With the discovery of yet another sense, this time in our guts, we’re starting to lose count.

Trying to capture antineutrinos at low energy has just become a lot easier.

As we age, our bodies gradually lose their ability to repair and regenerate. Stem cells diminish, making it increasingly difficult for tissues to heal and maintain balance. This reduction in stem cells is a hallmark of aging and a key driver of age-related diseases. Scientists have long debated whether this decline is the root cause of aging or a side effect. Efforts to use stem cell transplants to reverse aging have faced many challenges, such as ensuring the cells survive and integrate into the body without causing serious side effects, like tumors.
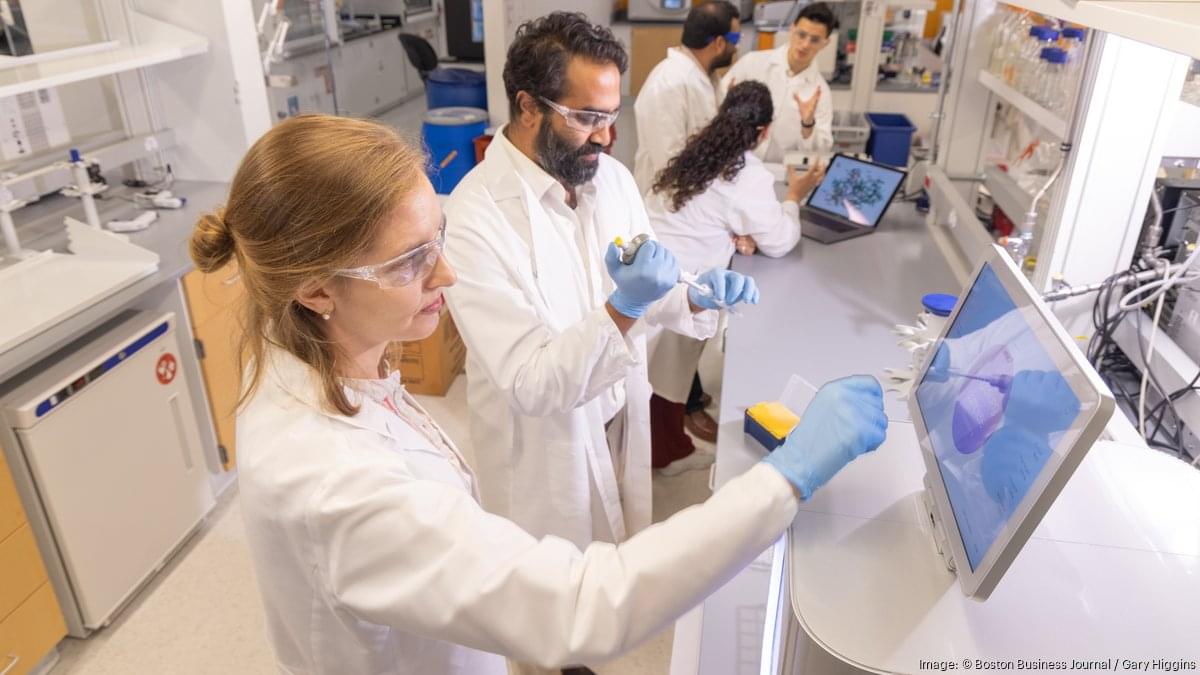
In a recent study published in Cell, researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Capital Medical University introduced a new type of human stem cell called senescence-resistant mesenchymal progenitor cells (SRCs) by reprogramming the genetic pathways associated with longevity. These cells, which resist aging and stress without developing tumors, were tested on elderly crab-eating macaques, which share physiological similarities with humans in their 60s and 70s.
The research team conducted a 44-week experiment on these macaques. The macaques received biweekly intravenous injections of SRCs, with a dosage of 2×106 cells per kilogram of body weight. The researchers found no adverse effects among the macaques. Detailed assessments confirmed that the transplanted cells did not cause tissue damage or tumors.
The researchers discovered that SRCs triggered a multi-system rejuvenation, reversing key markers of aging across 10 major physiological systems and 61 different tissue types. The treated macaques exhibited improved cognitive function, and tissue analyses indicated a reduction in age-related degenerative conditions such as brain atrophy, osteoporosis, fibrosis, and lipid buildup. 👍
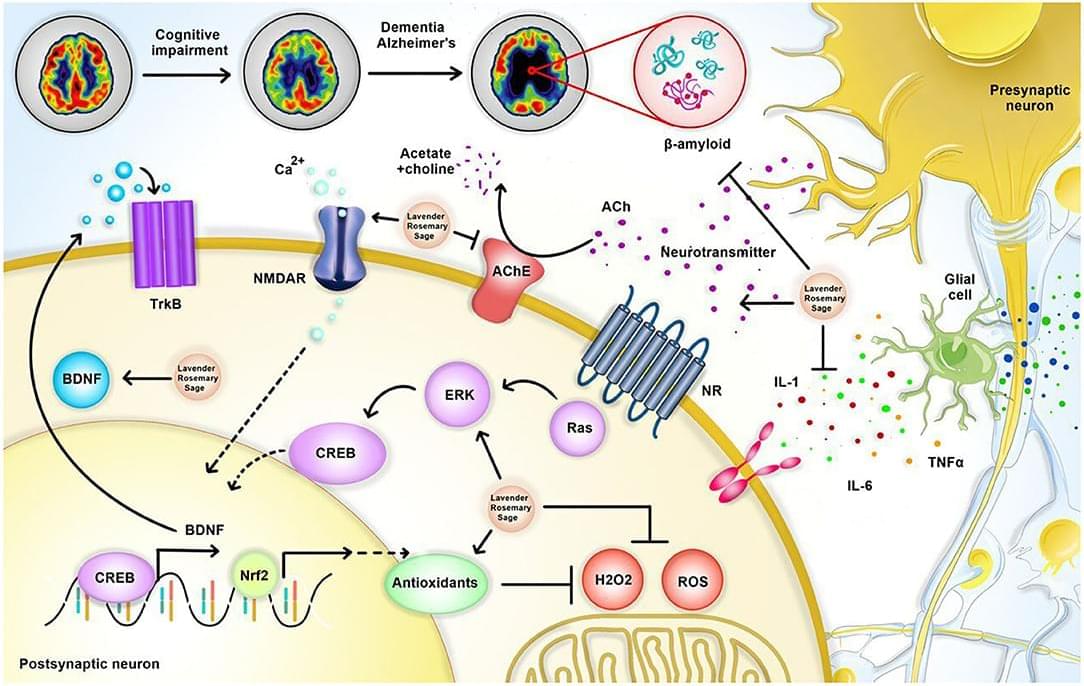
Hundreds of millions of people around the world suffer from neurological disorders or have experienced them intermittently, which has significantly reduced their quality of life. The common treatments for neurological disorders are relatively expensive and may lead to a wide variety of side effects including sleep attacks, gastrointestinal side effects, blood pressure changes, etc. On the other hand, several herbal medications have attracted colossal popularity worldwide in the recent years due to their availability, affordable prices, and few side effects. Aromatic plants, sage (Salvia officinalis), lavender (Lavandula angustifolia), and rosemary (Salvia Rosmarinus) have already shown anxiolytics, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and neuroprotective effects. They have also shown potential in treating common neurological disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, migraine, and cognitive disorders. This review summarizes the data on the neuroprotective potential of aromatic herbs, sage, lavender, and rosemary.
A neurological disorder is described as any condition that results in functional or structural damage to the nervous system. Neurological disorders account for the second main cause of death globally and the first main cause of disability as they typically cause cognitive impairment or sensorimotor dysfunction leading to reduced quality of daily life. Due to the high mortality and morbidity rate of neurological disorders, preventive and therapeutic strategies are crucial. The conventional medications administered for treating neurological disorders are associated with different adverse events; hence, the possible therapeutic effects of natural products on neurological conditions have been addressed by many researchers in the recent years (Ahmadi et al., 2022). A variety of herbal medications have gained the attraction of researchers in the last decade, due to their availability, lower price, and rare side effects (Abdel-Aziz et al., 2016).
Aromatic herbs such as sage (Salvia officinalis), rosemary (Salvia Rosmarinus), and lavender (Lavandula angustifolia) have shown promising neuroprotective effects in the recent studies (Kashani et al., 2011; Jamison, 2012; Jemia et al., 2013; Alvi et al., 2019; Mohseni et al., 2020; Caputo et al., 2021). Salvia Rosmarinus is an evergreen herb that belongs to the Lamiaceae family. Salvia Rosmarinus naturally grows in dry scrub and rocky areas in the Mediterranean regions of southern Europe to western Asia and has potential antibacterial, antifungal, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory features (Leporini et al., 2020). The therapeutic effects of Salvia Rosmarinus on a variety of cognitive disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, neuroblastoma, glioblastoma, and epilepsy have been suggested (Park et al., 2008; de Oliveira et al., 2016; Giacomelli et al., 2016; El Alaoui et al., 2017; Yildirim and Kitis, 2020). Lavandula angustifolia is a well-known aromatic herb in the Lamiaceae family.

