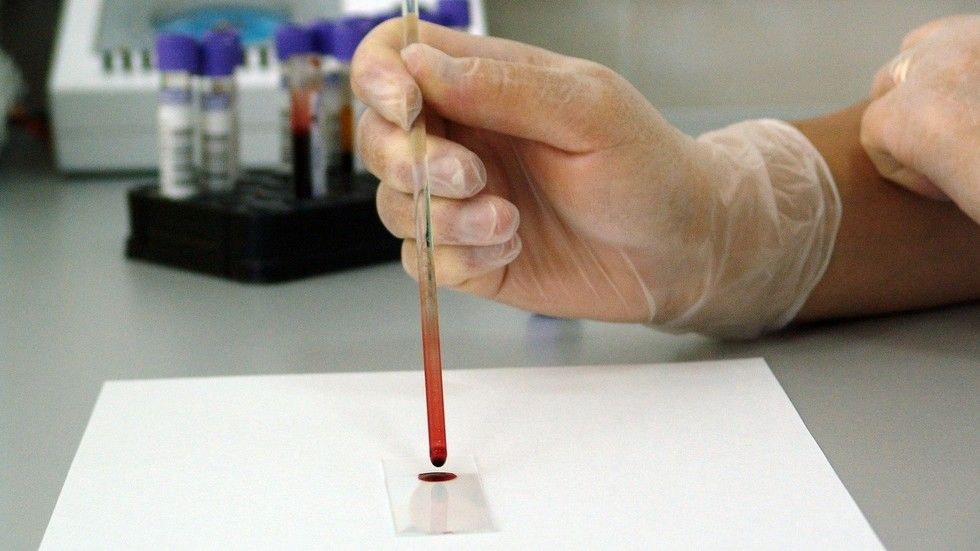
Researchers in the Netherlands have developed an incredibly accurate nanosensor which can detect metastatic cancer cells from just a single drop of blood in a major breakthrough for early detection and treatment of the disease.
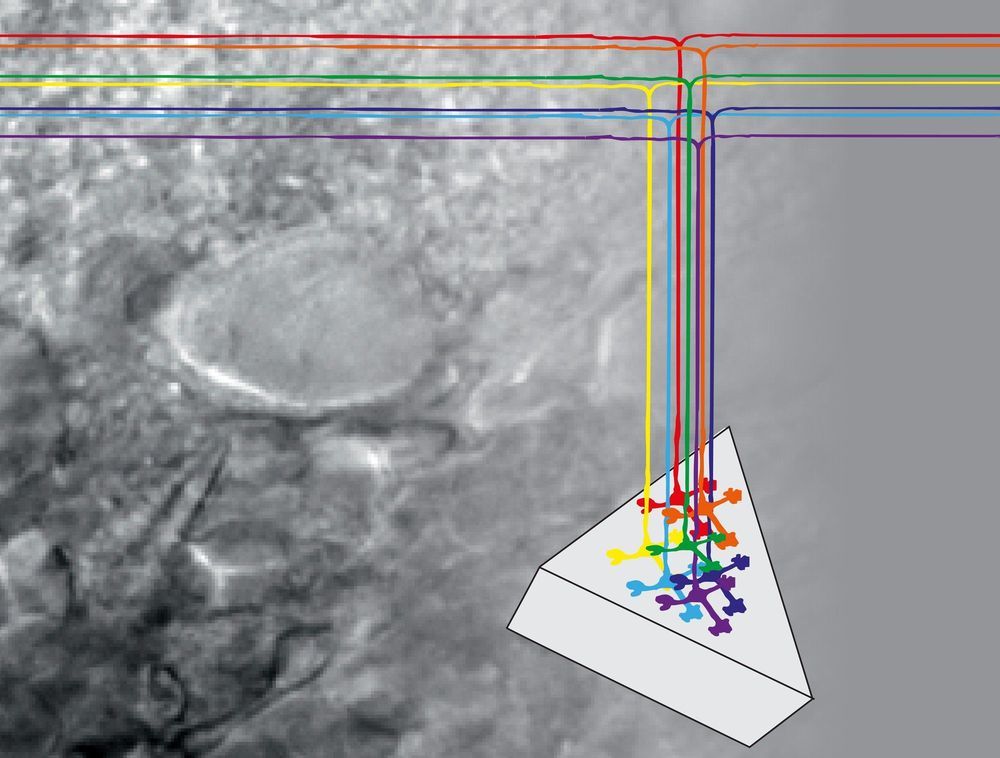
PhD students Dilu Mathew from University of Twente and Pepijn Beekman from Wageningen University pooled their resources and developed a tiny system to detect tumor-derived extracellular vesicles (tdEVs), a particular type of cancer biomarker.
Their nanosensor is so sensitive it can detect cancer biomarkers on a broad spectrum of concentrations from 10 particles per microliter to 1 million particles per microliter, thanks to its incredibly small and delicate electrodes, shaped like two combs facing each other, with a gap of just 120 nanometers between them.