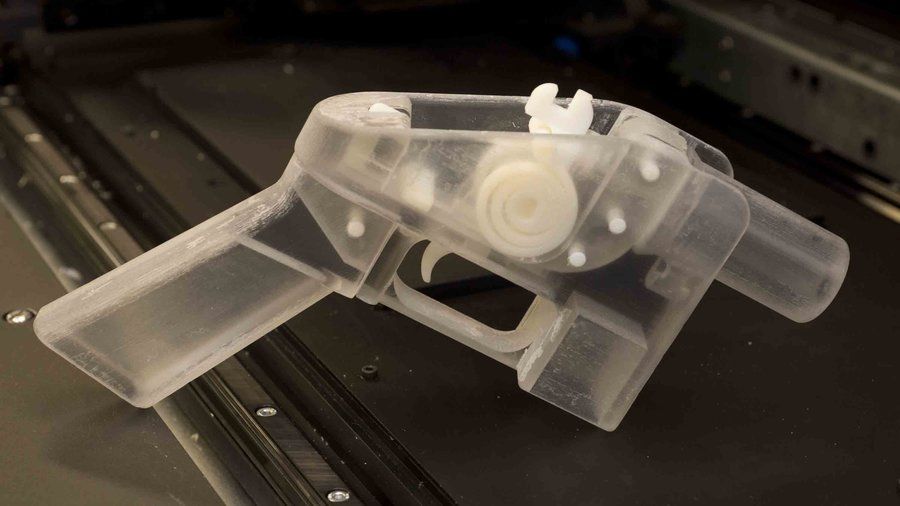
Every time there’s a new technology, criminals immediately take advantage of it, explains Steven Kotler. It’s only a matter of time before they find new, nefarious uses for 3D printing and synthetic biology.
Bitcoin has many characteristics of a currency. It is portable, fungible, divisible, resistant to forgery, and it clearly has value. Today, that value came close to $20,000 per coin. Whether it has ‘intrinsic value’ is somewhat of a moot question, because the US dollar hasn’t exhibited this trait since 1972. Today, economists don’t even recognize the intrinsic value of gold—beyond a robust, international, supply-demand network.
Lately, Bitcoin is failing as a viable currency, at least for everyday consumer transactions. The settlement of each transaction is bogged down with long delays and a very high cost. The situation has become critical because of squabbling between miners, users and developers over how to offer speed transactions or lower the cost of settlement. Bitcoin forks and altcoins such as Dash and Bitcoin Cash demonstrate that these technical issues have solutions. Since Bitcoin is adaptable, I believe that these issues are temporary.
 But an interesting question is not whether Bitcoin will eventually become a consumer currency. it is whether Bitcoin can distinguish itself as a store of value, rather than just an instrument for payment or debt settlement. After all, a Visa credit card, a traveler’s check and an Amazon gift card can all be used in retail payments, but none of them have value unless backed by someone or something. US Dollars on the other hand are perceived as inherently valuable. They carry the clout and gravitas of institutions and populations, without users questioning from where value arises. (This is changing, but bear with me)…
But an interesting question is not whether Bitcoin will eventually become a consumer currency. it is whether Bitcoin can distinguish itself as a store of value, rather than just an instrument for payment or debt settlement. After all, a Visa credit card, a traveler’s check and an Amazon gift card can all be used in retail payments, but none of them have value unless backed by someone or something. US Dollars on the other hand are perceived as inherently valuable. They carry the clout and gravitas of institutions and populations, without users questioning from where value arises. (This is changing, but bear with me)…
What about Bitcoin? Does owning some bitcoin represent a store of value? Yes: It absolutely does!
Bitcoin is a rapidly maturing two-sided network. Despite a meteoric rise in exchange value and wild fluctuations during the ride, it is the epitome of a stored value commodity. Regardless of government regulation, adoption as a consumer payment instrument, or the cost and speed of transactions, it has demonstrated stored value since May 22 2010, when Laszlo, a Bitcoin code developer, persuaded a restaurant to accept 10,000 BTC for 2 pizzas.
The “currency” accepted by the pizza parlor wasn’t a gift card. It was not backed by a government, a prior deposit, dollars, gold, the promise of redemption, or by threat of force or blackmail. When a large community of individuals value, exchange, and can easily authenticate something that has none of those underpinnings, that thing clearly has stored value.
In this case, value arises from its scarcity and a robust supply-demand-network. Because its value is not tied to a government or to other commodities, its exchange rate with other things will be bumpy, at first. But as it is recognized, traded and adopted as a stored value token, the wild spikes will smooth out.
