Lithium alters how we think by changing the levels of serotonin and norepinephrine secreted by our endocrine system. But the government is polluting our environment with the stuff.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
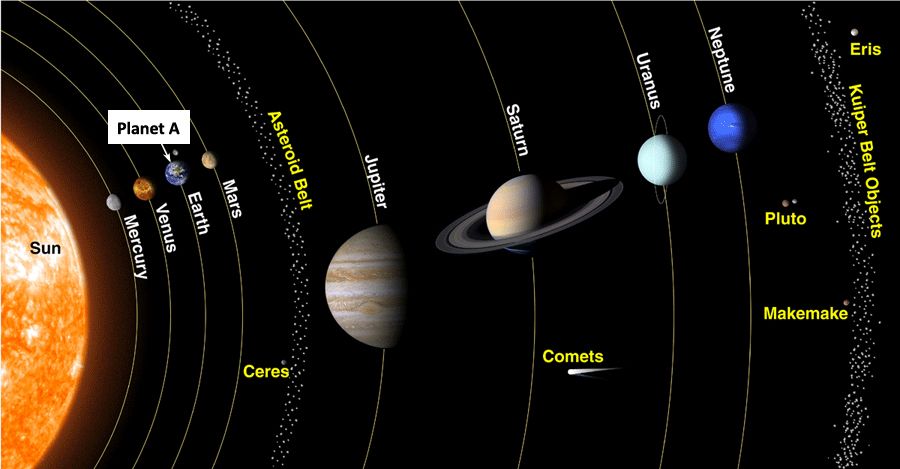
We don’t need a “Planet B”. We have an entire Solar System
A million and a half students, even very young ones, took to the streets Friday March 15th, in two thousand cities around the world, for the climate, responding to a Greta Thunberg’s call. Greta is a 16-year-old student in Stockholm: “I will not stop. Not until greenhouse gas emissions have fallen below the alarm level.” Considering the great support she had, it would seem that students were not waiting for anything else, with great outcry of the ecologists of various tendencies, who have for years repeated the same call, without being able to arouse mass movements of this magnitude.
There is no doubt that we are on the verge of great changes. The automotive industry — by far a leading industry in the world economy — is about to collapse, because it has not been able to innovate in time, and now it does not in fact have ready solutions, to satisfy a market that no longer intends to exchange mobility with health. Such imminent collapse will not do any good to economy. It will also offer vampire rulers new opportunities to increase the taxation, already exorbitant in many countries. And no one seems to realise that if producers die as a social category, consumers will soon die too, as they are the same people. There is no doubt, moreover, that the ruling politicians, more and more void of any basic culture, will find many ways to manage what Serge Latouche (in his essay on the so-called “happy de-growth”) called “inevitable social problems following de-growth”.
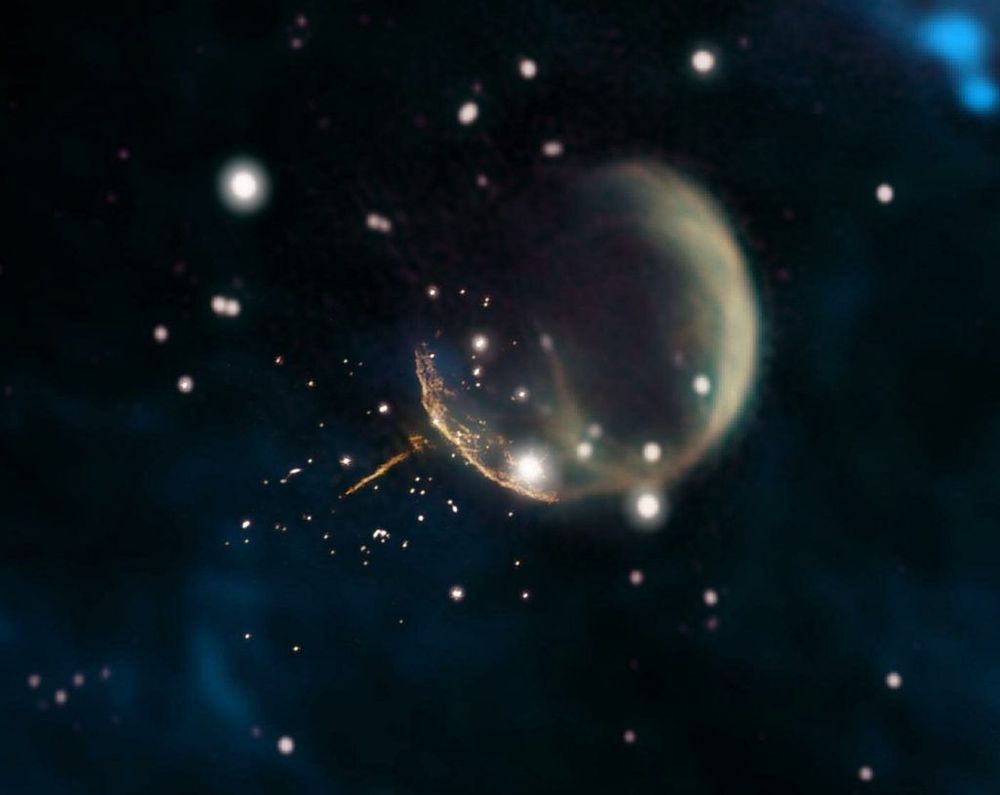


