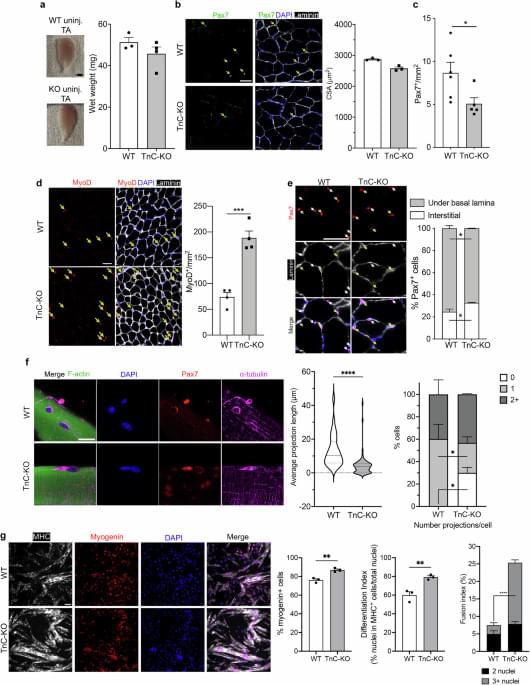
According to this study, temporal lobe sleep spindle activity is reduced in early clinical stages of Alzheimer disease and is associated with a faster rate of cognitive decline.



Physicists have so far failed to unify general relativity and quantum mechanics. As attempts to unite them into a quantum theory of gravity mount up, philosopher of physics Dean Rickles argues that the assumption of materialism is the problem. We need to look beyond the physical—beyond space, time and matter—to something primordial out of which minds can construct physical reality, and which explains both general relativity and quantum mechanics. Pioneers like John Wheeler and David Bohm have already begun to chart what such a realm of “pre-physics” might look like—it’s high time physics took their ideas more seriously.
A pair of recent physics Nobel prizes (2020 and 2022) were awarded for basic research in general relativity (Einstein’s theory of gravitation that explains gravity as the curvature of spacetime by matter and energy) and quantum mechanics (our best bet for a theory of matter and energy). The experimental successes of these theories keep piling up. There is clearly much truth in them. They both aim to describe the same world: this world. They should surely overlap, since the matter and energy described by quantum mechanics should curve spacetime as well as good old-fashioned non-quantum mechanical matter and energy. Why then can we not construct a theory in which they both appear? Why is it so difficult to build what would be a Quantum Theory of Gravity?

With this week’s launch, the company is poised to compete with SpaceX’s Starlink in beaming connectivity from space.
Size does matter
AST SpaceMobile launched its first satellite, BlueWalker 3, in September 2022 to test its ability to establsih cellphone towers in space. A year later, the company used its prototype satellite to carry out the first 5G phone call from space to a regular Samsung Galaxy S22.
The human brain is a fascinating and complex organ that supports numerous sophisticated behaviors and abilities that are observed in no other animal species. For centuries, scientists have been trying to understand what is so unique about the human brain and how it develops over the human lifespan.
Recent technological and experimental advances have opened new avenues for neuroscience research, which in turn has led to the creation of increasingly detailed descriptions of the brain and its underlying processes. Collectively, these efforts are helping to shed new light on the underpinnings of various neuropsychiatric and neurodevelopmental disorders.
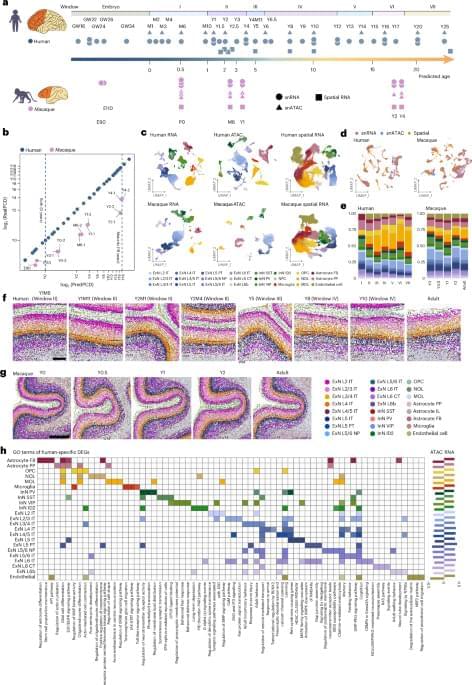
Researchers at Beijing Normal University, the Changping Laboratory and other institutes have recently set out to study both the human and macaque brain, comparing their development over time using various genetic and molecular analysis tools. Their paper, published in Nature Neuroscience, highlights some key differences between the two species, with the human pre-frontal cortex (PFC) developing slower than the macaque PFC.
“Unraveling the cellular and molecular characteristics of human prefrontal cortex (PFC) development is crucial for understanding human cognitive abilities and vulnerability to neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders,” wrote Jiyao Zhang, Mayuqing Li, and their colleagues in their paper. “We created a comparative repository for gene expression, chromatin accessibility and spatial transcriptomics of human and macaque postnatal PFC development at single-cell resolution.”
