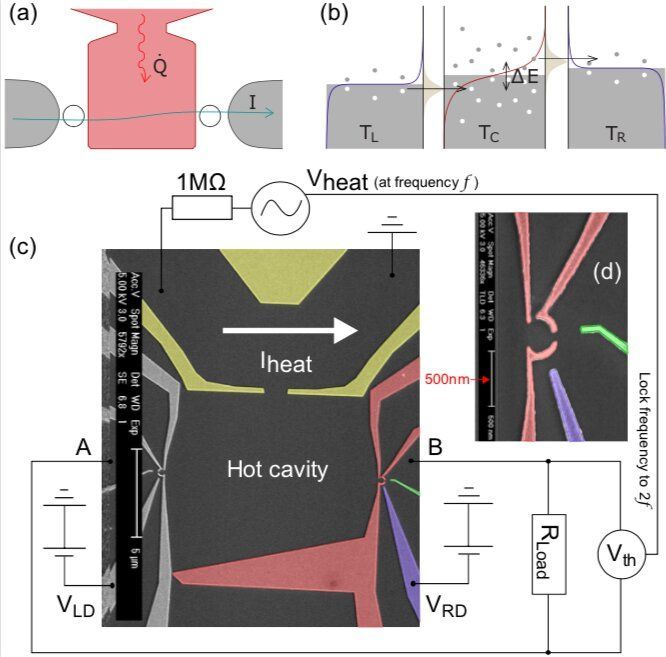
Over the past few years, thermoelectric generators have become the focus of a growing number of studies, due to their ability to convert waste heat into electrical energy. Quantum dots, semiconductor crystals with distinctive conductive properties, could be good candidates for thermoelectric generation, as their discrete resonant levels provide excellent energy filters.
In a recent study, researchers at the University of Cambridge, in collaboration with colleagues in Madrid, Rochester, Duisburg and Sheffield, have experimentally demonstrated the potential of an autonomous nanoscale energy harvester based on resonant tunneling quantum dots. This harvester is based on previous research carried out by part of their team, who had proposed a three-terminal energy harvester based on two resonant-tunneling quantum dots with different energy levels.
The energy harvester device was realized at Cavendish Laboratory in Cambridge by a researcher called Gulzat Jaliel. The original theoretical proposal for the device, however, was introduced by Andrew Jordan in 2013, and the theoretical work behind the harvester was carried out by him in collaboration with renowned semiconductor physicist Markus Büttiker and a team of post-doctoral students in Geneva.