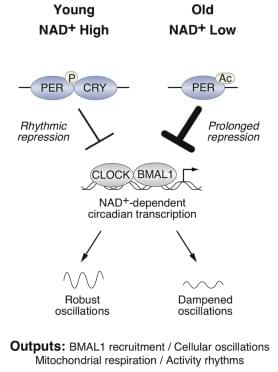
Disrupted sleep-wake and molecular circadian rhythms are a feature of aging associated with metabolic disease and reduced levels of NAD+, yet whether changes in nucleotide metabolism control circadian behavioral and genomic rhythms remains unknown. Here, we reveal that supplementation with the NAD + precursor nicotinamide riboside (NR) markedly reprograms metabolic and stress-response pathways that decline with aging through inhibition of the clock repressor PER2. NR enhances BMAL1 chromatin binding genome-wide through PER2 K680 deacetylation, which in turn primes PER2 phosphorylation within a domain that controls nuclear transport and stability and that is mutated in human advanced sleep phase syndrome.