Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

Coffee Improves Brain Health, Prevents Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Say Researchers
Summary: Researchers say coffee prevents Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s for those consuming 3 cups daily. The brain health benefits of the beverage seem to differ between decaf and regular coffee. [Author: Brady Hartman. This article first appeared on LongevityFacts.com.]
Perhaps you’ve heard the latest news – the evidence on coffee’s health benefits is increasing every day.
In fact, new research shows that coffee protects your brain, and recent studies show that daily coffee drinkers have a significantly reduced risk of both Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases.

In Space and Cyber, China is Closing In on the United States
WASHINGTON — It should be no surprise that China is moving to challenge the United States for dominance in space, cyber, artificial intelligence and other key technologies that have wide national security applications. But the question that is still being debated is whether the United States is taking this threat seriously.
This may not be a Sputnik moment, but the United States could soon be unpleasantly surprised as China continues to shore up its domestic capacity to produce high-end weapons, satellites and encryption technologies, a panel of analysts told the House Armed Services emerging threats and capabilities subcommittee.
At the Tuesday hearing, Subcommittee Chairman Rep. Elise Stefanik, R-N.Y., said lawmakers are not entirely convinced that China’s dominance in many technology sectors is a “foregone conclusion.” But the committee does believe that China’s technological accomplishments should inform U.S. policies and defense investments. [The Most Dangerous Space Weapons Concepts Ever].

DARPA Thinks Bioengineered Spy Plants Are “The Future Of Intelligence Gathering”
If any organization embodies our idea of the classic mad inventors, just running amock with crazy ideas, it’s DARPA jumping dog robot? Sure. Self-guiding bullets? What can go wrong? Vertical take-off plane? Well, why not? Bioengineered spy plants? Wait, what?
Yes, the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency – DARPA – the part of the US Department of Defense responsible for developing technologies to be used by the military, is planning to bioengineer plants for intelligence gathering.
DARPA says its new program “envisions plants as discreet, self-sustaining sensors capable of reporting via remotely monitored, programmed responses to environmental stimuli.” Because that doesn’t sound terrifying at all. Somewhere between 1984’s foliage microphones and the classic “bug” in a pot plant.

New Breakthrough Drug Canakinumab Slashes Heart Attack and Cancer in Clinical Trial
In last years CANTOS trial, the anti-inflammatory drug Canakinumab reduced heart attacks 25% and cancer by 50%.
(Part of the look back at the best of 2017)
Summary: The drug Canakinumab reduced heart attacks by 25% and cancer by 50% by reducing chronic inflammation, according to the authors of the recent CANTOS trial. [This report was originally published on LongevityFacts on Aug 27, 2017, and has been updated. Author: Brady Hartman]
In late August, researchers announced that they had found a breakthrough drug which reduces heart attack risk by one-fourth while cutting the risk of cancer in half. The researchers announced that the new medicine can prevent tens of thousands of deaths from heart attack and cancer.
Biggest Breakthrough Since Statins
Harvard researchers said the discovery promises to “usher in a new era” of treatment. Presenting their findings at one of the largest gatherings of heart experts, doctors hail the new drug as the “biggest breakthrough since statins.”
New RNA Telomere Therapy Reverses Aging
(Part of the look back at the best of 2017)
Summary: Doctors lengthen telomeres with RNA therapy to reverse aging in human cells, according to a new research report. Telomere attrition is one of the nine hallmarks of aging. [Author: Brady Hartman] This article first appeared on LongevityFacts.]
Dr. John Cooke is department chair of cardiovascular sciences at Houston Methodist Research Institute and is the lead author of a recent paper published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology. Dr. Cooke’s team used RNA therapy to lengthen the telomeres of patients’ cells, making them younger in the process. In a video statement accompanying the report, the lead author remarked:
“We can make aged cells younger.”

