The image tagging system that went viral on social media was part of artist Trevor Paglen and AI researcher Kate Crawford’s attempts to publicize how prejudiced technology can be.


After debuting just shy of two years ago, Boston Dynamics has finally made its Spot robotic dog available for sale, but don’t expect to find a great Black Friday deal on this bot at Best Buy come Thanksgiving. The company hasn’t made them available to the average consumer just yet—only businesses that can promise an interesting application for the technology.
A new twist on robotics.
New twist on robotics: Boston Dynamics showcases Atlas’ agility with gymnastics routine.
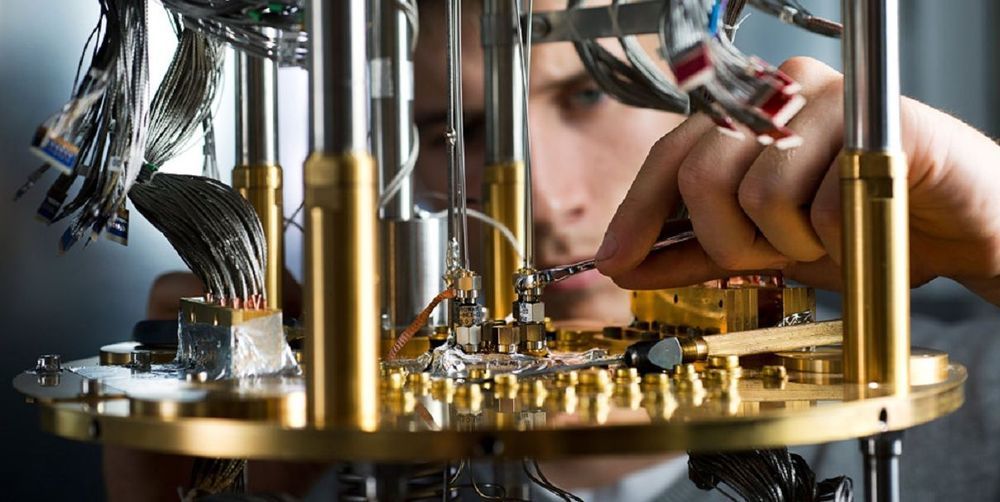
D-Wave today announced its next generation “Advantage” quantum computer system. It’ll pack a whopping 5,000 qubits and myriad improvements to processing speed and power. And the Los Alamos National Laboratory in New Mexico will be among the first to have access.
According to a press release from D-Wave, the new Advantage system improves on the previous generation’s 2000Q model – which sports a paltry-by-comparison 2,048 qubits – in nearly every conceivable way:
Designed to speed the development of commercial quantum applications, the Advantage quantum system will power a new hardware and software platform that will accelerate and ease the delivery of quantum computing applications. Reflecting years of customer feedback, the platform captures users’ priorities and business requirements and will deliver significant performance gains and greater solution precision.
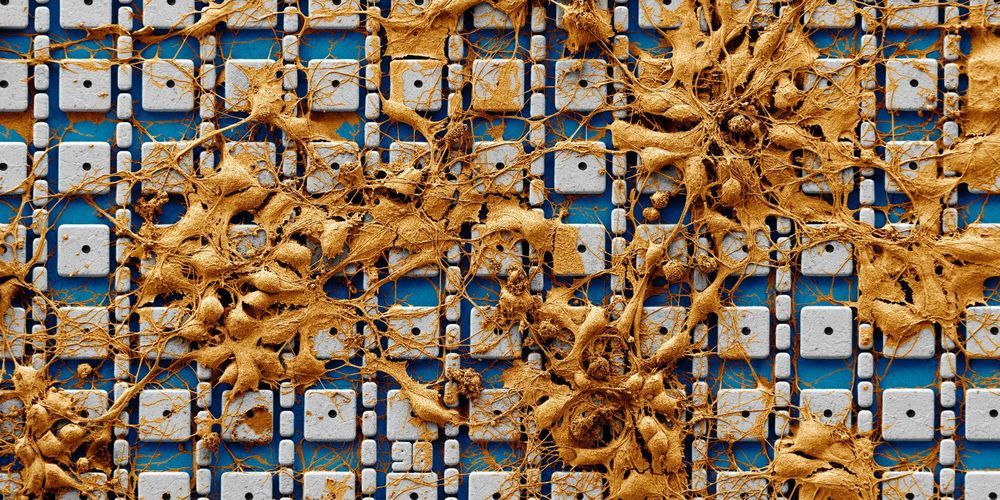


A nanoelectrode array that can simultaneously obtain intracellular recordings from thousands of connected mammalian neurons in vitro.
