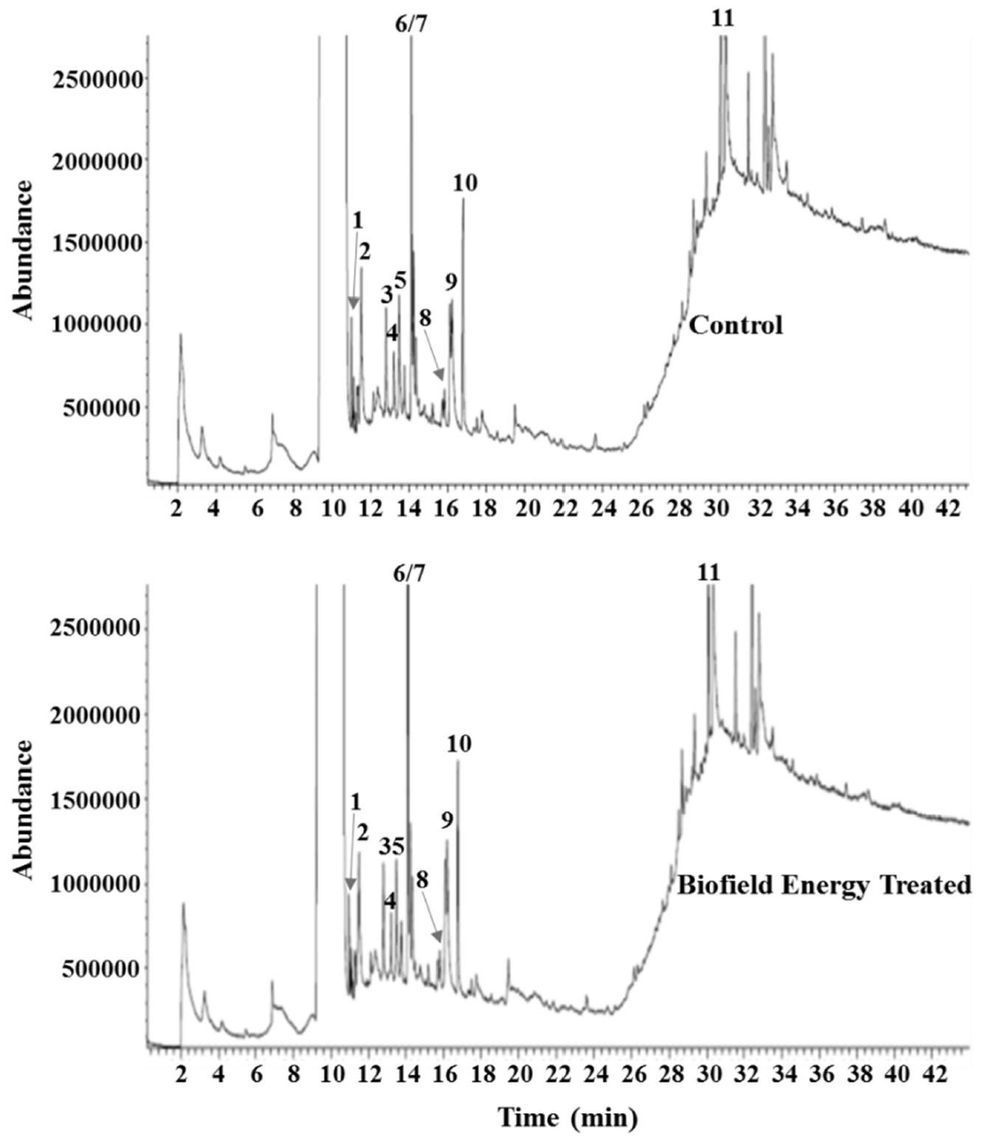
Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha) root extract is very popular ancient herbal medicine. The objective of the study was to characterize and evaluate the impact of The Trivedi Effect® — Energy of Consciousness Healing Treatment (Biofield Energy Healing) on phytoconstituents present in the ashwagandha root extract using GC-MS and NMR. Ashwagandha root extract was divided into two parts. One part was denoted as the control, while the other part was defined as The Trivedi Effect® — Biofield Energy Treated sample, which received The Trivedi Effect® — Energy of Consciousness Healing Treatment remotely from eighteen renowned Biofield Energy Healers. The GC-MS data indicated that the peak height and peak area of The Trivedi Effect® treated sample were found to be altered compared with the control sample. The peak height of the phytoconstituents present in the treated ashwagandha sample was altered significantly in the range of −8.32% to 89.25% compared with the control sample. Similarly, the peak area of the treated sample was altered significantly in the range of — 4.28% to 216.30% compared with the control sample. Overall, the change in the peak area% of the treated sample was significantly altered in the range of −18.29% to 170.18% compared with the control sample. The GC-MS and NMR analysis results identified the presence of withanolides such as glyco-withanolides, alkaloids, and sugars in the root extract in both the sample. The peak area of 2,3,4,5-tetrahydropyridazine , methyl ethyl sulfoxide , 5,6-dihydro-2-methyl-4(H)pyran-3,4-dione , diethoxy-2-methyl-propane , 2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxy-tetrahydro-pyran , and 3,4-dimethyl-2(3H)-furanone were significantly increased by 170.18%, 58.21%, 7.74%, 139.50%, 23.16%, and 45.63%, respectively in the treated sample compared with the control sample. On the contrary, the peak area% of 2-hydroxy-γ-butyrolactone was decreased by — 14.96% in the treated ashwagandha compared with the control sample. From the results, it can be hypothesized that The Trivedi Effect® — Biofield Energy Treatment might have the impact on the intrinsic physicochemical properties of the phytoconstituents present in the ashwagandha root extract and responsible for the alteration in the relative peak height/area of treated sample compared with the control sample. As a result, the concentrations of the phytoconstituents assumed to be increased in treated sample compared with the control sample. This treated ashwagandha root extract would be helpful for designing better nutraceutical/pharmaceutical formulations which might be providing a better therapeutic response against autoimmune diseases, nervous and sexual disorders, infectious diseases, antiaging, diabetes, cancer, immunological disorders, stress, arthritis, etc.
Keywords:
Biofield Energy Healing Treatment, Biofield Energy Healers, Consciousness Energy Healers, The Trivedi Effect®, Withania somnifera, Withanolides, GC-MS, NMR.