A tipping point will precipitate rapid adoption when…
- when some vendors begin to quote prices in Bitcoin (rather than national currency)
- when some of these vendors retain a fraction of their bitcoin-revenue for future purchases, payments or debt settlements—rather than converting revenue to fiat/national currency with each sale
 Bitcoin is clearly a store of value, and it is beginning to displace gold and the US dollar as the recognized reserve currency (it is gradually becoming the new gold standard). But before Bitcoin can serve as a widely adopted everyday currency (i.e. as a payment instrument—with or without the stored value of a currency unto itself), it must first incorporate technical improvements that speed transactions and lower cost.
Bitcoin is clearly a store of value, and it is beginning to displace gold and the US dollar as the recognized reserve currency (it is gradually becoming the new gold standard). But before Bitcoin can serve as a widely adopted everyday currency (i.e. as a payment instrument—with or without the stored value of a currency unto itself), it must first incorporate technical improvements that speed transactions and lower cost.
This is taking longer than many enthusiasts would have liked. But, that’s OK with anyone who keeps their eye on the big picture. Democracy is sometimes very sloppy.
Philip Raymond co-chairs CRYPSA, publishes A Wild Duck and hosts the New York Bitcoin Event. Last month, he kicked off the Cryptocurrency Expo in Dubai. Click Here to inquire about a live presentation or consulting engagement.
Brendan John Frey FRSC (born 29 August 1968) is a Canadian-born machine learning and genome biology researcher, known mainly for his work on factor graphs, the wake-sleep algorithm for deep learning, and using machine learning to model genome biology and understand genetic disorders. He founded Deep Genomics and is currently its CEO, and he is a Professor of Engineering and Medicine at the University of Toronto. He co-developed a new computational approach to identifying the genetic determinants of disease, was one of the first researchers to successfully train a deep neural network, and was a pioneer in the introduction of iterative message-passing algorithms.
Frey studied computer engineering and physics at the University of Calgary (BSc 1990) and the University of Manitoba (MSc 1993), and then studied neural networks and graphical models as a doctoral candidate at the University of Toronto under the supervision of Geoffrey Hinton (PhD 1997). He was an invited participant of the Machine Learning program at the Isaac Newton Institute for Mathematical Sciences in Cambridge, UK (1997) and was a Beckman Fellow at the University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign (1999).
Following his undergraduate studies, Frey worked as a Junior Research Scientist at Bell-Northern Research from 1990 to 1991. After completing his postdoctoral studies at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Frey was an Assistant Professor in the Department of Computer Science at the University of Waterloo, from 1999 to 2001.
In 2001, Frey joined the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the University of Toronto and was cross-appointed to the Department of Computer Science, the Banting and Best Department of Medical Research and the Terrence Donnelly Centre for Cellular and Biomolecular Research. From 2008 to 2009, he was a Visiting Researcher at Microsoft Research, Cambridge, UK, and a Visiting Professor in the Cavendish Laboratories and Darwin College at Cambridge University. Between 2001 and 2014, Frey consulted for several groups at Microsoft Research and acted as a member of its Technical Advisory Board.
Full Interview ► https://goo.gl/YYdVUH
BioViva ► http://bioviva-science.com
Liz Parrish is the Founder and CEO of BioViva Sciences USA Inc. BioViva is committed to extending healthy lifespans using gene therapy. Liz is known as “the woman who wants to genetically engineer you,” she is a humanitarian, entrepreneur and innovator and a leading voice for genetic cures. As a strong proponent of progress and education for the advancement of gene therapy, she serves as a motivational speaker to the public at large for the life sciences. She is actively involved in international educational media outreach and sits on the board of the International Longevity Alliance (ILA). She is the founder of BioTrove Investments LLC and the BioTrove Podcasts which is committed to offering a meaningful way for people to learn about and fund research in regenerative medicine. She is also the Secretary of the American Longevity Alliance (ALA) a 501©(3) nonprofit trade association that brings together individuals, companies, and organizations who work in advancing the emerging field of cellular & regenerative medicine with the aim to get governments to consider aging a disease. Parrish received two kinds of injections, which were administered outside the United States: a myostatin inhibitor, which is expected to prevent age-associated muscle loss; and a telomerase gene therapy, which is expected to lengthen telomeres, segments of DNA at the ends of chromosomes whose shortening is associated with aging and degenerative disease.
——-
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/agingreversed
Tumblr: http://agingreversed.tumblr.com
Twitter: https://twitter.com/Aging_Reversed
Another bit of science fiction is coming to life as scientists develop a highly elastic and adhesive surgical glue similar to the one Ryan Gosling used to seal his wound in Blade Runner 2049.
Surgeons use sutures, staples, and wires (sometimes in combination with adhesive substances) to facilitate healing of external and internal wounds. These methods, however, are not optimal, especially for reconnecting contracting tissues like those of lungs, arteries and the heart.
Sutures are also not ideal for preventing the leaking of liquids from incisions. In addition, piercing tissues to place sutures can further damage the surrounding wound area and can increase the risk for infection.