How our brain cells, or neurons, use electrical signals to communicate and coordinate for higher brain function is one of the biggest questions in all of science.
For decades, researchers have used electrodes to listen in on and record these signals. The patch clamp electrode, an electrode in a thin glass tube, revolutionized neurobiology in the 1970’s with its ability to penetrate a neuron and to record quiet but telltale synaptic signals from inside the cell. But this tool lacks the ability to record a neuronal network; it can measure only about 10 cells in parallel.
Now, researchers from Harvard University have developed an electronic chip that can perform high-sensitivity intracellular recording from thousands of connected neurons simultaneously. This breakthrough allowed them to map synaptic connectivity at an unprecedented level, identifying hundreds of synaptic connections.
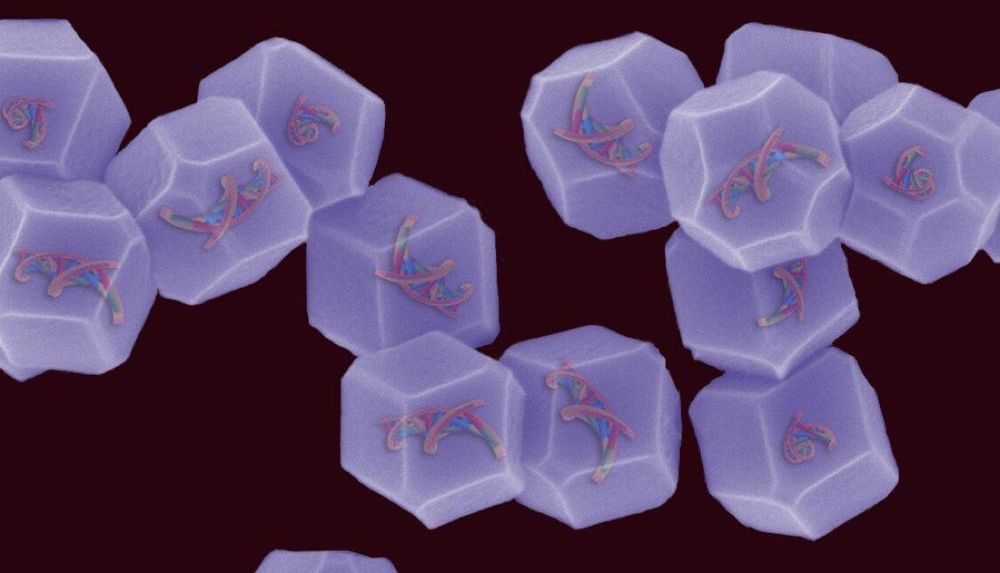
With metal organic frameworks.
The nonviral, bioinspired gene delivery method developed by researchers at RMIT University has proven effective in laboratory tests and is safer than standard viral approaches.
Widely considered the next frontier of cancer research, gene therapy involves introducing new genes into a patient’s cells to replace missing or malfunctioning ones that cause disease.
As cells are not designed to naturally take up genes or any foreign DNA material, the biggest challenge for gene therapy is getting the therapeutic genes into the cells.
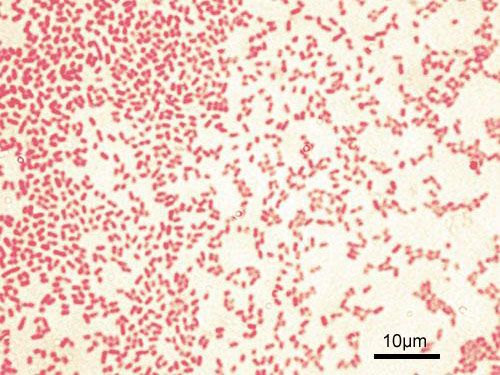
Scientists at the University of Surrey have discovered that a natural antioxidant commonly found in green tea can help eliminate antibiotic resistant bacteria.
