“Let’s start from the ground up. Forget the room scale debate: the VR setup of the future moves with you.”
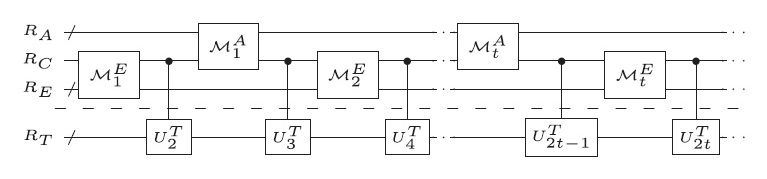
(Phys.org)—Over the past few decades, quantum effects have greatly improved many areas of information science, including computing, cryptography, and secure communication. More recently, research has suggested that quantum effects could offer similar advantages for the emerging field of quantum machine learning (a subfield of artificial intelligence), leading to more intelligent machines that learn quickly and efficiently by interacting with their environments.
In a new study published in Physical Review Letters, Vedran Dunjko and coauthors have added to this research, showing that quantum effects can likely offer significant benefits to machine learning.
“The progress in machine learning critically relies on processing power,” Dunjko, a physicist at the University of Innsbruck in Austria, told Phys.org. “Moreover, the type of underlying information processing that many aspects of machine learning rely upon is particularly amenable to quantum enhancements. As quantum technologies emerge, quantum machine learning will play an instrumental role in our society—including deepening our understanding of climate change, assisting in the development of new medicine and therapies, and also in settings relying on learning through interaction, which is vital in automated cars and smart factories.”
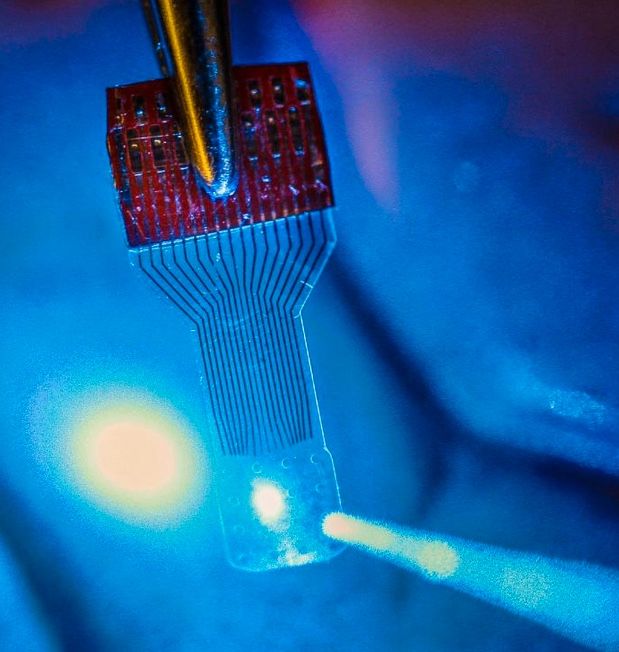
In an open-access paper published Thursday (Oct. 13, 2016) in the journal Nature Protocols, University of Wisconsin–Madison engineers have published details of how to fabricate and use neural microelectrocorticography (μECoG) arrays made with transparent graphene in applications in electrophysiology, fluorescent microscopy, optical coherence tomography, and optogenetics.
Graphene is one of the most promising candidates for transparent neural electrodes, because the material has a UV to IR transparency of more than 90%, in addition to its high electrical and thermal conductivity, flexibility, and biocompatibility, the researchers note in the paper. That allows for simultaneous high-resolution imaging and optogenetic control.
We live in an age of transformative scientific powers, capable of changing the very nature of the human species and radically remaking the planet itself.
Advances in information technologies and artificial intelligence are combining with advances in the biological sciences; including genetics, reproductive technologies, neuroscience, synthetic biology; as well as advances in the physical sciences to create breathtaking synergies — now recognized as the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
Archetype: Love this one
Posted in entertainment, military, robotics/AI
I hope the fickle gods of entertainment see fit to make this a regular show or movie…
Hollywood futuristic sci-fi | sci-fi short film.
RL7 is an eight-foot tall combat robot that goes on the run after malfunctioning with vivid memories of once being human. As its creators and the military close in, RL7 battles its way to uncovering the shocking truth behind its mysterious visions and past.
