Sound waves could help get quantum technology closer to reality, researchers say.

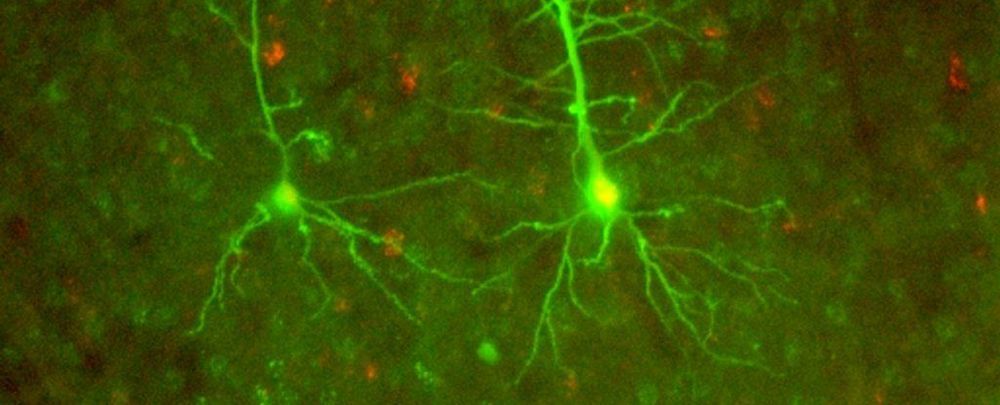
Scientists think they’ve identified a previously unknown form of neural communication that self-propagates across brain tissue, and can leap wirelessly from neurons in one section of brain tissue to another – even if they’ve been surgically severed.
The discovery offers some radical new insights about the way neurons might be talking to one another, via a mysterious process unrelated to conventionally understood mechanisms, such as synaptic transmission, axonal transport, and gap junction connections.
“We don’t know yet the ‘So what?’ part of this discovery entirely,” says neural and biomedical engineer Dominique Durand from Case Western Reserve University.

The immune system is incredibly important, thanks to its role in fighting off dangerous invaders in our bodies. But sometimes it gets it wrong, targeting harmless proteins from things like nuts or dairy products and triggering allergic reactions that ironically can themselves be fatal. Now, researchers from Michigan State University have identified a mechanism that helps keep the immune system in check, potentially paving the way for drugs that could prevent allergic reactions before they start.

But as the Chinese authorities embrace new information technology to monitor, manage and control the public like never before, the prospect of a sweeping social credit system has raised alarm around the world, especially with the ever-tightening grip on civil society, rights activism and religion.
A dozen or so cities are test beds for carrot-and-stick programmes to encourage businesses and individuals to comply with existing rules. The schemes have been criticised as Orwellian, but experience varies for those on the ground.
Join scientists atop the biggest trees on earth in this stunning 360° footage.

Researchers at IBM have recently devised a new technique to virtually patch security vulnerabilities before they are found. Their approach, presented at the International Workshop on Information and Operational Technology, co-located with RAID18, leverages testing techniques for supervised learning-based data generation.
“While researching a solution to find security vulnerabilities in popular software, we paused to think about the following problem: We know practically and theoretically that it is impossible to find all vulnerabilities in an application, and the security community is in a constant race to discover those vulnerabilities in the hope of finding them before the bad guys do,” Fady Copty, lead researcher of the study, told TechXplore. “This means enforcing regulations and constantly deploying security patches to systems.”
Deploying a security patch on an application is a tedious and time-consuming task, which entails a series of steps: identifying the vulnerable version of the application, managing this vulnerability, delivering the patch, deploying it and then restarting the application. Often, patches are deployed over long periods of time, hence applications can remain vulnerable for a period after a vulnerability has been discovered. To speed up this process, researchers have recently introduced virtual patches, which are enforced using intrusion detection and prevention systems.

Researchers this week announced they had developed an automatic text generator using artificial intelligence which is very good—so good, it is keeping details private for now.
That software developed by OpenAI could be used to generate news stories, product reviews and other kinds of writing which may be more realistic than anything developed before by computer.
OpenAI, a research center backed by Tesla’s Elon Musk, Amazon and Microsoft, said the new software “achieves state-of-the-art performance on many language modeling benchmarks,” including summarization and translating.

