Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize technology, medicine, and science by providing faster and more efficient processors, sensors, and communication devices.
But transferring information and correcting errors within a quantum system remains a challenge to making effective quantum computers.
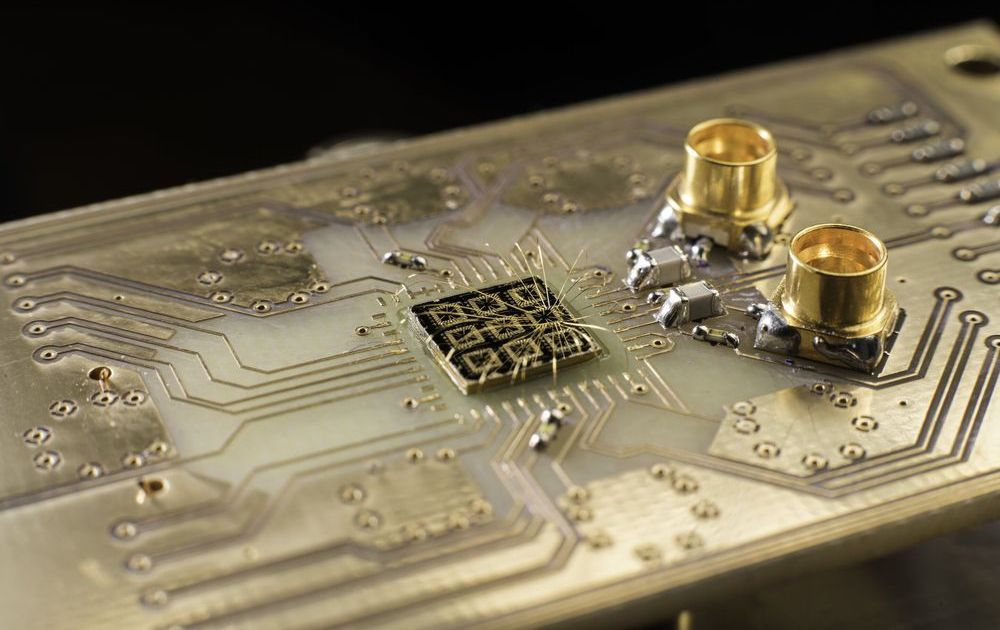
In a paper in the journal Nature, researchers from Purdue University and the University of Rochester, including John Nichol, an assistant professor of physics, and Rochester Ph.D. students Yadav P. Kandel and Haifeng Qiao, demonstrate their method of relaying information by transferring the state of electrons. The research brings scientists one step closer to creating fully functional quantum computers and is the latest example of Rochester’s initiative to better understand quantum behavior and develop novel quantum systems. The University recently received a $4 million grant from the Department of Energy to explore quantum materials.