DARPA HQ, ARLINGTON, Va.: Reporters must stop asking Will Roper about the Arsenal Plane, because he hasn’t picked which aircraft will be rebuilt as a high-tech truck for long-range missiles and other weapons. Speculation has centered on the Air Force B-52, but the Strategic Capabilities Office director made clear that choice is, well, up in the air.
Now this, this will accelerate AI autonomous capabilities. However, still should be done with a QC secured infrastructure.
WASHINGTON — The Pentagon’s research agency has a new challenge for scientists: make wireless radios with artificial intelligence that can figure out the most effective, efficient way to use the radio frequency spectrum, and win a pile of cash.
Winners of the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency’s (DARPA) Spectrum Collaboration Challenge (SC2) could take home up to $3.5 million, but to do that, teams will have to demonstrate new technologies that represent a “paradigm shift” with both military and commercial applications, said Paul Tilghman, a DARPA program manager who is leading the challenge.
“The real crux of the problem is — when you look at users of the spectrum, whether they are commercial users of the spectrum, whether they’re consumers or they’re the military — the thing that is ubiquitously true is we all are placing more and more and more demand on the spectrum, and all of that demand is really adding up.
Advanced warfare platforms are increasingly using unused spectrum, now the Pentagon needs a system to cripple it
The US military is cultivating new electronic warfare technologies that, in real time, use artificial intelligence to learn how to jam enemy systems that are using never-before-seen frequencies and waveforms.
Although this “cognitive electronic warfare” is still in its nascent stages of development, scientists developing these systems told Defense News the technology could appear on the battlefield within the next decade.
Nice.
“We’ve managed to put quantum-based technology that has been used in high profile science experiments into a package that might allow it to be used commercially.”
Random number generators are crucial to the encryption that protects our privacy and security when engaging in digital transactions such as buying products online or withdrawing cash from an ATM. For the first time, engineers have developed a fast random number generator based on a quantum mechanical process that could deliver the world’s most secure encryption keys in a package tiny enough to use in a mobile device.
In The Optical Society’s journal for high impact research, Optica, the researchers report on their fully integrated device for random number generation. The new work represents a key advancement on the path to incorporating quantum-based random number generators — delivering the highest quality numbers and thus the highest level of security — into computers, tablets and mobile phones.
As I mentioned 4 months ago when an article came out stating that this type of concept of a scalable quantum chip was at least 15 years away was bunk; this is again one more example where contributors really need to do their homework and make sure they are speaking to the real folks on the frontlines of QC.
Quantum-based random number generators are now small enough that they could fit in mobile devices.
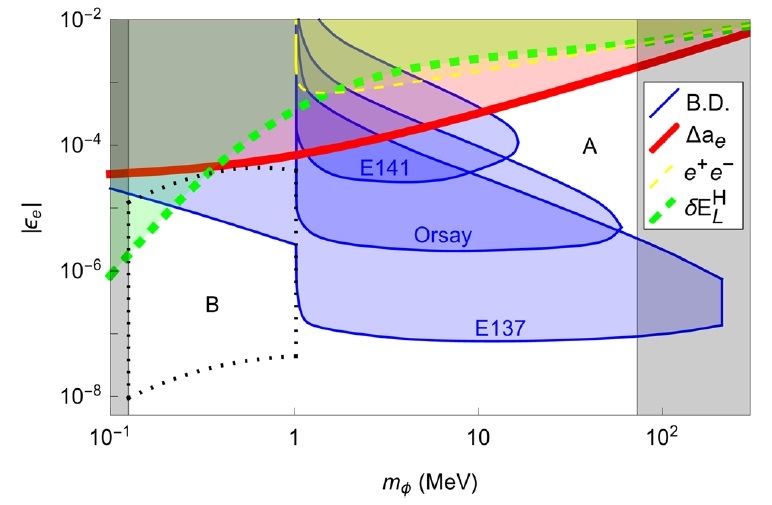
(Phys.org)—Although the Large Hadron Collider’s enormous 13 TeV energy is more than sufficient to detect many particles that theorists have predicted to exist, no new particles have been discovered since the Higgs boson in 2012. While the absence of new particles is informative in itself, many physicists are still yearning for some hint of “new physics,” or physics beyond the standard model.
In a new paper published in Physical Review Letters, physicists Yu-Sheng Liu, David McKeen, and Gerald A. Miller at the University of Washington in Seattle have hypothesized the existence of a new particle that looks very enticing because it could simultaneously solve two important problems: the proton radius puzzle and a discrepancy in muon anomalous magnetic moment measurements that differ significantly from standard model predictions.
“The new particle can account for two seemingly unrelated problems,” Miller told Phys.org. “We also point out several experiments that can further test our hypothesis.”
A Cornucopia of Sensory Perception
Posted in futurism
Growing up in Generation AI
Posted in computing, economics, robotics/AI
Imagine a five-year-old watching Mum talking to Siri, and Dad talking to Alexa, on a daily basis — what must she think of such interactions? Children nowadays witness computers that seem like they have a mind of their own — and even a personality with which to engage. It can be taken for granted that their perception of machines, and thus of the world itself, differs a lot from our own.
Artificial intelligence is one of the most promising areas of tech today, if not even the one that is likely to entail the most striking changes in our way of living, the way our economy works and how society functions. Thanks to enormous amounts of data, coupled with compute power to analyze it, technology companies are making strides in AI that resembles something of a gold rush.
New approaches, including use of deep neural networks, have led to groundbreaking achievements in AI, some of which weren’t predicted to happen for another decade. Google defeating the world champion at the ancient game of Go is just one prominent example. Many more are to be expected, including advances in deep learning combined with reasoning and planning — or even emulating creativity and artwork.
Elon Musk has recently hinted that he may be working on a “neural lace,” a mesh of electronics that will allow AI and the brain to work together. This could help human brains keep up with future enhancements in AI.
There’s no doubt that Elon Musk is one busy individual. When not playing on the Tesla factory floor, he may be bringing electric roofs to electric vehicles, or dreaming up the Hyperloop, or toying with the future of AI.
If not any of those, he is apparently busy protecting us from being treated like house pets after the Singularity. To that end, the billionaire polymath has revealed he may be working on something called a “neural lace.”