A new United Nations report on the world’s biodiversity found that between 500,000 and 1 million species face extinction due to habitat destruction.




Do you hear that? It’s the sound of Google executives practicing their lines ahead of Google I/O. The company’s annual developer conference in Mountain View, California, kicks off this Tuesday. The three-day event gives Google a chance to show off its latest work and set the tone for the year to come.
Can’t make it to the Shoreline Amphitheater? You can watch the entire keynote on the event page or on the Google Developers YouTube channel. It begins at 10 am PT (1 pm ET) on May 7 and should last for about 90 minutes. We’ll liveblog the whole thing here on WIRED.com.
Google I/O is technically a developer’s conference, and there should be plenty of talk about all the fun things developers can build using Google’s latest tools. But it’s also an opportunity to get consumers excited about what’s cooking in Mountain View. Last year, the company used the conference to debut its “digital wellness” initiative and a suite of new visual search tools for Google Lens. It also introduced Duplex, the eerily realistic AI assistant that can make dinner reservations and schedule haircuts like a human would.

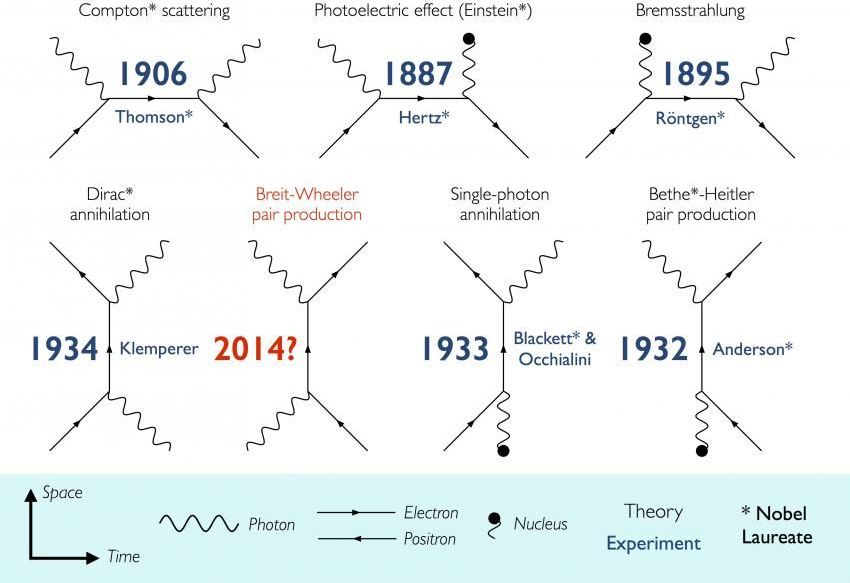
2014 Basically a real replicator could be possible with this discovery.
Imperial College London physicists have discovered how to create matter from light — a feat thought impossible when the idea was first theorised 80 years ago.
In just one day over several cups of coffee in a tiny office in Imperial’s Blackett Physics Laboratory, three physicists worked out a relatively simple way to physically prove a theory first devised by scientists Breit and Wheeler in 1934.
Breit and Wheeler suggested that it should be possible to turn light into matter by smashing together only two particles of light (photons), to create an electron and a positron – the simplest method of turning light into matter ever predicted. The calculation was found to be theoretically sound but Breit and Wheeler said that they never expected anybody to physically demonstrate their prediction. It has never been observed in the laboratory and past experiments to test it have required the addition of massive high-energy particles.

Electric bicycles are becoming so popular that they are now available in a wide range of styles. While conventional categories like electric road bikes and cruisers are common, a new wave of vintage-inspired electric bicycles is gaining in popularity. The Titan R electric bicycle is the latest to offer an eye catching cafe racer design.

Many in-development cures for type 1 diabetes have understandably focused on tackling the autoimmune aspect of the disease before figuring out a way to replace the destroyed beta cells. But what if focusing on the beta cells first could prevent their destruction altogether?
Researchers at Joslin have found that increasing the proliferation and turnover of beta cells before signs of type 1 diabetes could halt the development of the disease. In animal models, researchers in the lab of Rohit N. Kulkarni MD Ph.D., HMS Professor of Medicine and Co-Section Head of Islet and Regenerative Biology in the Joslin Diabetes Center, pushed the growth of beta cells while the animals were still young—meaning organs of the immune system were still developing, and still susceptible to manipulation. The results were published today in Nature Metabolism.
“We are clearly the first to show that if you push the proliferation to continuously generate new insulin producing beta-cells before the immune cell invasion starts then, for some reason we are still trying to figure out, immune cells stop attacking the beta cell,” says Dr. Kulkarni.
