Researchers at the University of Strathclyde have developed a new method for assembling ultra-small, light-controlling devices, paving the way for scalable manufacturing of advanced optical systems used in quantum technologies, telecommunications and sensing.
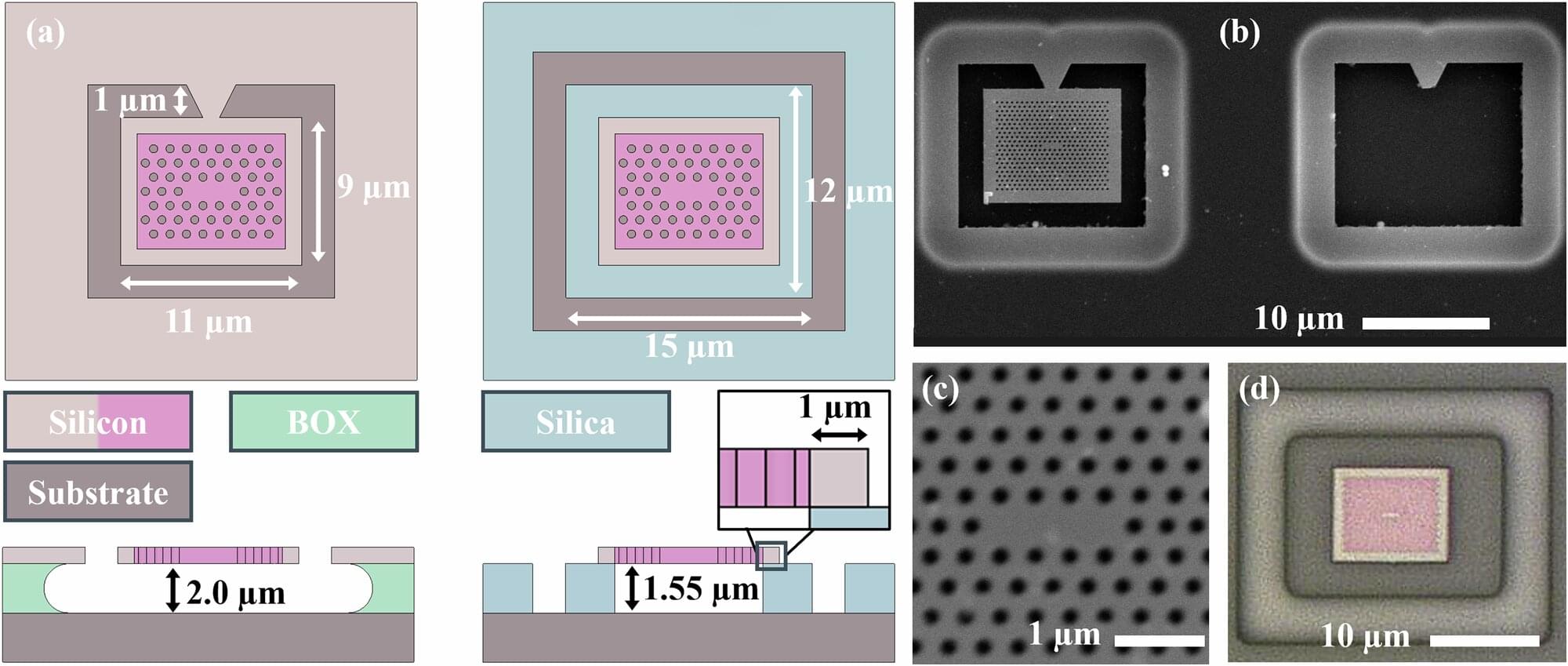
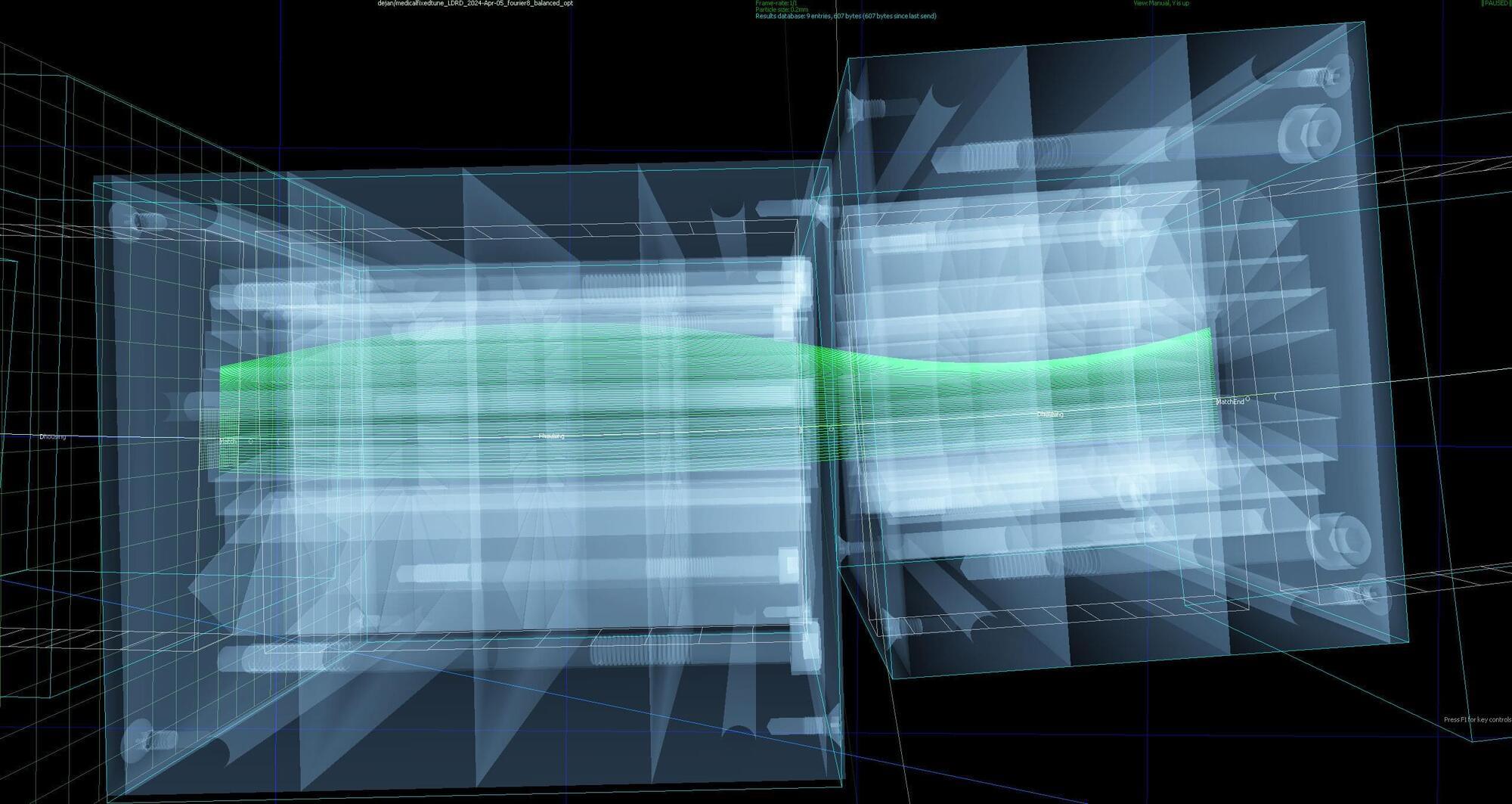
The study, published in Nature Communications, centers on photonic crystal cavities (PhCCs), micron-scale structures that trap and manipulate light with extraordinary precision. These are essential components for high-performance technologies ranging from quantum computing to photonic artificial intelligence.
Until now, the creation of large arrays of PhCCs has been severely limited by the tiny variations introduced during fabrication. Even nanometer-scale imperfections can drastically shift each device’s optical properties, making it impossible to build arrays of identical units directly on-chip.