Artificial eggs have been grown in a petri dish for the first time and used to create living animals in a breakthrough hailed as ‘remarkable’ by British experts.
Scientists in Japan proved it is possible to take tissue cells from the tail of a mouse, reprogramme them as stem cells and then turn them into eggs in the lab.
The ‘eggs in a dish’ were then fertilised and the resulting embryos were implanted in female mice which went on to give birth to 11 healthy pups.
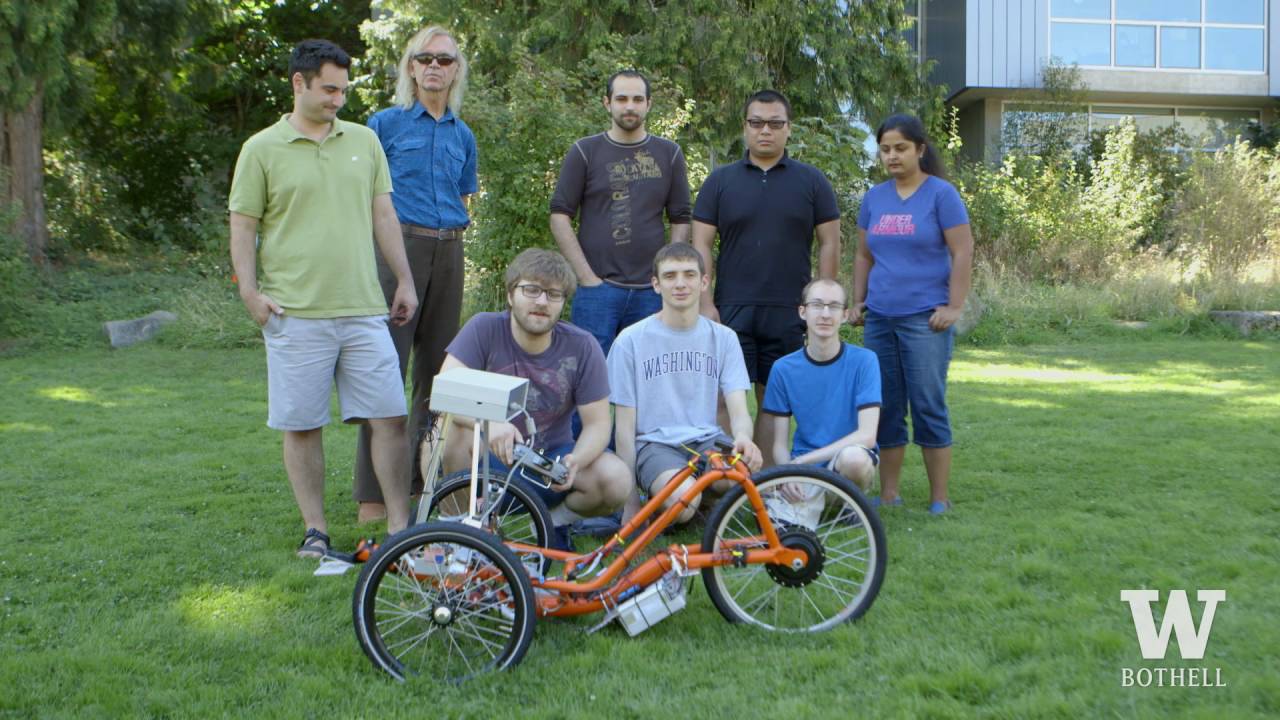
Self-driving cars, trucks and buses might get the bulk of the headlines, but a team at the University of Washington Bothell (UWB) is developing a smaller kind of autonomous vehicle. With the aim of providing a relatively inexpensive alternative to owning an autonomous car, the team is creating a self-driving trike that may even open up the possibility of an automated ride-sharing network, like a bike version of Uber’s or NuTonomy’s proposed services.
Can We Make It In Space?
Posted in space
When we type in a search query, access our email via the cloud or stream a viral video, chances are we don’t spend any time thinking about the technological plumbing that is behind that instant gratification.
Sitaram Lanka and Derek Chiou are two exceptions. They are engineers who spend their days thinking about ever-better and faster ways to get you all that information with the tap of a finger, as you’ve come to expect.
Now, they have a new superpower to help them out.