WASHINGTON – The U.S. Air Force is working closely with industry partners to strengthen cyber security for larger service platforms such as an F-22 or F-35 fighters. Business Insider reports.
A strange beeping noise in the Arctic has Canadians puzzled. Is it marine mammals doing something weird? A foreign submarine? Collective hallucination?
A military patrol and acoustic specialists are being dispatched to investigate, the army said Thursday.
Speculation has abounded since Inuit hunters in the village of Igloolik heard the beep several times off the Fury and Hecla Straight late last year.
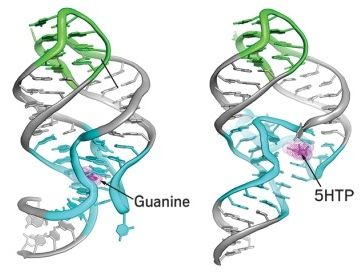
Scientists simulate evolution in the lab by introducing mutations iteratively into biomolecules such as nucleic acids and selecting for desired properties. When carrying this process out specifically on RNA molecules, they can evolve the RNAs to bind specific small molecules. But many of these so-called aptamers don’t bind well to their targets when put inside cells because they don’t fold into stable structures.
“As we solved the structures of naturally occurring aptamers, we noticed they had much more complex secondary and tertiary structures” than versions made in the lab, says Robert T. Batey of the University of Colorado, Boulder. “So we decided to use these naturally occurring RNA folds as starting points” for producing more stable artificial aptamers.
To prove their concept, Batey and coworkers used RNA sequences from naturally occurring ribozymes and riboswitches as scaffolds to evolve aptamers that bind amino acids and other small molecules used to make neurotransmitters (Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.2278). The resulting aptamers are selective for these precursor molecules over structurally similar amino acids and the neurotransmitters themselves.
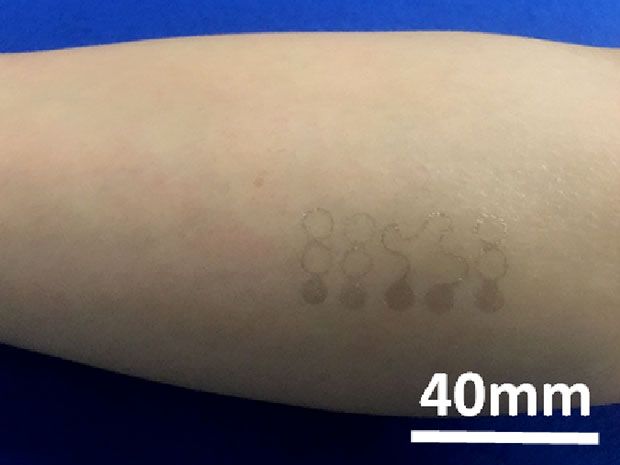
The graphene temporary tattoo seen here is the thinnest epidermal electronic device ever and according to the University of Texas at Austin researchers who developed it, the device can take some medical measurements as accurately as bulky wearable sensors like EKG monitors. From IEEE Spectrum:
Graphene’s conformity to the skin might be what enables the high-quality measurements. Air gaps between the skin and the relatively large, rigid electrodes used in conventional medical devices degrade these instruments’ signal quality. Newer sensors that stick to the skin and stretch and wrinkle with it have fewer airgaps, but because they’re still a few micrometers thick, and use gold electrodes hundreds of nanometers thick, they can lose contact with the skin when it wrinkles. The graphene in the Texas researchers’ device is 0.3-nm thick. Most of the tattoo’s bulk comes from the 463-nm-thick polymer support.
The next step is to add an antenna to the design so that signals can be beamed off the device to a phone or computer, says (electrical engineer Deji) Akinwande.
A simple technique for producing oxide nanowires directly from bulk materials could dramatically lower the cost of producing the one-dimensional (1D) nanostructures.
That could open the door for a broad range of uses in lightweight structural composites, advanced sensors, electronic devices – and thermally-stable and strong battery membranes able to withstand temperatures of more than 1,000 degrees Celsius.
The technique uses a solvent reaction with a bimetallic alloy – in which one of the metals is reactive – to form bundles of nanowires (nanofibers) upon reactive metal dissolution.
