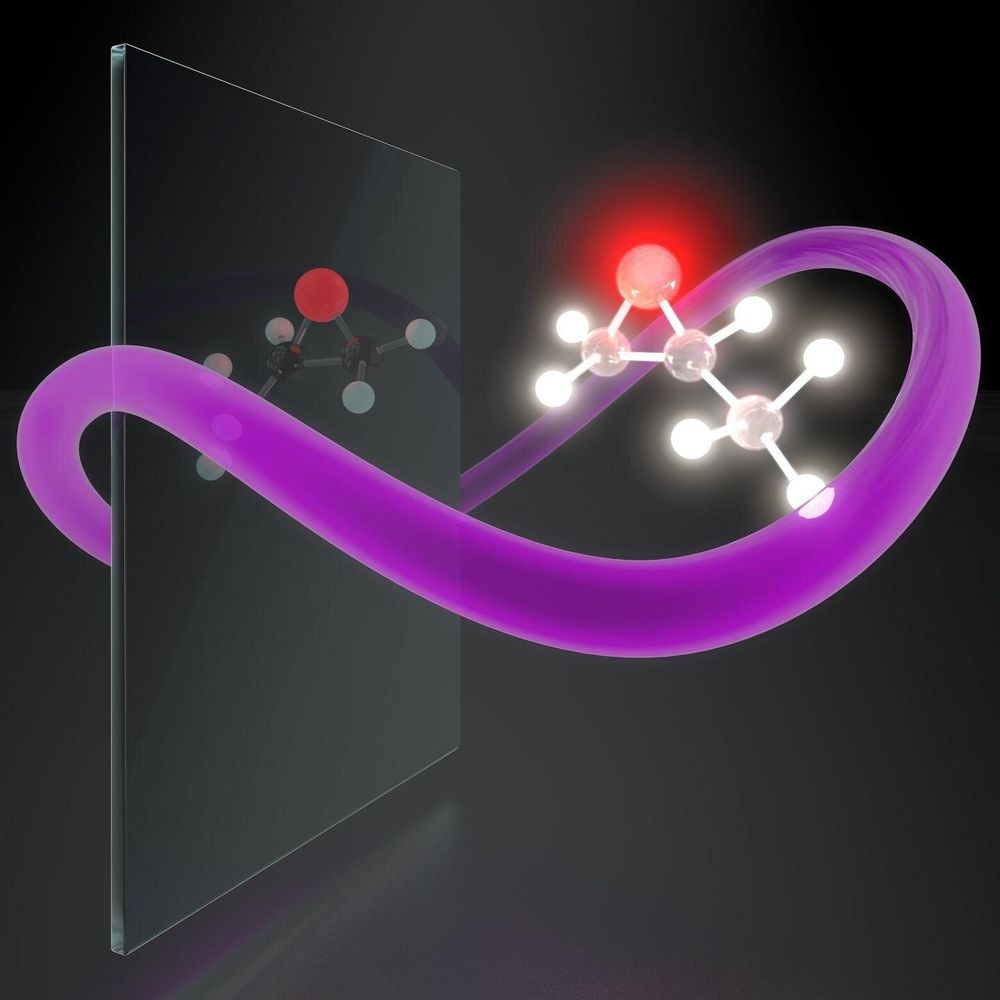
Light is the fastest way to distinguish right- and left-handed chiral molecules, which has important applications in chemistry and biology. However, ordinary light only weakly senses molecular handedness. Researchers from the Max Born Institute for Nonlinear Optics and Short Pulse Spectroscopy (MBI), the Israel Institute of Technology (Technion) and Technische Universitaet Berlin (TU Berlin) now report a method to generate and characterize synthetic chiral light, which identifies molecules’ handedness exceptionally distinctly. The results of their joint work have just appeared in Nature Photonics.
Like left and right hands, some molecules in nature have mirror twins. However, while these twin molecules may look similar, some of their properties can be very different. For instance, the handedness—or chirality—of molecules plays an essential role in chemistry, biology, and drug development. While one type of a molecule can cure a disease, its mirror twin—or enantiomer—may be toxic or even lethal.
It is extremely hard to tell opposite chiral molecules apart because they look identical and behave identically unless they interact with another chiral object. Light has long been used to detect chirality—oscillations of the electromagnetic field draw a chiral helix in space along the light propagation direction. Depending on whether the helix twirls clockwise or counterclockwise, the light wave is either right- or left-handed. However, the helix pitch, set by the light wavelength, is about 1000 times bigger than the size of a molecule. So the light helix is a gigantic circle compared to the tiny molecules, which hardly react to its chirality.