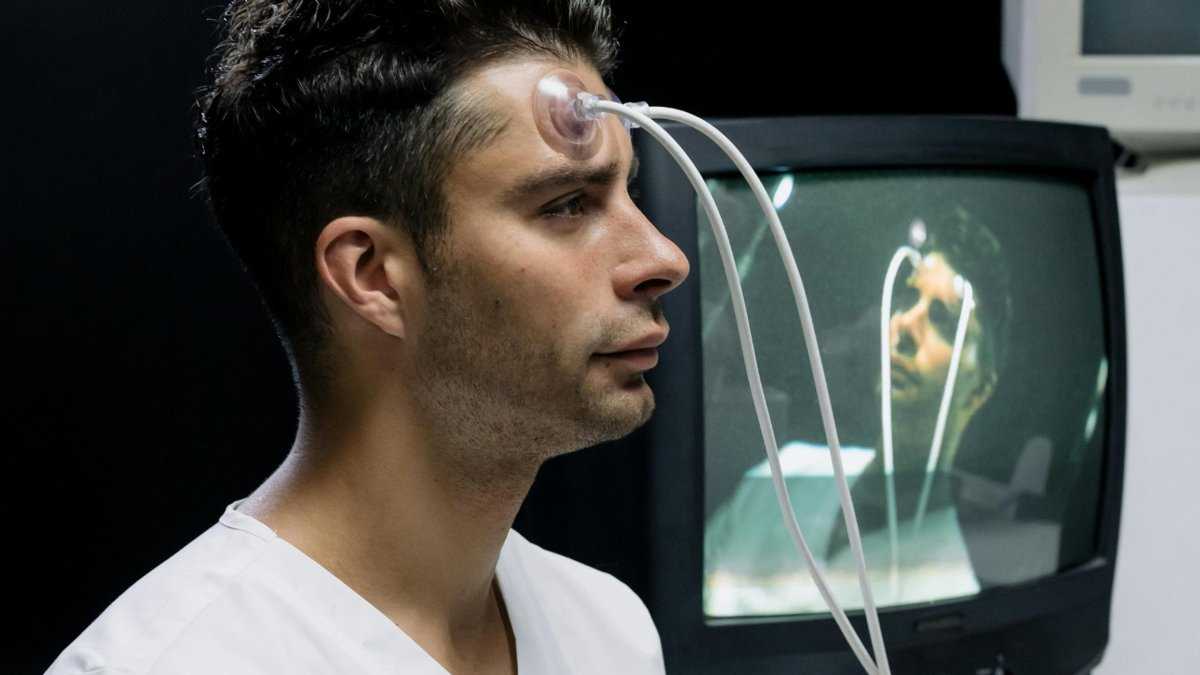
We can’t see what other people are thinking, so we have to infer it and that’s very crucial for our communication as humans. That’s how we create shared meaning and that’s how we choose our words to be understood, a kind of mental empathy.
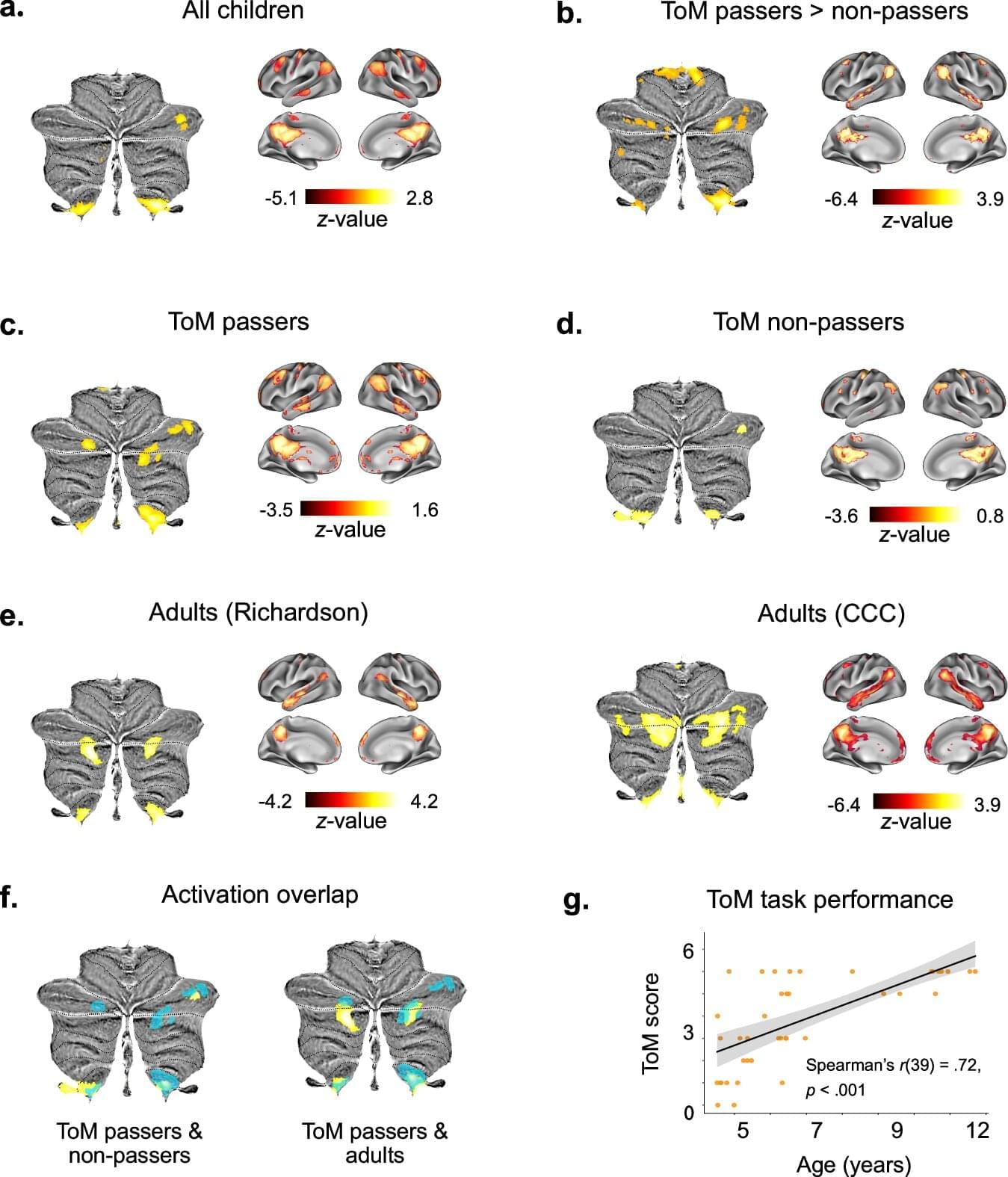
A pivotal milestone in the development of Theory of Mind reasoning occurs between the ages of 3 and 5 years, a breakthrough period in which children typically start succeeding in false-belief tasks, widely regarded as a critical test of Theory of Mind abilities. These tasks require children to recognize false beliefs held by a story character, typically in the context of the character’s mental misrepresentations regarding an object’s location, content, or nature. Successfully passing false-belief tasks is argued to reflect the emergence of representations of others’ mental states.
To find out more about this critical period where social cognition evolves, scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences used collected data from 41 children between 3 and 12 years old.