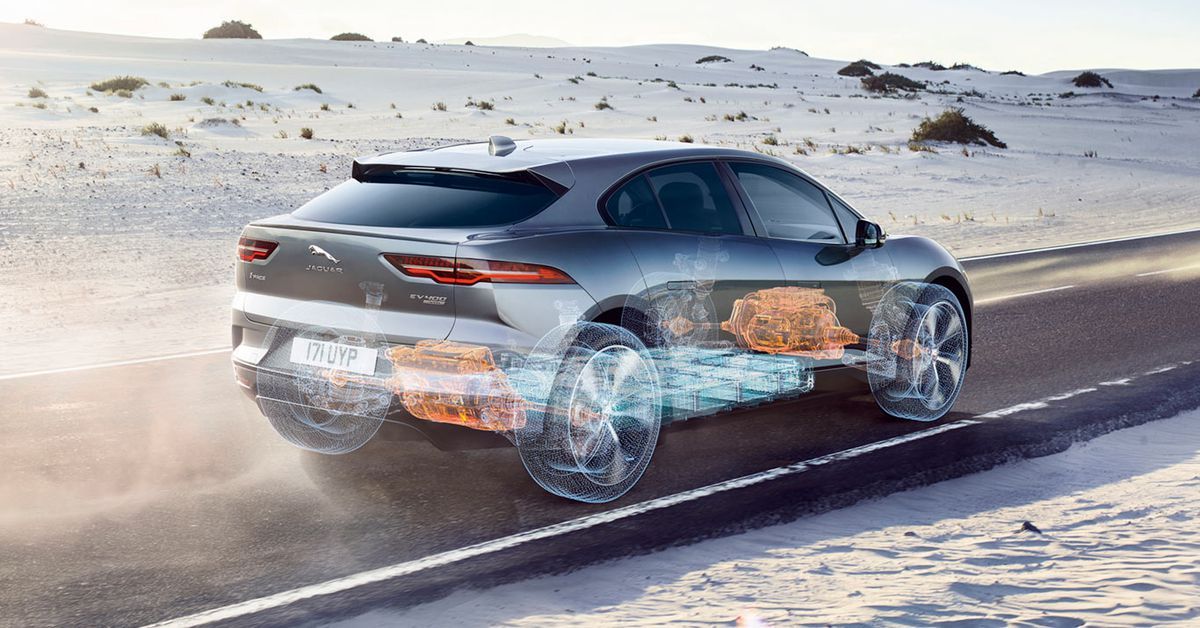
Policymakers and analysts are digging into the details of how to get more EVs on the road.
Dreeming big.
Dreem Announces $35 Million Financing from lead investors Johnson & Johnson Innovation and Bpifrance (press release):
“Dreem, a neurotechnology company, today announced the closing of a new round of funding, raising $35 million USD to rapidly accelerate product development, invest in strategic research and development, and advance the future of sleep technology. Last year, Dreem introduced a comprehensive solution to address a suite of sleep problems and enhance the quality of rest during the night. The Dreem headband monitors brain activity to track sleep accurately and uses auditory stimulation as a medium to help people fall asleep faster, get deeper sleep, and wake up refreshed.
With the $35 million investment, led by strategic investor JJDC, Dreem will bring next-generation sleep technology to markets across the globe and continue to invest in R & D for future sleep-related scientific discoveries and technological innovations … Dreem previously raised a total of $22 million, from billionaire French entrepreneur Xavier Niel, entrepreneur and biotech investor Dr. Laurent Alexandre, and one of the top French insurance leaders — MAIF. With additional investment from JJDC and Bpifrance, Dreem has raised nearly $60 million in less than four years.”
Ocasio-Cortez’s 100%-renewable plan puts her in agreement with a coalition of US mayors who have committed to the goal of complete decarbonization within their own cities. But Ocasio-Cortez, who has an economics degree, also couples that plank with an economic plan she is calling the Green New Deal.
In a major upset on Tuesday night, Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez, a 28-year-old Latina democratic socialist from the Bronx, beat out the longtime US representative Joe Crowley in the New York primaries. In the overwhelmingly Democratic district, she is practically certain to win a seat in Congress during the general election in November.