.com Launches Bitcoin Cash Notary Service
Back in April of 2017 Bitcoin.com launched a notary service that was based on top of the bitcoin core (BTC) blockchain. However, due to the transaction bottleneck and extremely high fees, the notary service became unsustainable. Now Bitcoin.com has re-launched the notary using the bitcoin cash (BCH) blockchain, and anyone in the world can prove ownership for only 0.0005 BCH (about $0.97).
Also read: Lots of Optimism at the Miami Bitcoin Conference This Week
This week Bitcoin.com has re-launched the blockchain-based notary service that was once tethered to the bitcoin core blockchain. Unfortunately, the service did not work correctly because of transaction backlog, and high network fees to verify documents. Now the infrastructure is tied to the bitcoin cash blockchain making document verification extremely cheap, and fees are practically non-existent. Right now a user can upload a document for only 0.0005 BCH ($0.97), and the network transaction fee is less than a penny. (It’s important to note that records don’t actually “exist” on the chain per say, it is merely timestamped encrypted data that is tied to the file that’s processed into a valid BCH transaction.) Not only that but the proof will be verified in less than ten minutes, and you can rest assure the notarization service will be validated.
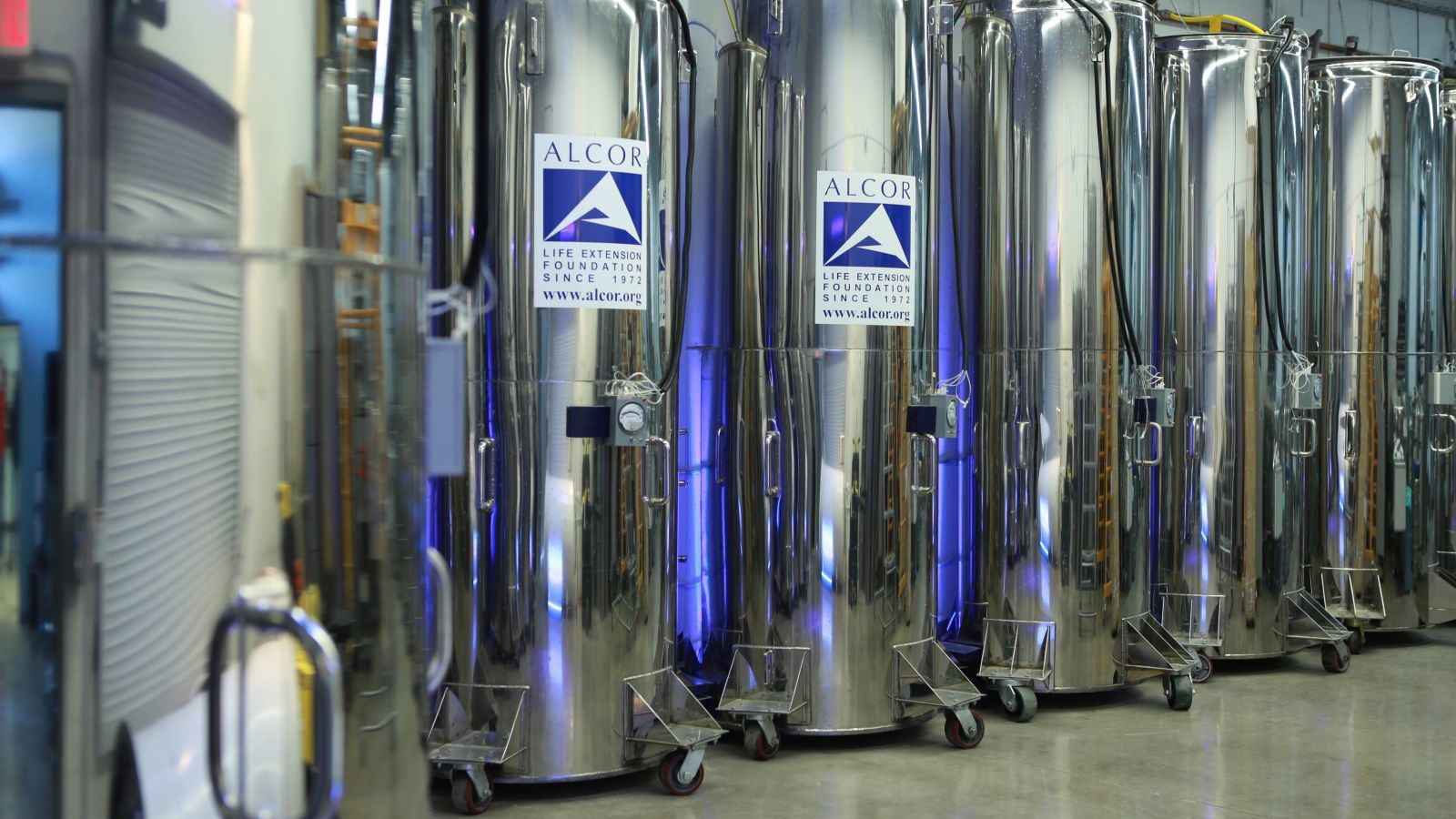

