The microglia are central to aging in the brain and science is already finding ways to reverse it like introducing young microglia to the brain to remove plaques associated with Alzheimers. Brain aging is not a one way process!
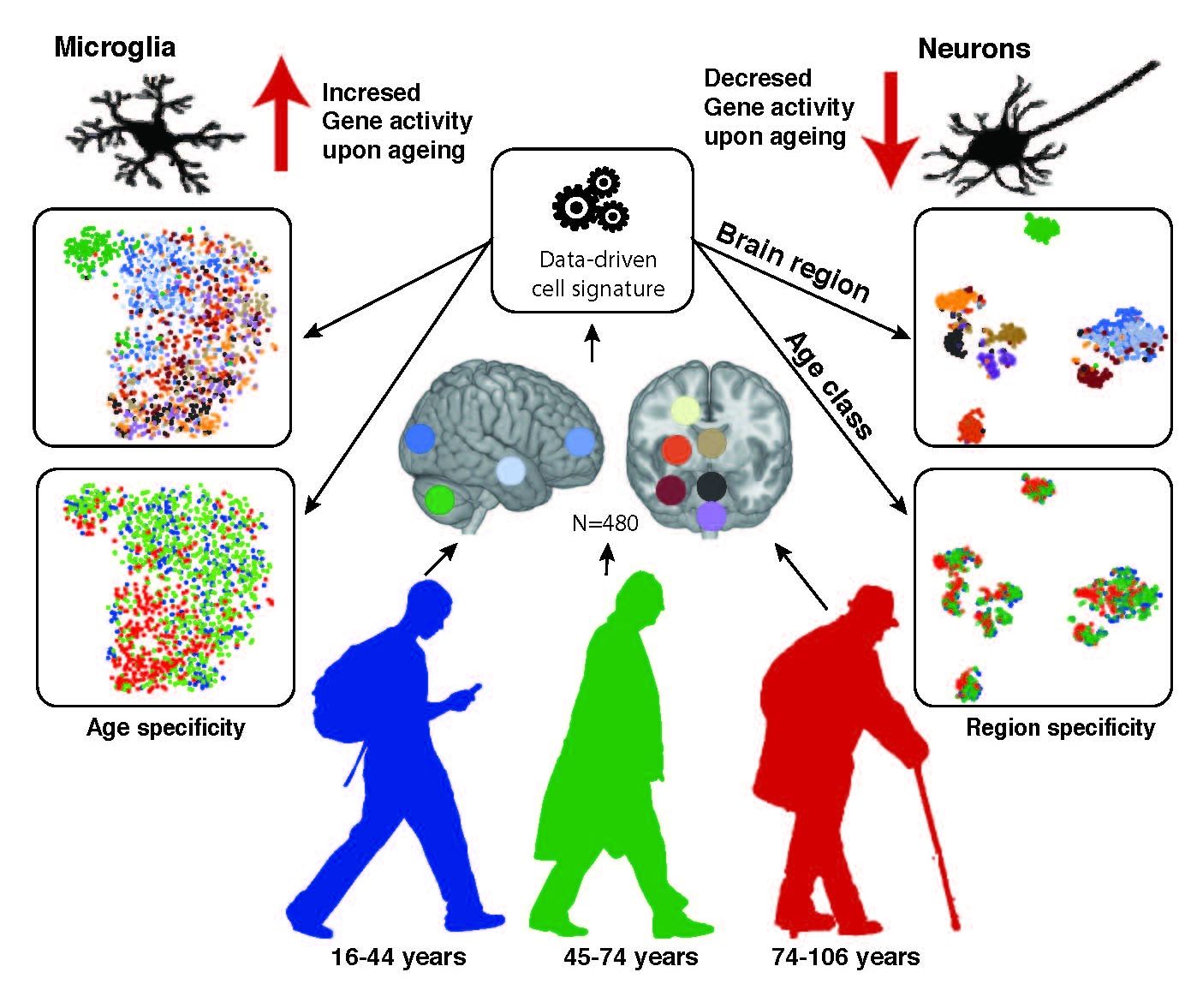
The difference between an old brain and a young brain isn’t so much the number of neurons but the presence and function of supporting cells called glia. In Cell Reports on January 10, researchers who examined postmortem brain samples from 480 individuals ranging in age from 16 to 106 found that the state of someone’s glia is so consistent through the years that it can be used to predict someone’s age. The work lays the foundation to better understand glia’s role in late-in-life brain disease.
“We extensively characterized aging-altered gene expression changes across 10 human brain regions and found that, in fact, glial cells experience bigger changes than neurons,” says Jernej Ule, a neurobiologist at the Francis Crick Institute and the University College London, who led the study with departmental colleague Rickie Patani (@PataniLab) and first author Lilach Soreq. “There’s quite a bit of regional information that will be of interest to different people—for example some will notice a very unique pattern of astrocyte-specific changes in the substantia nigra—and we provide a lot of data that still needs to be analyzed.”
There are three types of glia cells, each providing different kinds of support to neurons: oligodendrocytes insulate, microglia act as immune cells, and astrocytes help with neuron metabolism, detoxification, among many functions. Based on analysis of human brain tissue samples, primarily from the UK Brain Expression Consortium, the researchers show that astrocytes and oligodendrocytes shift their regional gene expression patterns upon aging, (e.g., which genes are turned on or off) particularly in the hippocampus and substantia nigra—important brain regions for memory and movement, respectively—while the expression of microglia-specific genes increases in all brain regions.