“Escaping the Milky Way” –Ghostly Neutron Star Racing Through Galaxy at 2.5 Million MPH
Astronomers observed a ghostly pulsar, a superdense, rapidly spinning neutron star exploded from a supernova 10,000 years ago, racing through space at nearly 2.5 million miles an hour—so fast it could travel the distance between Earth and the Moon in just 6 minutes. The discovery was made using NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope and the National Science Foundation’s Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA).
The pulsar lies about 53 light-years from the center of a supernova remnant called CTB 1. Its rapid motion through interstellar gas results in shock waves that produce the tail of magnetic energy and accelerated particles detected at radio wavelengths using the VLA. The tail extends 13 light-years and clearly points back to the center of CTB 1.
This one, dubbed PSR J0002+6216 (J0002 for short), sports a radio-emitting tail pointing directly toward the expanding debris of a recent supernova explosion. “Thanks to its narrow dart-like tail and a fortuitous viewing angle, we can trace this pulsar straight back to its birthplace,” said Frank Schinzel, a scientist at the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO) in Socorro, New Mexico. “Further study of this object will help us better understand how these explosions are able to ‘kick’ neutron stars to such high speed.”
Childhood trauma scars the brain and boosts depression risk
Childhood trauma such as neglectful parenting causes physical scarring to the brain and increases the risk of severe depression, a new study has found.
For the first time, scientists have linked changes in the structure of the brain both to traumatic early-years experiences and poor mental health in later life.
Published in the Lancet, the study found a “significant” link between adults who had experienced maltreatment as children with a smaller insular cortex, part of the brain believed to help regulate emotion.


VA to Offer New Ketamine-Based Nasal Spray for Depression
The newest FDA-approved medication to treat severe depression, a nasal spray based on the anesthetic (and misused hallucinogenic party drug) ketamine, will soon be available to veterans treated within the Department of Veterans Affairs.
In a move that may help thousands of former service members with depression that has not improved with other treatments, VA officials announced Tuesday that the department’s doctors are now authorized to prescribe Spravato, the brand name for esketamine, a molecular variation of ketamine.
The decision to offer a drug hailed by many as a breakthrough in treatment for its speedy results — often relieving symptoms in hours and days, not weeks — shows the VA’s “commitment to seek new ways to provide the best health care available for our nation’s veterans,” Secretary Robert Wilkie said in a release.


Blue Origin studying repurposing of New Glenn upper stages
SILVER SPRING, Md. — Blue Origin has studied repurposing upper stages of its future New Glenn launch vehicle to serve as habitats or for other applications as part of a series of NASA-funded commercialization studies.
Brett Alexander, vice president of government sales and strategy at Blue Origin, said the company looked at ways it could make use of the second stage of New Glenn rather than simply deorbiting the stage at the end of each launch, but emphasized the company currently had no firm plans to reuse those stages at this time.
That study was part of a series of study contracts awarded by NASA last August to study future concepts to support commercial human spaceflight in low Earth orbit. “We focused there on the reuse of the second stage of New Glenn and what we might be able to do with that volume and capacity once we’re on orbit,” he said during a panel discussion about low Earth orbit commercialization at the American Astronautical Society’s Goddard Memorial Symposium here March 20.

With Launch Of New CRISPR Company, Competition Extends To Diagnostics
The gene editing technology CRISPR, which has spawned several startups aiming to use the tool to develop new therapies, is now the inspiration for a new company in a less-crowded space: diagnostic testing.
Sherlock Biosciences is launching in Cambridge, Massachusetts, with $35 million in funding. That includes $17.5 million in the form of a non-dilutive grant from the Open Philanthropy Project, an organization primarily funded by Dustin Moskovitz, the billionaire cofounder of Facebook and Asana, and his spouse, Cari Tuna. The Open Philanthropy Project is also making a separate investment in Sherlock, along with other undisclosed investors. CEO Rahul Dhanda says he’s still raising more funding for the company’s Series A.
One of Sherlock Biosciences’ key technologies comes from the Broad Institute lab of Feng Zhang, who did some of the early work elucidating the DNA-modifying potential of CRISPR and its associated enzymes after their discovery in bacteria.