Fifty years frozen: The world’s first cryonically preserved human’s disturbing journey to immortality
“Yes, Mr. Bedford is here.”
That’s what Marji Klima, executive assistant at the Alcor Life Extension Foundation in Scottsdale, Arizona, told me over email this week. She was referring to Dr. James Hiram Bedford, a former University of California-Berkeley psychology professor who died of renal cancer on Jan. 12, 1967. Bedford was the first human to be cryonically preserved—that is, frozen and stored indefinitely in the hopes that technology to revive him will one day exist. He’s been at Alcor since 1991.
His was the first of 300 bodies and brains currently preserved in the world’s three known commercial cryonics facilities: Alcor; the Cryonics Institute in Clinton Township, Michigan; and KrioRus near Moscow. Another 3,000 people still living have arranged to join them upon what cryonicists call “deanimation.” In other words, death.
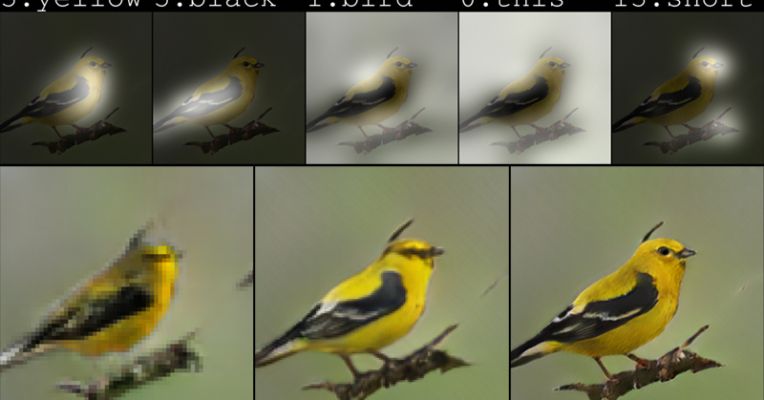


Microsoft’s new drawing bot is an AI artist
Microsoft today is unveiling new artificial intelligence technology that’s something of an artist – a “drawing bot.” The bot is capable of creating images from text descriptions of an object, but it also adds details to those images that weren’t included the text, indicating that the AI has a little imagination of its own, says Microsoft.
“If you go to Bing and you search for a bird, you get a bird picture. But here, the pictures are created by the computer, pixel by pixel, from scratch,” explained Xiaodong He, a principal researcher and research manager in the Deep Learning Technology Center at Microsoft’s research lab in Redmond, Washington, in Microsoft’s announcement. “These birds may not exist in the real world — they are just an aspect of our computer’s imagination of birds.”
The bot is able to generate a variety of images, researchers say, including everything from “ordinary pastoral scenes,” like those with grazing livestock, to the absurd – like “a floating double-decker bus.”