Deep-learning neural networks have come a long way in the past several years—we now have systems that are capable of beating people at complex games such as shogi, Go and chess. But is the progress of such systems limited by their basic architecture? Shimon Ullman, with the Weizmann Institute of Science, addresses this question in a Perspectives piece in the journal Science and suggests some ways computer scientists might reach beyond simple AI systems to create artificial general intelligence (AGI) systems.
Deep learning networks are able to learn because they have been programmed to create artificial neurons and the connections between them. As they encounter new data, new neurons and communication paths between them are formed—very much like the way the human brain operates. But such systems require extensive training (and a feedback system) before they are able to do anything useful, which stands in stark contrast to the way that humans learn. We do not need to watch thousands of people in action to learn to follow someone’s gaze, for example, or to figure out that a smile is something positive.
Ullman suggests this is because humans are born with what he describes as preexisting network structures that are encoded into our neural circuitry. Such structures, he explains, provide growing infants with an understanding of the physical world in which they exist—a base upon which they can build more complex structures that lead to general intelligence. If computers had similar structures, they, too, might develop physical and social skills without the need for thousands of examples.
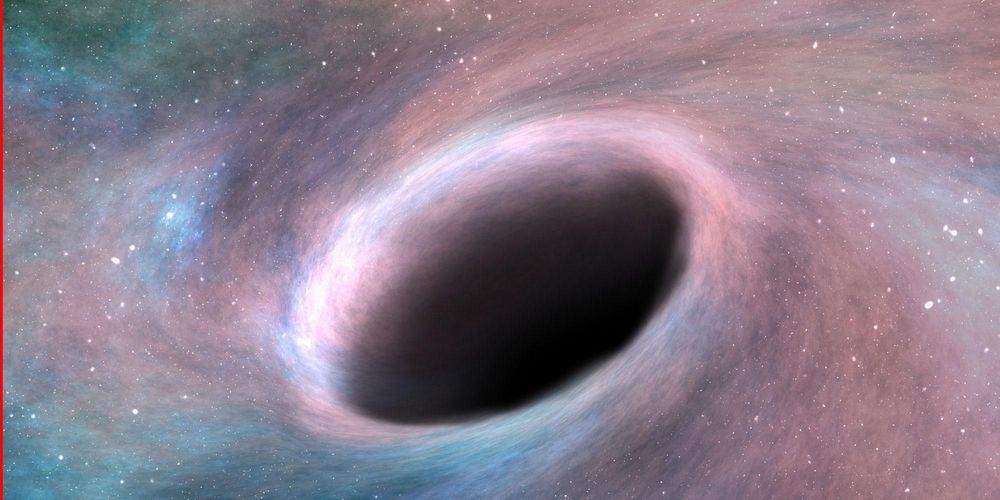

According to most astrophysicists, once you enter a black hole, that’s it for you: gravity will drag you to the singularity — a one-dimensional infinitely small space containing a huge mass — at the speed of light. Then, the black hole will ‘spaghettify you”. Nice.
However, a new study from Berkley University theorises not only that humans could survive going into a black hole, but that their past could be erased, giving way to “infinite futures”.
Physicist Peter Hintz argues that if a human traveller entered a “relatively benign” black hole, they might be able to shed the natural laws of physics — and survive.
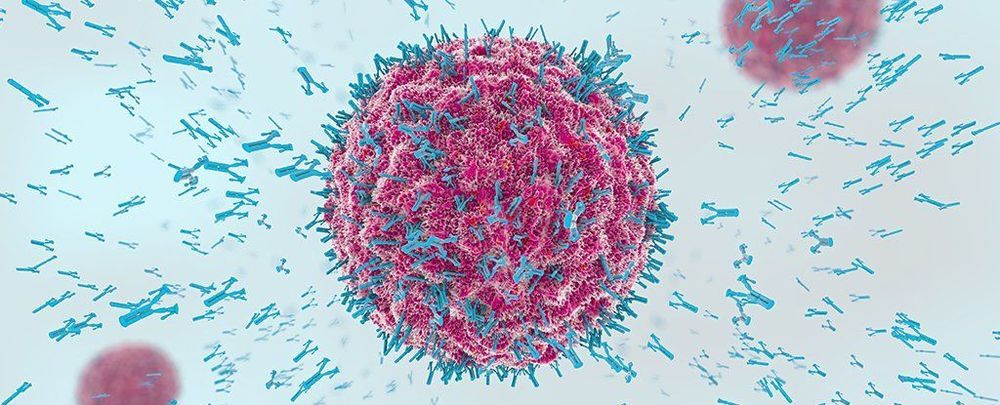
A toxic antibody is the latest weapon to show promise as a broad spectrum treatment for multiple forms of advanced cancer.
Dubbed a ‘Trojan horse’ approach to chemotherapy, the new drug has proven itself worthy of moving up the chain of clinical trials to being tested on a greater variety of patients. It’s not a fabled cure-all, but this approach might be as close as we’re going to get.
Researchers from The Institute of Cancer Research, London, and The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust tested the new treatment in a clinical trial involving 147 patients to evaluate its potential benefits and risks of side effects.