We developed a robust epigenetic clock to estimate age from two wild polar bear subpopulations using blood samples. There was a correlation between epigenetic (DNAm) and chronological age throughout the polar bear lifespan. Polar bears in the wild have a lifespan of approximately 25 years (Rode and Stirling 2018), thus the clock estimates age to ±3% of the polar bear lifespan, although we caution that age estimates may be less accurate for older individuals. Advantages to this method include obtaining more accurate age estimates compared to cementum annuli-derived ages and leveraging samples likely already routinely collected (e.g., blood, tissue) during capture, as opposed to pulling teeth. Further, archived samples or previously extracted DNA may be used for DNAm analysis, extending the value of existing samples and saving money on DNA extraction costs. Our results complement other polar bear clocks (Newediuk et al. 2024, 2025) and provide additional support for the use of DNAm methods to estimate the age of wild mammals (De Paoli-Iseppi et al. 2017).
Our DNAm method estimates polar bear age with a MAE of 0.75 years. In contrast, accuracy of cementum annuli for aging polar bears to within 1 year of actual age has ranged from 32% to 75% (Calvert and Ramsay 1998 ; Christensen-Dalsgaard et al. 2010 ; Hensel and Sorensen 1980). Cementum annuli age estimates are less accurate when made by less experienced observers (Christensen-Dalsgaard et al. 2010 ; Hensel and Sorensen 1980 ; McLaughlin et al. 1990) and can vary between laboratories by 10 years (Christensen-Dalsgaard et al. 2010). For example, in one lab, multiple female polar bears were aged at ~10 years, while a second laboratory aged them at 20 years old (Christensen-Dalsgaard et al. 2010). Our method removes these sources of error. We do, however, acknowledge a potential source of technical error, given that all but three of the tooth-aged samples were run on one plate, and the majority of our known age samples were run on another plate.


Health officials are sending a warning to residents in Gulf Coast states after eight people are dead from the flesh-eating bacteria called Vibrio vulnificus.
On Thursday, July 31, the Louisiana Department of Heath confirmed 17 cases of the flesh-eating bacteria this year, all of which resulted in hospitalizations. Additionally four cases resulted in death. About 75% of those cases were due to wound infection via seawater.
Additionally, the Florida Department of Health confirmed 13 cases and four deaths from Vibrio this year. Both Mississippi and Alabama have also reported single cases, neither fatal.
