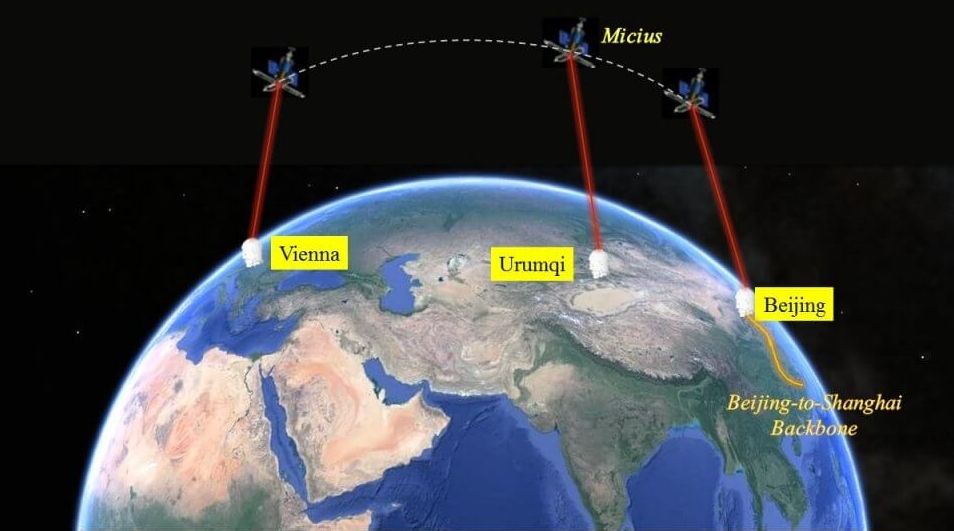
Cryptography and radar were technologies that won World War 2. Broken codes let the allies know where major forces were being moved. So the US fleet could choose where to intercept the Japanese Navy for the Battle of Midway. Radar and sonar then provided realtime tracking of the Japanese forces during the battle.
This is a summary of information from a Foreign Policy article by Thomas E. Ricks.
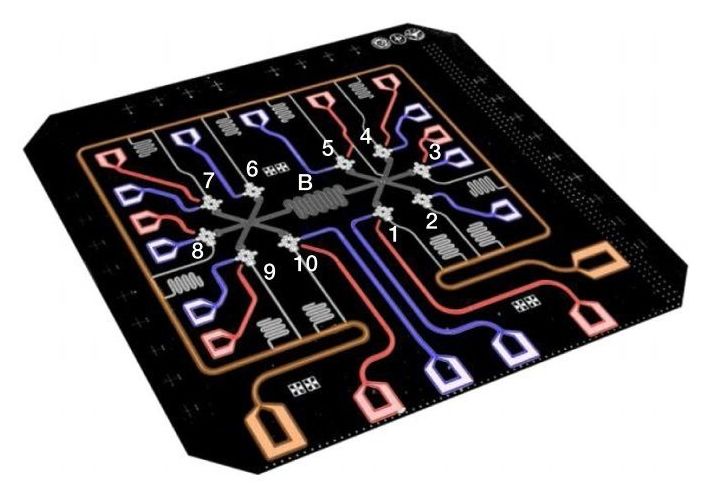
Quantum entanglement, quantum superposition, and quantum tunneling can be applied in new forms of computation, sensing, and cryptography.