Neural Nanonics here we come: “Could lead to future autonomous, fully implantable neuroprosthetic devices”
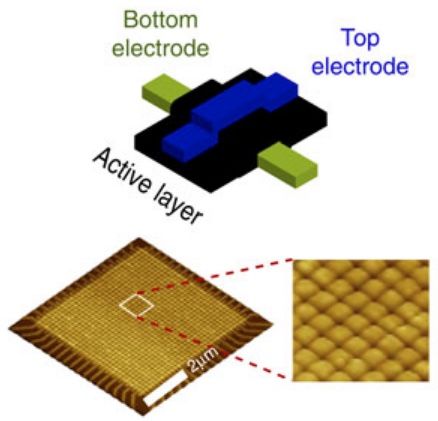
A bio-inspired electronic device called a memristor could allow for real-time processing of neuronal signals (spiking events), new research led by the University of Southampton has demonstrated.
The research could lead to using multi-electrode array implants for detecting spikes in the brain’s electrical signals from more than 1,000 recording channels to help treat neurological conditions, without requiring expensive, high-bandwidth, bulky systems for processing data. The research could lead to future autonomous, fully implantable neuroprosthetic devices.