The study, published in the Journal of Medical Microbiology, found that epigallocatechin (EGCG) can restore the activity of aztreonam, an antibiotic commonly used to treat infections caused by the bacterial pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
P. aeruginosa is associated with serious respiratory tract and bloodstream infections and in recent years has become resistant to many major classes of antibiotics. Currently a combination of antibiotics is used to fight P. aeruginosa. However, these infections are becoming increasingly difficult to treat, as resistance to last line antibiotics is being observed.
“Her” is one of the top 20 artificial intelligence films — in pictures for The…
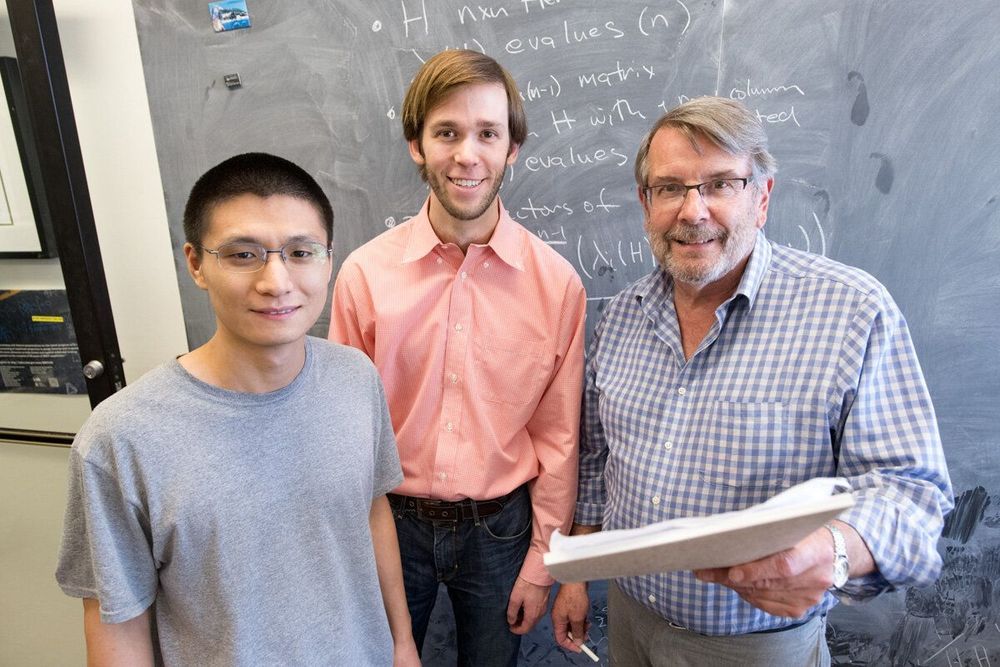
Linear algebra is a field of mathematics that has been thoroughly investigated for many centuries, providing invaluable tools used not only in mathematics, but also across physics and engineering as well as many other fields. For years physicists have used important theorems in linear algebra to quickly calculate solutions to the most complicated problems.
This August, three theoretical physicists—Peter Denton, a scientist at Brookhaven National Laboratory and a scholar at Fermilab’s Neutrino Physics Center; Stephen Parke, theoretical physicist at Fermilab; and Xining Zhang, a University of Chicago graduate student working under Parke—turned the tables and, in the context of particle physics, discovered a fundamental identity in linear algebra.
The identity relates eigenvectors and eigenvalues in a direct way that hadn’t been previously recognized. Eigenvectors and eigenvalues are two important ways of reducing the properties of a matrix to their most basic components and have applications in many math, physics and real-world contexts, such as in analyzing vibrating systems and facial recognition programs. The eigenvectors identify the directions in which a transformation occurs, and the eigenvalues specify the amount of stretching or compressing that occurs.