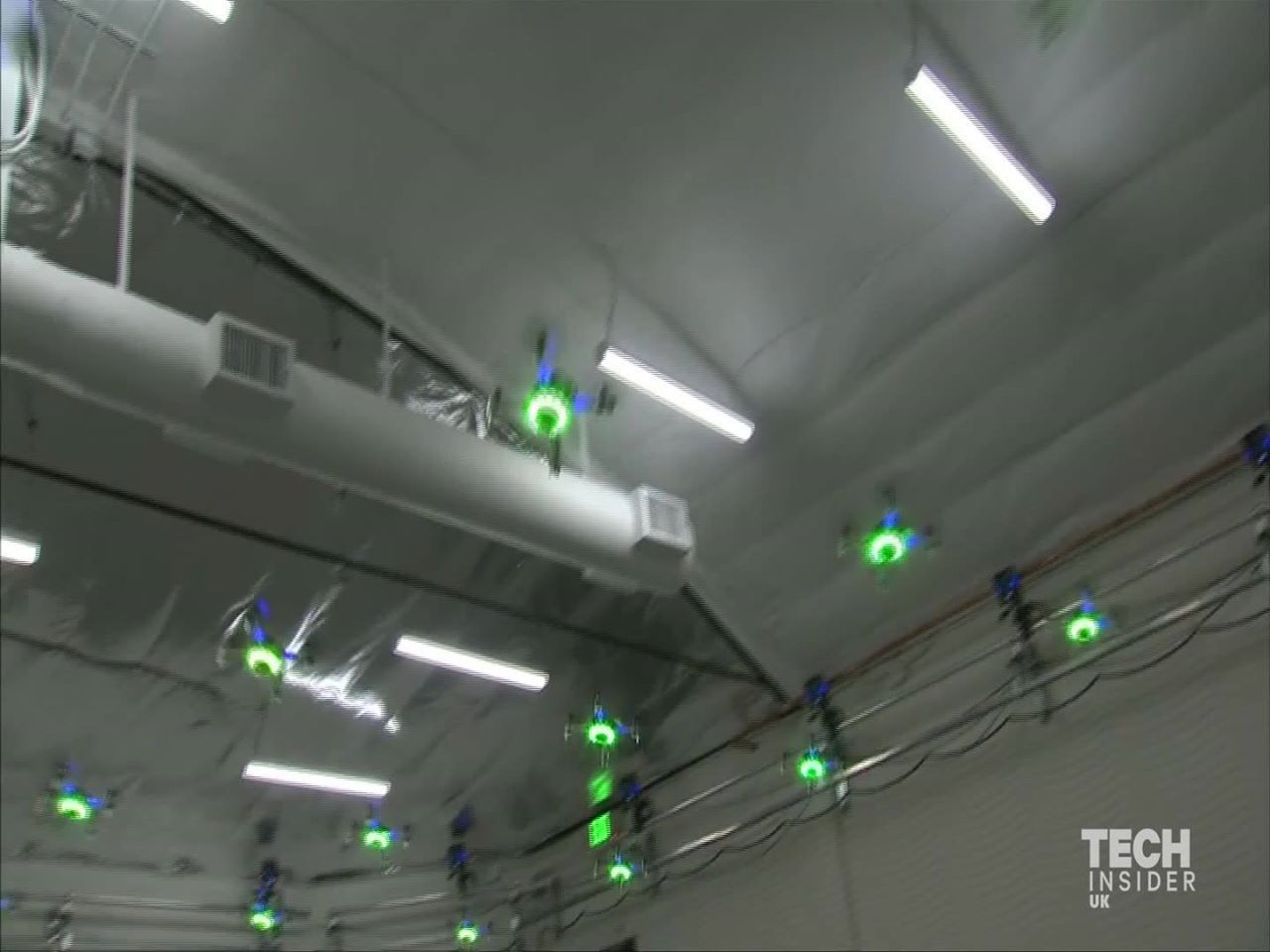
Two separate teams of researchers have been working on ways to exploit these lava tubes.
They are found in many volcanic areas on Earth, including Lanzarote, Hawaii, Iceland, North Queensland in Australia, Sicily and the Galapagos islands.
Previous research identified the potential for the underground networks of tubes, which can stretch up to 40 miles (65 kilometres), as habitats for future space dwellers.