Ocasio-Cortez’s climate-change platform would become the most progressive of that of any sitting Congressperson in the Democratic party—and her primary victory catapults that platform into the mainstream.
“We need more environmental hardliners in Congress,” she told In These Times magazine earlier this week. “We need a Marshall Plan for renewable energy in the United States. The idea that the Democratic Party needs to be moderate is what’s holding us back on this.”
Kroger Co. is about to test whether it can steer supermarket customers away from crowded grocery aisles with a fleet of diminutive driverless cars designed to lower delivery costs.
The test program announced Thursday could make Kroger the first U.S. grocer to make deliveries with robotic cars that won’t have a human riding along to take control in case something goes wrong.
Cincinnati-based Kroger is teaming up with Nuro, a Silicon Valley startup founded two years ago by two engineers who worked on self-driving cars at Google. That Google project is now known as Waymo, which plans to introduce a ride-hailing service that is supposed to begin picking up passengers in fully autonomous cars by the end of this year.
An interview with regenerative medicine luminary Dr. Anthony Atala.
After meeting him at the Astana Global Challenges Summit 2018, we’ve kindly been granted an interview by Dr. Anthony Atala, M.D., Director of the Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine and the W. Boyce Professor and Chair of Urology at Wake Forest University.
Dr. Atala is one of the most influential names in the field of regenerative medicine and biotechnology. His research focuses on growing human cells and tissues for use in transplants, and given the constant dire need for organ donors worldwide, his work is poised to improve—and save—the lives of millions. He and his team have already successfully engineered and transplanted bladders into living patients, and as he’s told us himself, more types of tissue have been engineered and tested in models; hopefully, they will one day be usable in patients as well.
Dr. Atala’s groundbreaking work has earned him countless awards, prizes, and nominations in well-known magazines, such as Scientific American, Time Magazine, the Huffington Post, and many others; he has also served on the boards and committees of several organizations, such as the National Institutes of Health, the National Cancer Institute, and SENS Research Foundation. A more detailed biography of Dr. Atala can be found here.
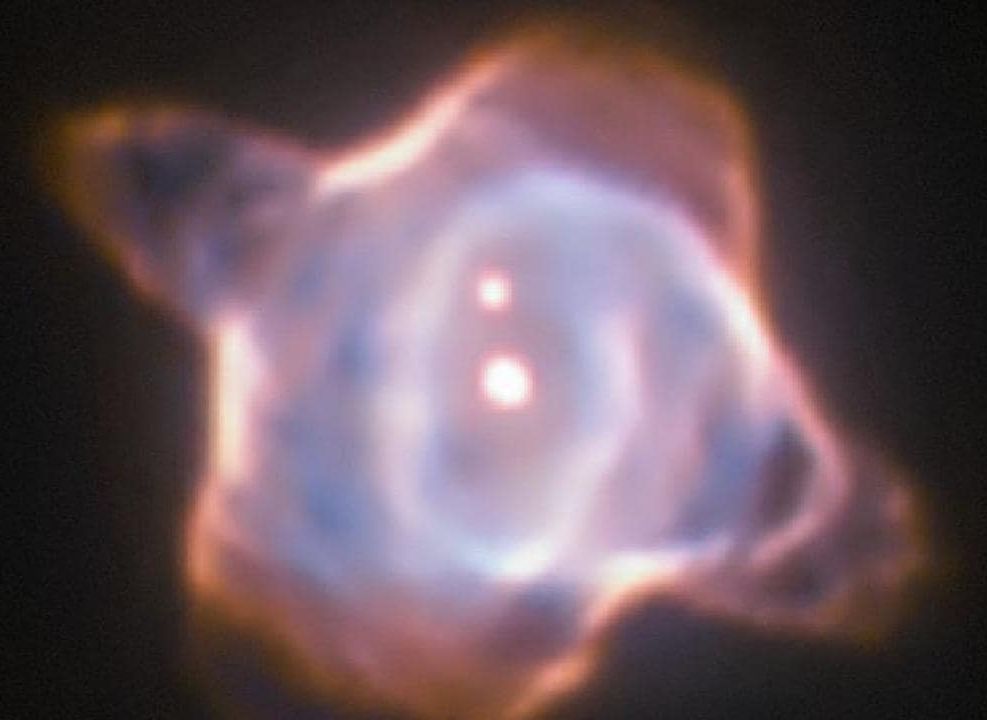
IT’S a moment of conception on an interstellar scale. Australian astronomers have watched the death — and rebirth — of a distant solar system. Now they’re watching its embryonic nebula form.