Human-specific molecular and cellular regulatory programs prolong prefrontal cortical maturation by orchestrating postnatal development of neurons and glia, with implications for cognitive function and susceptibility to neurodevelopmental disorders.
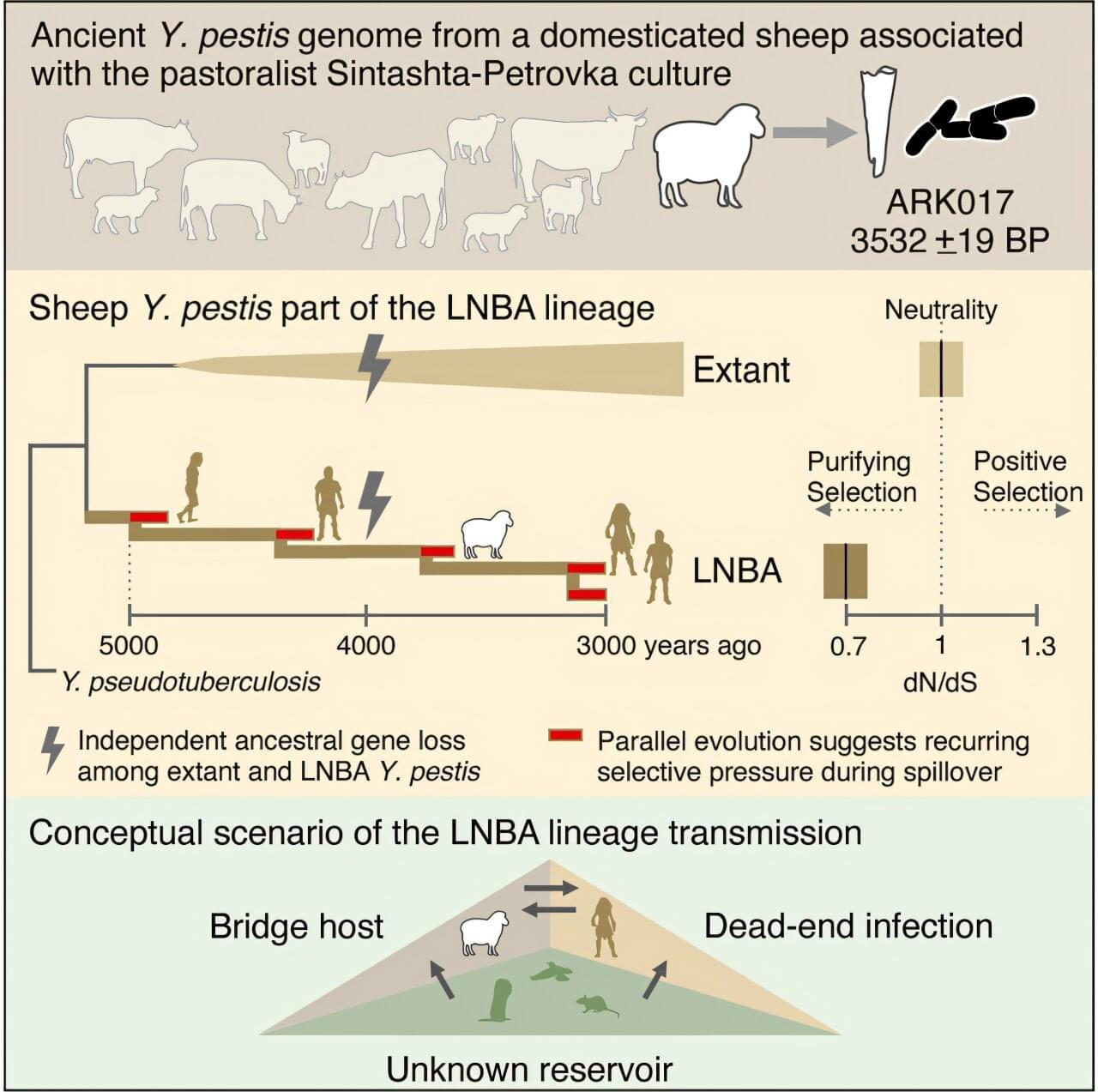
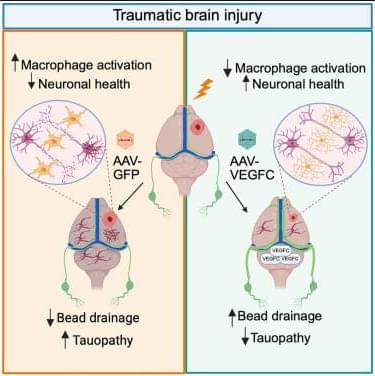
How traumatic brain injury (TBI) mechanistically contributes to neurodegenerative disease remains poorly understood. Marco et al. find that therapeutic viral vector-based delivery of VEGFC recuperates meningeal lymphatic drainage deficits post-TBI and protects against severe development of tauopathy, neurodegeneration, and cognitive decline in the PS19 mouse model of tauopathy.

