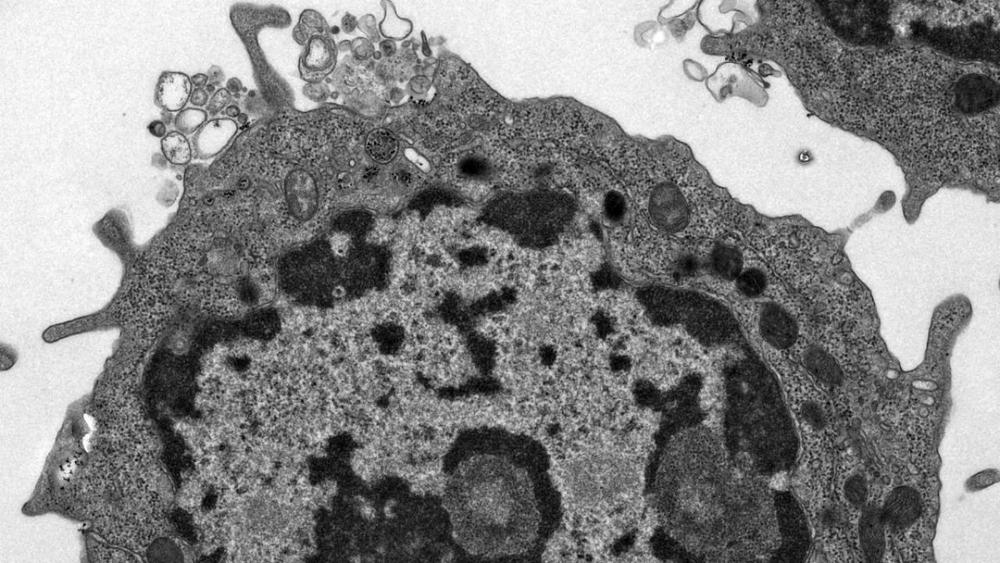
Cancer cells use a bizarre strategy to reproduce in a tumor’s low-energy environment; they mutilate their own mitochondria! Researchers at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) also know how this occurs, offering a promising new target for pancreatic cancer therapies.
Why would a cancer cell want to destroy its own functioning mitochondria? “It may seem pretty counterintuitive,” admits M.D.-Ph. D. student Brinda Alagesan, a member of Dr. David Tuveson’s lab at CSHL.
According to Alagesan, the easiest way to think about why cancer cells may do this is to think of the mitochondria as a powerplant. “The mitochondria is the powerhouse of the cell,” she recites, recalling the common grade school lesson. And just like a traditional powerplant, the mitochondria create their own pollution.