Professor Lisa Harvey-Smith of the CSIRO has told the annual meeting of the Astronomical Society of Australia hosted at Swinburne University this week that the opportunity to observe the climactic phase in the life cycle of a star was extraordinary.
The cycle of a star’s life begins as it ends.
July 12th our special one-day biotech and business conference launches in New York City. This event brings together some of the leading experts in aging research and investment and promises to be an action-packed day.
For more information please visit: https://www.eventbrite.com/e/ending-age-related-diseases-inv…5733391806
Video Creator: Jason Shulkin, Motion Graphics Artist. www.jasonshulkin.com
Recommended Books ➤
📖 Life 3.0 — http://azon.ly/ij9u
📖 The Master Algorithm — http://azon.ly/excm
📖 Superintelligence — http://azon.ly/v8uf
This video is the twelfth and final in a multi-part series discussing computing. In this video, we’ll be discussing the future of computing, more specifically – the evolution of the field of computing and extrapolating forward based on topics we’ve discussed so far in this series!
[0:31–5:50] Starting off we’ll discuss, the 3 primary eras in the evolution of the field of computing since its inception, the: tabulating, programming and cognitive eras.
Afterwards, we’ll discuss infinite computing, a paradigm that incorporates cloud computing and the principles of heterogenous architecture that is accelerating the transition to cognitive computing.
Finally, to wrap up, we’ll discuss the future of computing, ubiquitous computing, fueled by the rise of abundant, affordable and smart computing devices, where computing is done using any device, in any location and in any format.
The deadlines set for “singularity” are also seen by some as an attempt to scare and coerce governments into implementing the movement’s social and technological “agenda”. However, when the names of major tech corporations of the world like Google, Nokia and Tesla are associated with the transhumanist ideology, it is difficult to dismiss the premise and prospects of this new revolutionary socio-technological movement.
For several centuries, political movements have emanated from nationalist or religious convictions, socio-political and economic theories or even environmental concerns. However, issues of science and technology have rarely driven mainstream socio-political discourse as scientists have hardly ever indulged in propounding societal constructs for the future.
However, a technology-oriented intellectual movement may soon become the focus of political debate as 21st century science stands at the brink of reshaping human identity itself.
By the turn of the millennium, Transhumanism rose as a futurist social movement, led by some of the leading researchers and heads of global tech corporations (mostly based in the super-rich Silicon Valley), but has only recently gained greater media coverage and popularity apart from inspiring the plotlines for many Hollywood films.
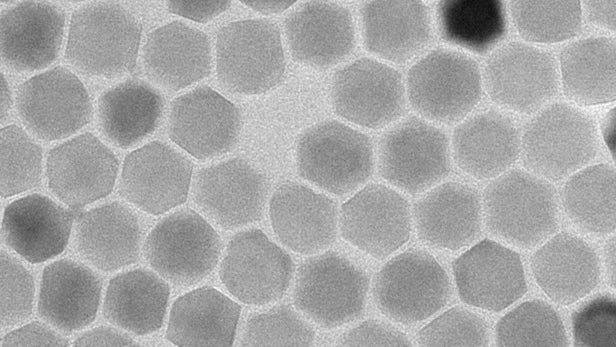
Cancer is one of humanity’s biggest killers, but scientists are coming up with some creative ways to fight back. Researchers at the University at Buffalo have developed new kinds of nanoparticles that can infiltrate, heat up and kill cancer cells more effectively and efficiently than similar methods.
Using nanoparticles to fight cancer has become a growing area of research in recent years. The general concept is to get the particles into tumors, before activating them with radiation to trigger a reaction that destroys the cancer cells without harming healthy tissue. What kind of nanoparticle and radiation are used can vary, as can the type of reaction that’s triggered.
Previous work has killed tumors by activating CeF3 nanoparticles with X-rays to create toxic singlet oxygen, used infrared light to ramp up cancer’s pH balance, used laser pulses to heat up gold nanoparticles, or a combination of several of these.