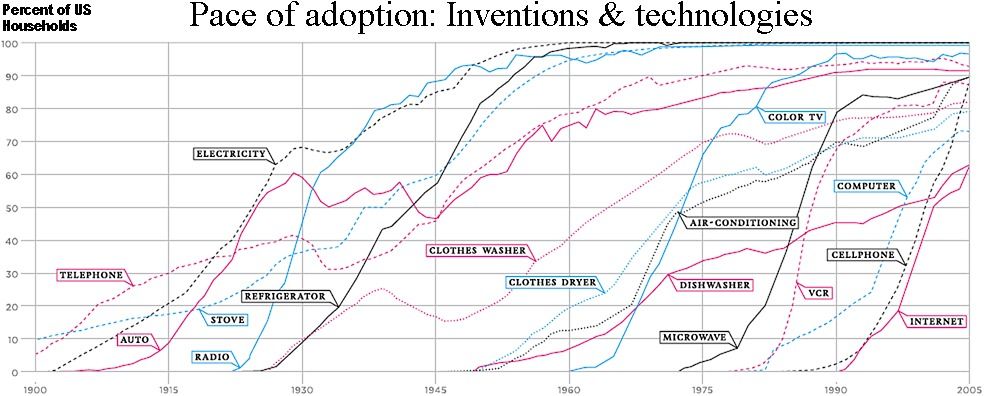
What about early adopters? Can they drive mass adoption?
Somewhat, but not much beyond market awareness. Generally, early adopters drive mass adoption only for evolutionary inventions. For example:
- The automobile was an evolutionary change to transportation. Although it changed our behavior (maintenance procedures and frequency / distance of travel), it did not require an educational seminar to ride in a car. You either had access to a horse or a car.
- Likewise, the audio CD and DVD improved media acquisition and enjoyment. But books and seminars were not needed to understand these inventions. Their purpose and use was very similar to the preceding technology: audio tape, records and video recorders.
But some inventions are different. Their use requires that users become acquainted with a technology or process that they didn’t realize they needed! [continue below image]…
The telephone and the Internet led to radical changes in the way we work and interact. You might think that the benefits of a telephone were obvious, even in 1876—and that adoption was driven only by cost and speed-to-market. But this is not the case. When the phone was demonstrated between two cities in Massachusetts, everyone was already aware of Alexander Graham Bell’s clever new gadget. But few people wanted one. A New York Times reporter scoffed that investors were wasting money, because the invention would be of little use to consumers and businesses. It didn’t occur to him that instant, ubiquitous communication (using a device that requires only a voice) would change the face of emergency services or allow close relatives to live far apart without wondering what happened to each other. He wrote that it was a rich man’s toy, useful only for hearing a voice from down the street.
What is required to shift Bitcoin into the mainstream?
Right now, only a small fraction of individuals believe that cryptocurrency presents an improvement over fiat (money issued by a government or bank). Most people don’t yet understand (or accept) that it is backed by something far more tangible than Dollars or Euros—or that it is more fair, or less susceptible to theft and manipulation. And because of spectacular press coverage, many people believe that it facilitates tax evasion, drug deals or worse. There are more misconceptions. For example, realizing that Bitcoin is open source, some individuals feel that other cryptocurrencies could improve on it, and displace it without recognizing the equity of past stakeholders. And finally, many individuals suspect that governments will ban it or issue their own crypto, making the whole issue moot.
Everything in the above paragraph—except the first sentence—is a false perception. But mass appeal and adoption is greatly retarded by false perception.
The adoption of cryptocurrency by mainstream businesses and consumers (not just as a payment instrument, but as the money itself) requires a series of events that are largely predicated on a recent past event. Think of this process as a row of dominos tumbling down—each one falling into the next domino.
The dominos have already started to fall. The process is slow, and it requires a few technical fixes related to cost, scalability, and ease of use. But they are falling and it is becoming clear that secure, decentralized, transparent cryptocurrency will replace nationally minted currencies all over the world. For some influential individuals, this is frightening, impossible or too radical. But this change is inevitable, because the cat is already out of the box and because the benefits to consumers, business and government are almost overwhelming
What are the ‘falling domino’ events and will they occur?
They are listed in the first article below—and, Yes—they are already occuring.
Philip Raymond co-chairs CRYPSA, hosts the New York Bitcoin Event and is keynote speaker at Cryptocurrency Conferences. He sits on the New Money Systems board of Lifeboat Foundation. Book a presentation or consulting engagement.