For the same price as an international economy airline ticket, the SpaceX Starship will fly in 20 minutes what takes a normal airliner 20 hours!


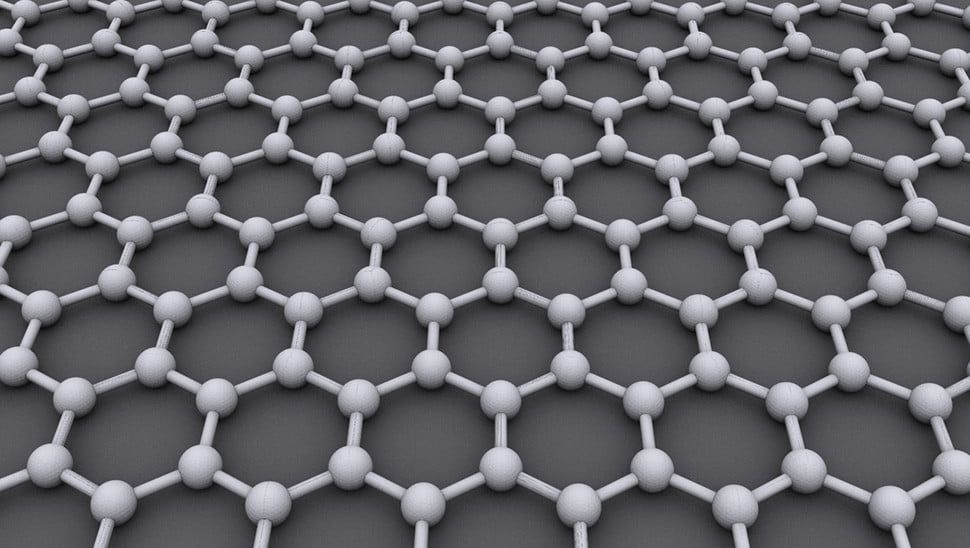
There’s no doubting that graphene, a single layer of graphite with the atoms arranged in a honeycomb hexagonal pattern, is one of science’s most versatile new materials. Capable of doing everything from filtering the color out of whisky to creating body armor that’s stronger than diamonds, graphene exhibits some truly unique qualities. However, while some mainstream uses of graphene have emerged, its use remains limited due to the challenge of producing it at scale. The most common way to make graphene still involves using sticky tape to strip a layer of atoms off ordinary graphite.
That’s something that researchers from the University of Rochester and the Netherlands’ Delft University of Technology have been working to change. They’ve figured out a way to mass produce graphene by mixing oxidized graphite with bacteria. Their method is cost-efficient, time-efficient, and sustainable — and may just make graphene a whole lot more available in the process.
“In our research, we have used bacteria to produce graphene materials on a bulk scale, and we showed that our material is conductive, and both thinner and able to be stored longer than chemically produced graphene materials,” Anne Meyer, professor of biology at the University of Rochester, told Digital Trends. “These properties demonstrate that our bacterial graphene would be well suited for a variety of applications, such as electrical ink or lightweight biosensors. Our approach is also incredibly simple and environmentally friendly compared to chemical approaches. All we have to do is mix our bacteria with the graphene precursor material, and leave them sitting on the benchtop overnight.”

Washington | Australian resources industry giants such as BHP and Rio Tinto could soon play a crucial role in NASA’s Mars mission, building and operating mines on the moon to extract rocket fuel for interplanetary travel.
In an interview with The Australian Financial Review on Tuesday (Wednesday AEST), NASA’s top boss, administrator Jim Bridenstine, urged Australian mining companies to grasp the opportunity and challenge of applying the industry’s expertise in remote resource extraction to the moon.
Known inside NASA as Artemis (the twin sister of Apollo in Greek mythology) the lunar missions will rely on turning hundreds of millions of tons of mined water ice recently discovered on the moon into liquid forms of hydrogen and oxygen to power spacecraft.
Palm oil is in almost everything, and it’s responsible for huge amounts of deforestation across the globe. These guys have found a way to replace it, using nothing more than a cup of coffee. #YEARSproject
This is an algae “biocurtain” and it’s cleaning up the air. 💚.

American scientist and best-selling #scifi author David Brin predicts what our world would like in the year 2050. Read it on our #Earth2050 platform:
By 2040, the international community has concluded that using nonrenewable resources is irrational. The first kind of asteroid to be mined was of the carbonaceous variety, to get water that can keep astronauts alive, or be used to create rocket fuel. Later, explorers prospected dozens of other varieties of asteroids with suitable iron, nickel, cobalt, platinoid, and rare-earth element deposits. Odyssey is the first ever space base focused on mining these minerals.
The station was launched in 2049. Because of magnetic storms and drastic changes in temperature, the main part of the base had to be built several meters below the asteroid’s surface. Almost all work on the base was automated. Small teams of engineers and technicians needed for station management stay for 6-month shifts. Using solar mirrors, they melt and refine precious metal ores and blow them into gleaming bubbles that can safely descend through Earth’s atmosphere to float in the ocean, for collection. The iron is used for construction in space.
This space project — the Odyssey — is so profitable that on April 22, 2055, Earth Day, the UN’s General Assembly adopts a resolution: to decrease mineral mining on our planet and to transfer some profits made from space to restore and preserve the Earth’s ecology.
The success of the project is based not only on the commercial value of mining but also on scientific advancements. The Odyssey houses laboratories with different specializations. New space discoveries make it possible to create new stations and even cities farther away from Earth.

10 best 3D map photogrammetry software reviewed. Top drone mapping and modelling solutions from DroneDeploy, Open Drone Map, Pix4D, PhotoScan, Precision Mapper, AutoDesk plus more.
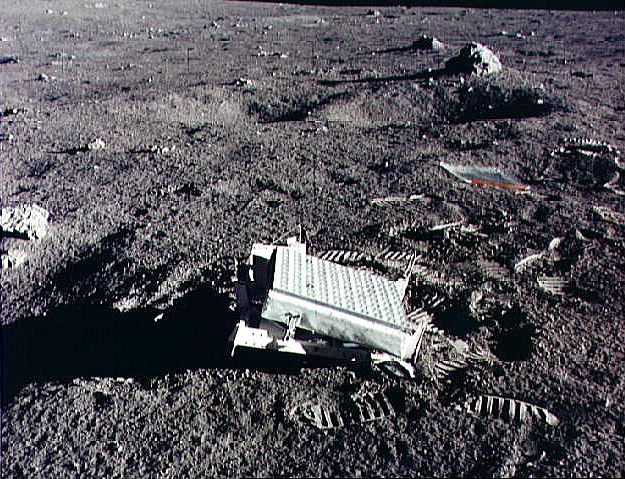
An epic lunar laser experiment is still going strong, five decades after the Apollo astronauts set it up on the surface.
The moonwalking crew of Apollo 11, which landed on the moon 50 years ago this month, put special retroreflectors on the lunar surface, as did the later crews of Apollo 14 and 15, in 1971. (Another retroreflector, built by the French, sits on the Soviet Lunokhod 2 rover that landed without a crew in 1973.)