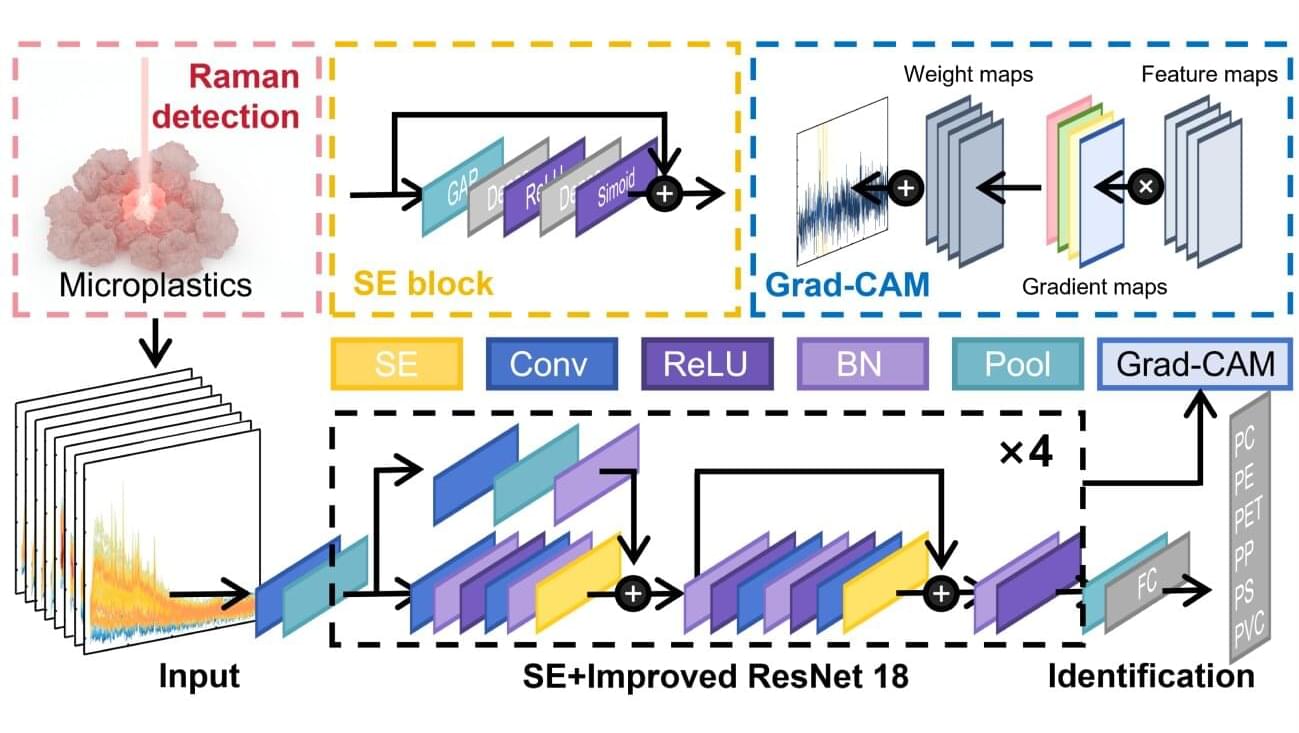
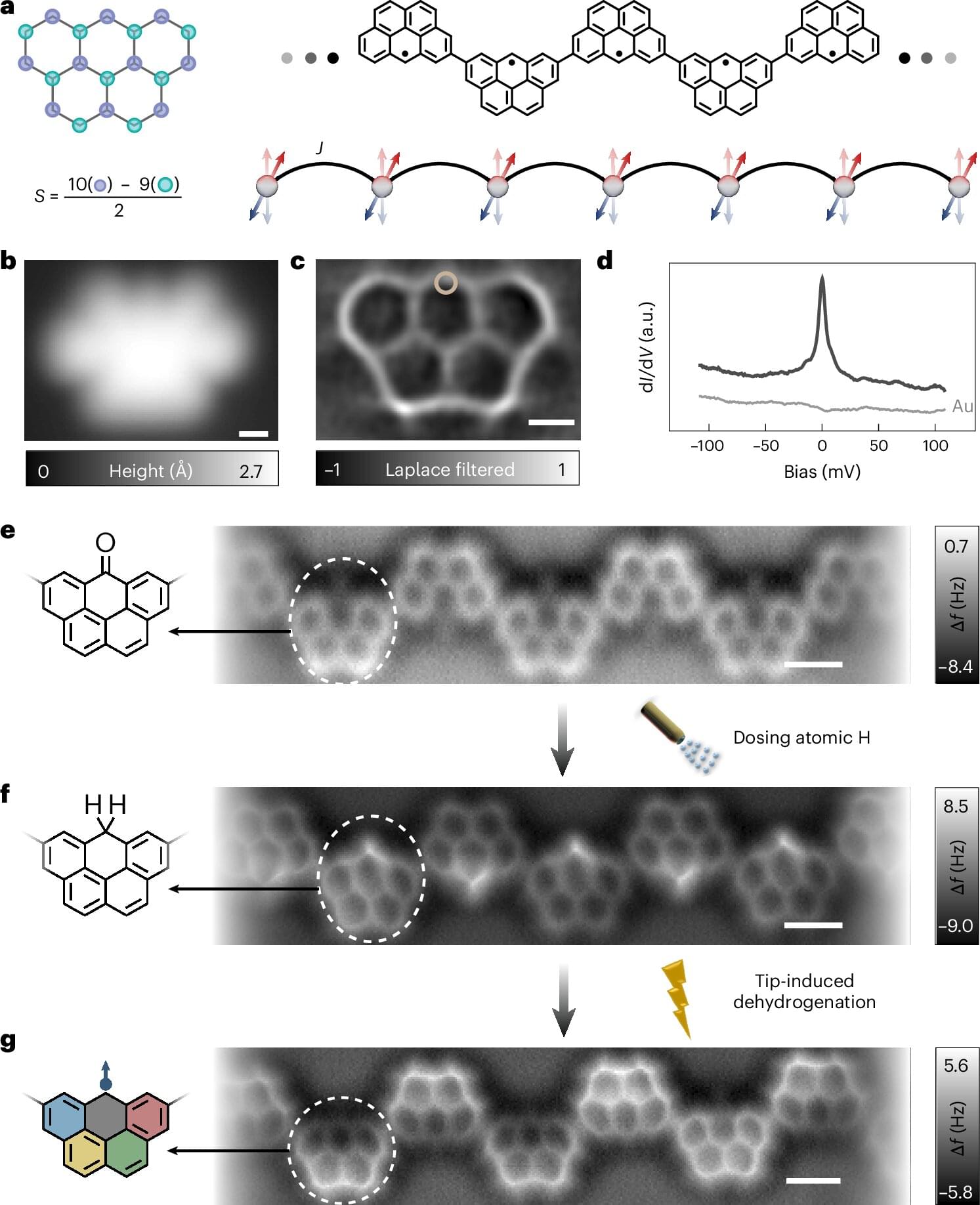
In a new publication in Nature Materials, an international team of researchers has developed groundbreaking artificial chains of the iconic “olympicene” molecules to realize the antiferromagnetic (AF) spin-½ Heisenberg model, a flagship quantum spin model that has been the cornerstone of quantum magnetism, since the seminal work of Bethe, for almost a century now. This study makes nanographenes (NGs) an ideal platform for realizing and studying highly entangled quantum spin systems, with potential applications in insulator-based AF spintronics.
In one-dimensional quantum magnets, strong quantum fluctuations prevent spontaneous symmetry breaking, leading to the formation of quantum-disordered many-body states such as resonating valence bond states. Half-integer spin chains are expected to exhibit a gapless excitation spectrum in the thermal dynamic limit, with the elemental excitations comprising at least two fractional spin-½ with well-defined energy-momentum relation, known as spinons.
In finite length, confinement effects introduce a quantization gap, which gradually approaches zero as the chain length increases (L→∞). Despite the theoretical appeal, the experimental realization of the isotropic spin-½ Heisenberg model faces significant challenges. Furthermore, the lack of access to well-defined finite chains hampers systematic studies on how spin excitations evolve with chain length and how even-and odd-numbered chains exhibit distinct behaviors.