All over Silicon Valley and the regions that imitate it, executives follow weird revitalization fads. They think the code of aging can be hacked and death made optional. Daniel Gross, a partner at Y Combinator, fasts enthusiastically—and encourages others to do so—because he believes it will extend his life. Inventor Ray Kurzweil swallows 100 supplements a day for the same reason, presumably so he’ll live long enough to be uploaded into the singularity, circa 2045.
But you don’t have to be a prophet of posthumanism to wish for a few more good years. I’ve followed my own antiaging routines: For a time I ate 30 percent fewer calories than recommended, and I now starve myself for 16 of every 24 hours. And while there’s certainly plenty of folly in the tech elite’s quest for immortality, I’m glad they’ve embarked on it—for reasons that go beyond sheer entertainment value.
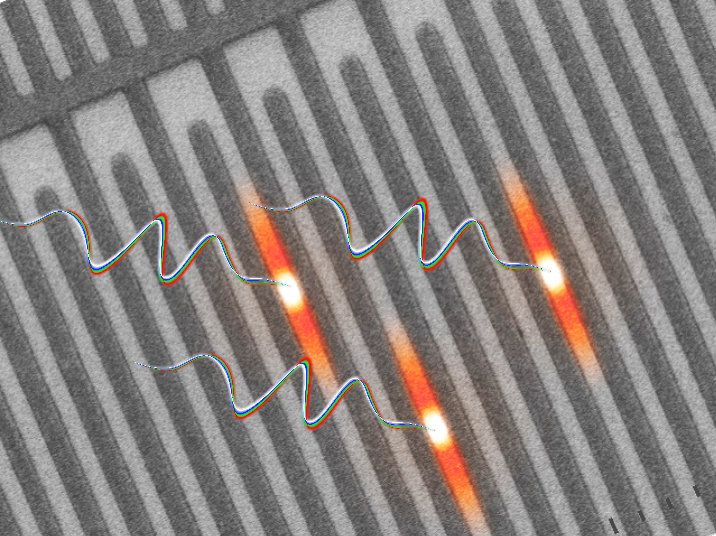
Engineers have shown that a widely used method of detecting single photons can also count the presence of at least four photons at a time. The researchers say this discovery will unlock new capabilities in physics labs working in quantum information science around the world, while providing easier paths to developing quantum-based technologies.
The study was a collaboration between Duke University, the Ohio State University and industry partner Quantum Opus, and appeared online on December 14 in the journal Optica.
“Experts in the field were trying to do this more than a decade ago, but their back-of-the-envelope calculations concluded it would be impossible,” said Daniel Gauthier, a professor of physics at Ohio State who was formerly the chair of physics at Duke. “They went on to do different things and never revisited it. They had it locked in their mind that it wasn’t possible and that it wasn’t worth spending time on.”
A cylindrical rod is rotationally symmetric — after any arbitrary rotation around its axis it always looks the same. If an increasingly large force is applied to it in the longitudinal direction, however, it will eventually buckle and lose its rotational symmetry. Such processes, known as “spontaneous symmetry breaking”, also occur in subtle ways in the microscopic quantum world, where they are responsible for a number of fundamental phenomena such as magnetism and superconductivity. A team of researchers led by ETH professor Tilman Esslinger and Senior Scientist Tobias Donner at the Institute for Quantum Electronics has now studied the consequences of spontaneous symmetry breaking in detail using a quantum simulator. The results of their research have recently been published in the scientific journal Science.
Phase transitions caused by symmetry breaking
In their new work, Esslinger and his collaborators took a particular interest in phase transitions — physical processes, that is, in which the properties of a material change drastically, such as the transition of a material from solid to liquid or the spontaneous magnetization of a solid. In a particular type of phase transition that is caused by spontaneous symmetry breaking, so-called Higgs and Goldstone modes appear. Those modes describe how the particles in a material react collectively to a perturbation from the outside. “Such collective excitations have only been detected indirectly so far,” explains Julian Léonard, who obtained his doctorate in Esslinger’s laboratory now works as a post-doc at Harvard University, “but now we have succeeded in directly observing the character of those modes, which is dictated by symmetry.”
Breakthrough research from The University of Texas at Arlington and The University of Vermont could lead to a dramatic reduction in the cost and energy consumption of high-speed internet connections.
Nonlinear-optical effects, such as intensity-dependent refractive index, can be used to process data thousands of times faster than what can be achieved electronically. Such processing has, until now, worked only for one optical beam at a time because the nonlinear-optical effects also cause unwanted inter-beam interaction, or crosstalk, when multiple light beams are present.
An article published in the prestigious Nature Communications journal, by the research group of Michael Vasilyev, an electrical engineering professor at UTA, in collaboration with Taras I. Lakoba, a mathematics professor at UVM, detailed an experimental demonstration of an optical medium in which multiple beams of light can autocorrect their own shapes without affecting one another.