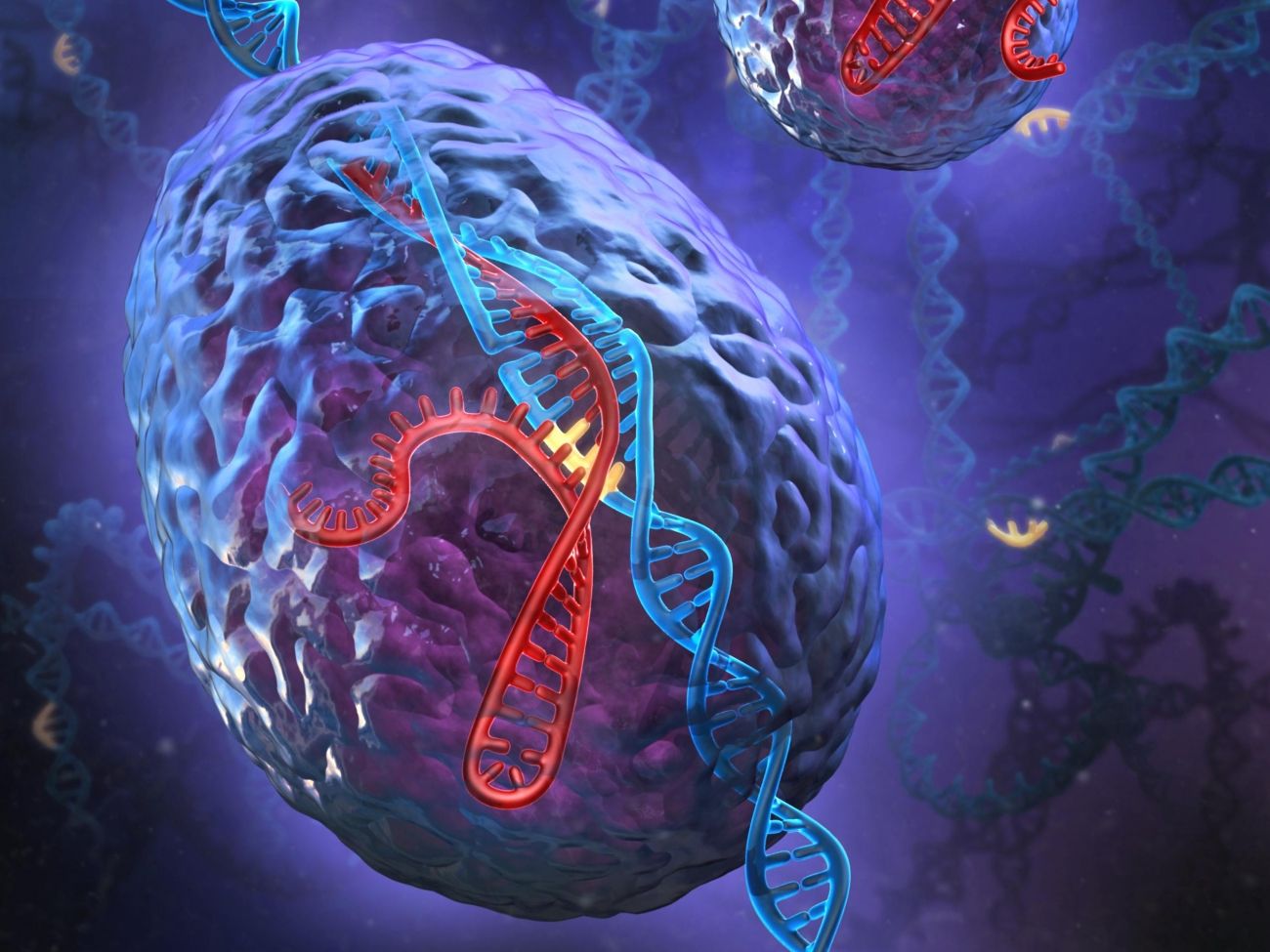
After getting off its $100 million-plus IPO in the summer, gene editing biotech Intellia Therapeutics is getting ready for human tests of its preclinical CRISPR tech with new digs designed to help bolster its research capabilities.
The biotech, which has the backing and partnerships of the likes of Atlas, Novartis and Regeneron, is on the move as it heads over to its new lab facilities at 40 Erie Street, in Cambridge, MA.
“The field of genome editing is rapidly evolving and our work to develop therapies for patients requires that we have the infrastructure necessary for R&D growth and prepare for preclinical studies and clinical trials,” said Dr. Nessan Bermingham, CEO and founder of Intellia Therapeutics.