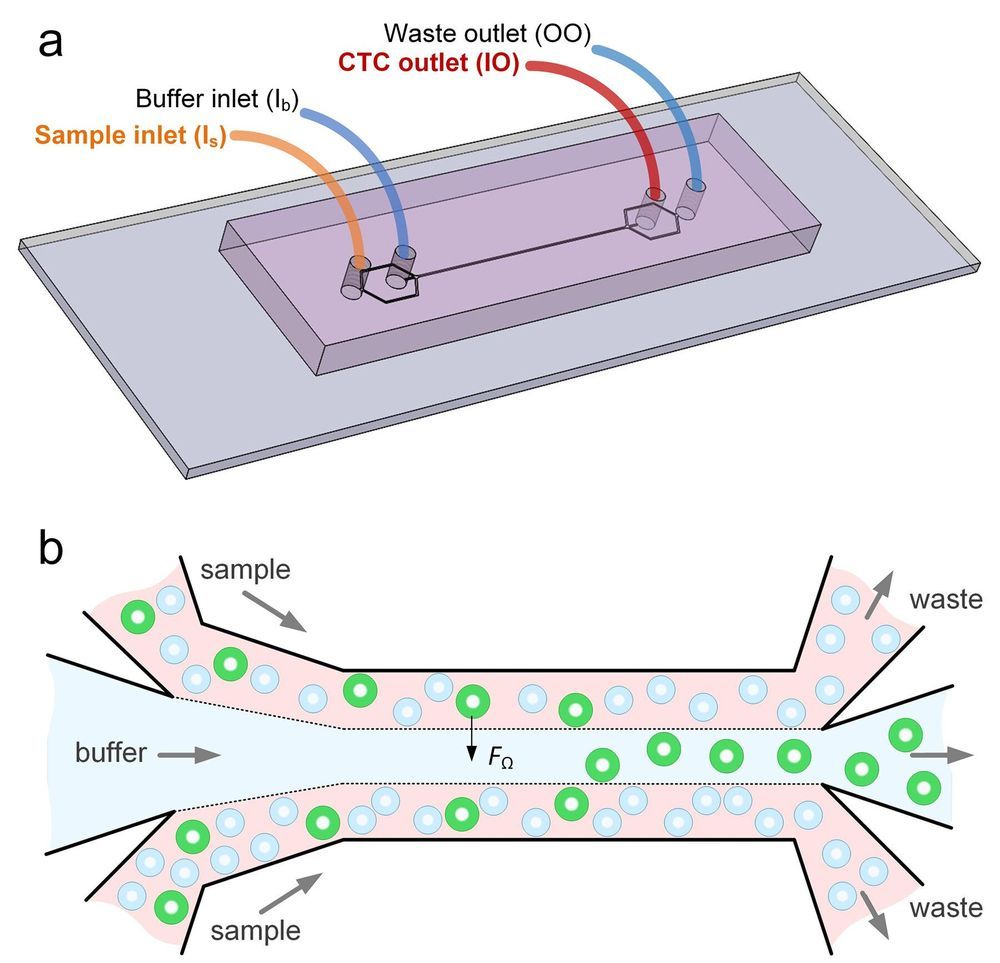
New microfluidics device can detect cancer cells in blood
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago and Queensland University of Technology of Australia, have developed a device that can isolate individual cancer cells from patient blood samples. The microfluidic device works by separating the various cell types found in blood by their size. The device may one day enable rapid, cheap liquid biopsies to help detect cancer and develop targeted treatment plans. The findings are reported in the journal Microsystems & Nanoengineering.
“This new microfluidics chip lets us separate cancer cells from whole blood or minimally-diluted blood,” said Ian Papautsky, the Richard and Loan Hill Professor of Bioengineering in the UIC College of Engineering and corresponding author on the paper. “While devices for detecting cancer cells circulating in the blood are becoming available, most are relatively expensive and are out of reach of many research labs or hospitals. Our device is cheap, and doesn’t require much specimen preparation or dilution, making it fast and easy to use.”
The ability to successfully isolate cancer cells is a crucial step in enabling liquid biopsy where cancer could be detected through a simple blood draw. This would eliminate the discomfort and cost of tissue biopsies which use needles or surgical procedures as part of cancer diagnosis. Liquid biopsy could also be useful in tracking the efficacy of chemotherapy over the course of time, and for detecting cancer in organs difficult to access through traditional biopsy techniques, including the brain and lungs.
Discovery of colon cancer pathway could lead to new targeted treatments
University of Massachusetts Amherst food science researchers have pinpointed a set of enzymes involved in tumor growth that could be targeted to prevent or treat colon cancer.
“We think this is a very interesting discovery,” says Guodong Zhang, assistant professor of food science, whose study was published in the journal Cancer Research. “Our research identifies a novel therapeutic target and could help to develop novel strategies to reduce the risks of colon cancer.”
Colon cancer is the third most common cancer and the second leading cause of cancer-related death in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, claiming some 50,000 lives each year. Those statistics emphasize the need to discover new cellular targets that are crucial in the development of colon cancer, Zhang says.

Chinese internet users turn to the blockchain to fight against government censorship
Thanks to blockchain, internet users have achieved some victories in the fight against China’s strict internet censorship.
A historic moment was made on April 23. Peking University’s former student, Yue Xin, had penned a letter detailing the university’s attempts to hide sexual misconduct. The case involved a student, Gao Yan, who committed suicide in 1998 after a professor sexually assaulted and then harassed her.
The letter was blocked by Chinese social networking websites, but an anonymous user posted it on the Ethereum blockchain.

Elon Musk: Mars Base Will Have “Outdoorsy, Fun Atmosphere”
In an interview newly published by Popular Mechanics, SpaceX CEO Elon Musk shared his thoughts on colonizing Mars — from how the first settlers will grow food to the friendly vibe he envisions at the first base on the Red Planet.
“For having an outdoorsy, fun atmosphere, you’d probably want to have some faceted glass dome, with a park, so you can walk around without a suit,” Musk told the magazine. “Eventually if you terraform the planet, then you can walk around without a suit. But for say, the next 100-plus years, you’ll have to have a giant pressurized glass dome.”

Superintelligence as a Service is Coming and It Can Be Safe AGI
Drexler and the Oxford Future of Humanity Institute proposing that artificial intelligence is mainly emerging as cloud-based AI services and a 210-page paper analyzes how AI is developing today.
AI development is developing automation of many tasks and automation of AI research and development will enable acceleration of AI improvement.
Accelerated AI improvement would mean the emergence of asymptotically comprehensive, superintelligent-level AI services that—crucially—can include the service of developing new services, both narrow and broad, guided by concrete human goals and informed by strong models of human (dis)approval. The concept of comprehensive AI services (CAIS) provides a model of flexible, general intelligence in which agents are a class of service-providing products, rather than a natural or necessary engine of progress in themselves.