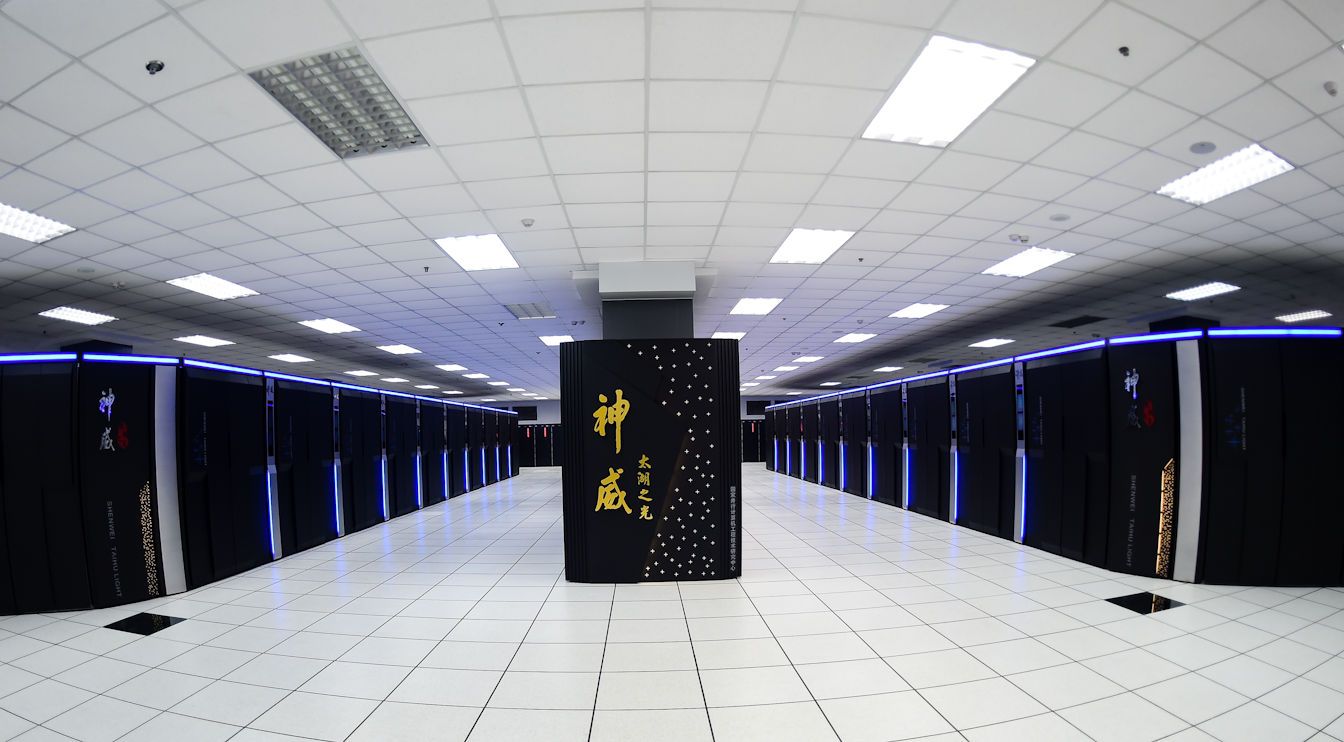
Back in June, China debuted the world’s fastest supercomputer, the Sunway TaihuLight (pictured), with a Linpack benchmark result of 93 petaflop/s. That machine contains 40,960 locally developed ShenWei processors, each with 260 cores and roughly comparable with Intel’s Knight’s Landing Xeon Phi CPU. China also developed a 136GB/sec memory controller and custom interconnect that delivers 16GB/sec of peak bandwidth between nodes.
Now China is working on a prototype exascale (1,000-petaflop) system that it aims to complete by the end of this year, according to state media. An exascale computer is capable of a quintillion calculations per second, and could deliver vast dividends in deep learning and big data across a variety of disciplines as varied as nuclear test research, code breaking, and weather forecasting.
“A complete computing system of the exascale supercomputer and its applications can only be expected in 2020, and will be 200 times more powerful than the country’s first petaflop computer Tianhe-1, recognized as the world’s fastest in 2010,” said Zhang Ting, an application engineer at Tianjin’s National Super Computer Center, to Xinhua news agency (via AFP).
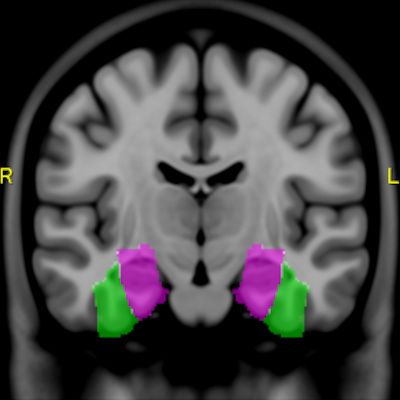
January 20, 2017 — Researchers have developed a high-resolution, interactive anatomic brain-mapping atlas they say can overcome the limitations of functional MRI (fMRI) and expand the modality’s value to conventional MR brain imaging and standard MRI applications.
The Gibby-Cvetko atlas is designed to segment the brain into finite anatomic regions with a resolution of 1 mm or less to correct for variations in the brain sizes of patients and better delineate the location of cortical structures and skull morphology.
“Having a high-resolution, interactive, quantitative brain atlas that we warp to fit the patient and run inside a PACS improves accuracy and speed of reading fMRI studies,” said co-developer Dr. Wendell Gibby, an adjunct professor of radiology at the University of California, San Diego. “It is a big step toward routine utilization of fMRI in clinical practice.”
It was when we tried virtual reality (VR) for the first time that we realized our method of controlling computers is likely to change. When you realize your VR headset is acting as a pointer in virtual reality, and you begin using your head like a mouse without even thinking about it, you start to grasp that there are much easier ways to control computers. Take foveated rendering (eye tracking) as an example. Soon computers will know exactly where you are looking – blink twice for double click!
Last November 2016, we posted an article, “Brain Implants that Augment the Human Brain Using AI” where we talked about exploring the hippocampus to solve brain disorders associated with memory loss. Much work has been done by Dr. Theodore W. Berger into neurobiological issues related to the hippocampus, primarily around implants to explore signal processing of hippocampal neurons. As it turns out, the hippocampus is the storage for our short-term memory working much like the RAM does in your computer. This is the motivation behind Bryan Johnson’s $100 million investment into his brain augmentation startup Kernel.
A Brain Computer Interface (BCI) or Brain Machine Interface (BMI) has numerous definitions, but the common elements found among all the definitions are as follows: