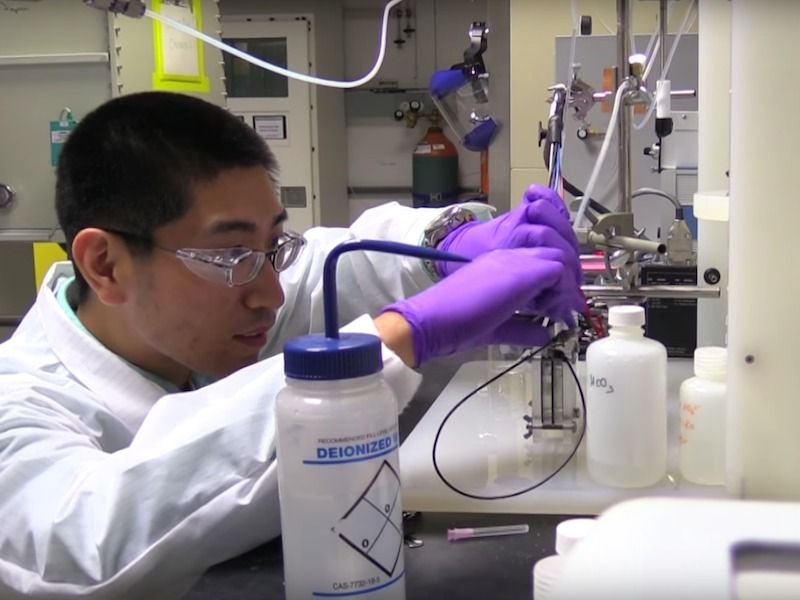
While self-driving vehicles will be revolutionary, having self-driving vehicles communicate with one another and with road infrastructure will take that revolution to the Nth degree. In a UK-first, a cross-company collaborative demonstration of these technologies working together has taken place.
ESA’s Mars Test Lander likely exploded on impact after dropping from a height of four kilometers after its retrorockets prematurely switched off. Just another lesson in how difficult these missions actually are; a cautionary tale for new space entrepreneurs.
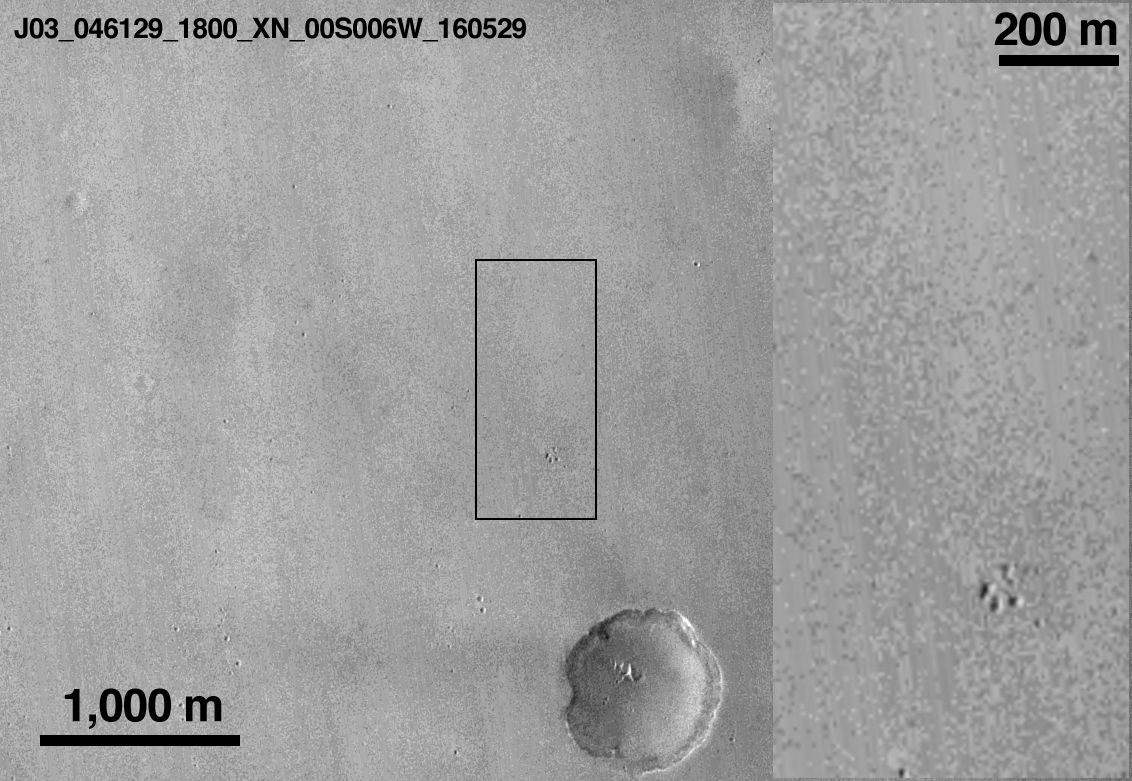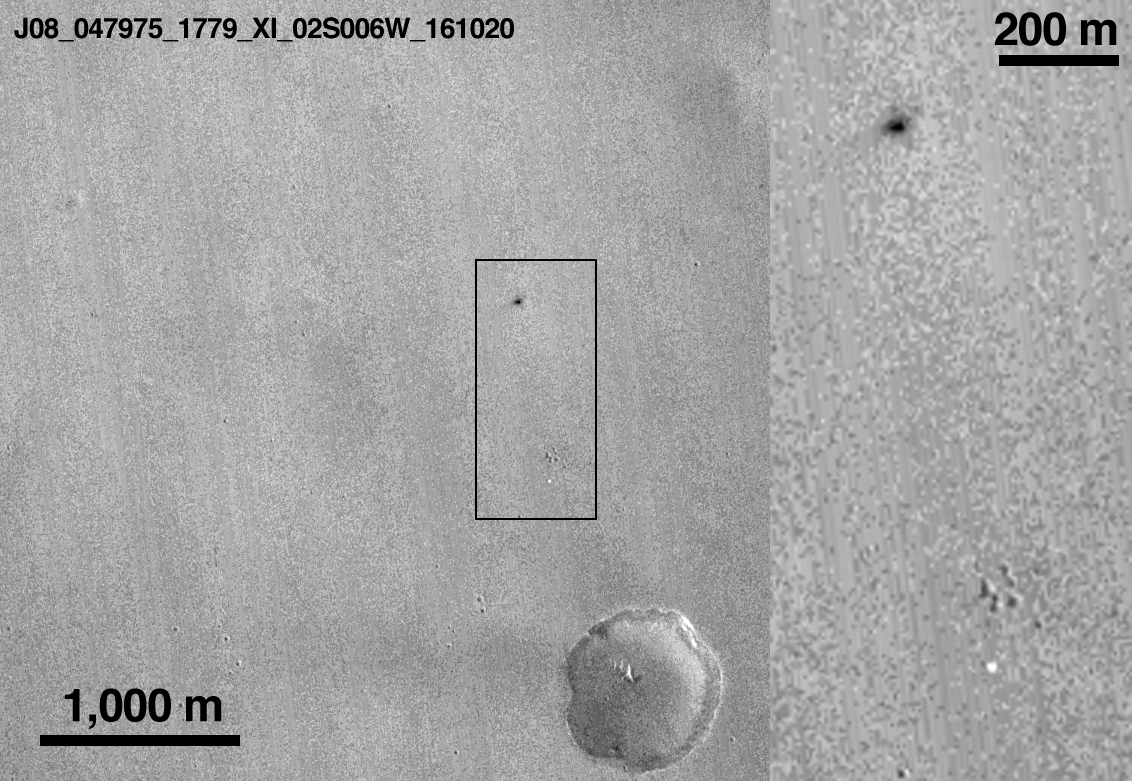
New NASA images of the Martian surface indicate that the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Schiaparelli ExoMars 2016 test lander likely crashed from a height of at least two to four kilometers as it made its way through the Red planet’s thin atmosphere.
Surface markings imaged by NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter and released via NASA JPL, identifies new markings believed to be related to ESA’s Schiaparelli Entry, Descent and Landing Demonstrator Module (EDM), which arrived at Mars on Oct. 19th. Schiaparelli may have exploded on impact after impacting at speeds greater than 300 kilometers per hour.
ESA’s ExoMars 2016 Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO) released the lander for what was to have been a six minute descent to the touchdown site at Meridiani Planum, a plain near Mars’ equator.
Researchers at Microsoft have published details of new speech recognition technology that they say transcribes conversational speech as well as a human does. “We’ve reached human parity,” says Microsoft’s chief speech scientist Xuedong Huang in a statement. “This is an historic achievement.”
The system’s word error rate is reported to be 5.9 percent, which Microsoft says is “about equal” to professional transcriptionists asked to work on speech taken from the same Switchboard corpus of conversations. It uses neural language models that group similar words together, allowing for efficient generalization. Microsoft plans to use the technology in Cortana, its personal voice assistant for Windows and the Xbox One, as well as speech-to-text transcription software.
Although the results are impressive, it’s far from an endgame for speech recognition. Microsoft still needs to tune the technology to work as well with conversations in a wider range of more challenging real-life situations and with a broader selection of voices. And for use cases such as Cortana, much of the difficulty comes from teaching the artificial intelligence to understand the meaning of words and act on them, not just accurately hear them.
Studies of different animal species suggest a link between eating less and living longer, but the molecular mechanisms by which caloric restriction affords protection against disease and extends longevity are not well understood.
New clues to help solve the mystery are presented in an article published in the September issue of Aging Cell by scientists at the Center for Research on Redox Processes in Biomedicine (Redoxoma), one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDCs) funded by FAPESP.
The results of in vitro and in vivo experiments performed by the Redoxoma team included the finding that a 40% reduction in dietary caloric intake increases mitochondrial calcium retention in situations where intracellular calcium levels are pathologically high. In the brain, this can help avoid the death of neurons that is associated with Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy and stroke, among other neurodegenerative conditions.
Group metals, a lil history on aluminum, technology needed, space law and more. The one great idea presented here is that many folks think stuff will be brought back to Earth. Though there would be some of that the resources out there will be used out there.
As Humans venture out far away from the Earth into the solar system, they will need material resources to keep us going. Where do we get those from? One for-profit company, Planetary Resources, wants to be the one to make it happen.
We had a chance to speak with the company’s President and CEO, Chris Lewicki about the company’s plans to survey, prospect, and exploit near-Earth asteroids. The company has a lot of financial backing and has plans to send its first satellite to an asteroid in 2020.
For the first time, a team including scientists from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have used neutron beams to create holograms of large solid objects, revealing details about their interiors in ways that ordinary laser light-based visual holograms cannot.
Holograms—flat images that change depending on the viewer’s perspective, giving the sense that they are three-dimensional objects—owe their striking capability to what’s called an interference pattern. All matter, such as neutrons and photons of light, has the ability to act like rippling waves with peaks and valleys. Like a water wave hitting a gap between the two rocks, a wave can split up and then re-combine to create information-rich interference patterns (link is external).
An optical hologram is made by shining a laser at an object. Instead of merely photographing the light reflected from the object, a hologram is formed by recording how the reflected laser light waves interfere with each other. The resulting patterns, based on the waves’ phase differences (link is external), or relative positions of their peaks and valleys, contain far more information about an object’s appearance than a simple photo does, though they don’t generally tell us much about its hidden interior.