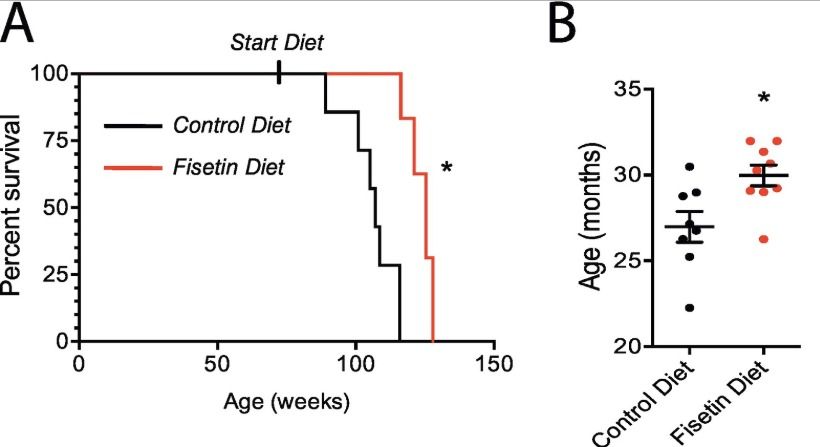
More information on the search for natural senolytics (that clear the senescent cells and potentially make us younger)- on ficetin, found in abundance for example in strawberries, a newly published study and discussion in the blog of Josh Mitteldorf. But we still would have to consume around 20 kg strawberries for two consecutive days to reach the dose used in the happy longer living mice!
Senolytic drugs have been the most promising near-term anti-aging therapy since the ground-breaking paper by van Deursen of Mayo Clinic published in 2011 . The body accumulates senescent cells as we age, damaged cells that send out signal molecules that in turn modify our biochemistry in a toxic, pro-inflammatory direction. Though the number of such cells is small, the damage they do is great. Van Deursen showed that just getting rid of these cells could increase lifespan of mice by ~25%. But he did it with a trick, using genetically engineered mice in which the senescent cells had a built-in self-destruct switch.
After that, the race was on to find chemical agents that would do the same thing without the genetically engineered self-destruct. They must selectively kill senescent cells, while leaving all other cells unharmed. It’s a tall order, because even a little residual toxicity to normal cells can be quite damaging. Before last week, the two best candidates were FOXO4-DRI and a combination of quercetin with dasatinib .
I’ve written in the past ( here and here ) that senolytic drugs are our best prospect for a near-term lift on the road to anti-aging medicine.