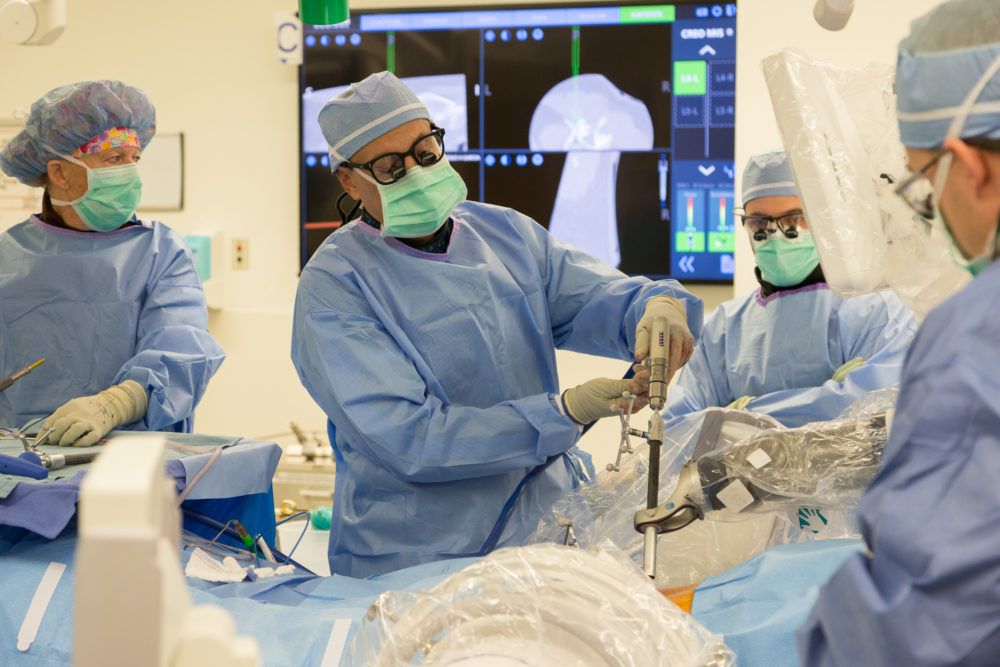
The Globus Medical ExcelsiusGPS, a spine surgery robot developed at Barrow, provides patients with less-invasive and more precise surgery. Learn More.
A faster way to fusion
Posted in engineering, nuclear energy
The benefits of fusion power are globally recognised. But the process of creating and commercialising fusion energy is a considerable scientific and engineering challenge.
This challenge is the sole focus of our work at Tokamak Energy. We believe we have a unique solution that will enable fusion to be implemented efficiently and quickly.
We are pioneering the compact spherical tokamak route to fusion power – exploring and developing our own compact spherical tokamaks (the device in which controlled fusion can take place) that will use high temperature superconductors to create strong magnetic fields to contain the hot plasma.
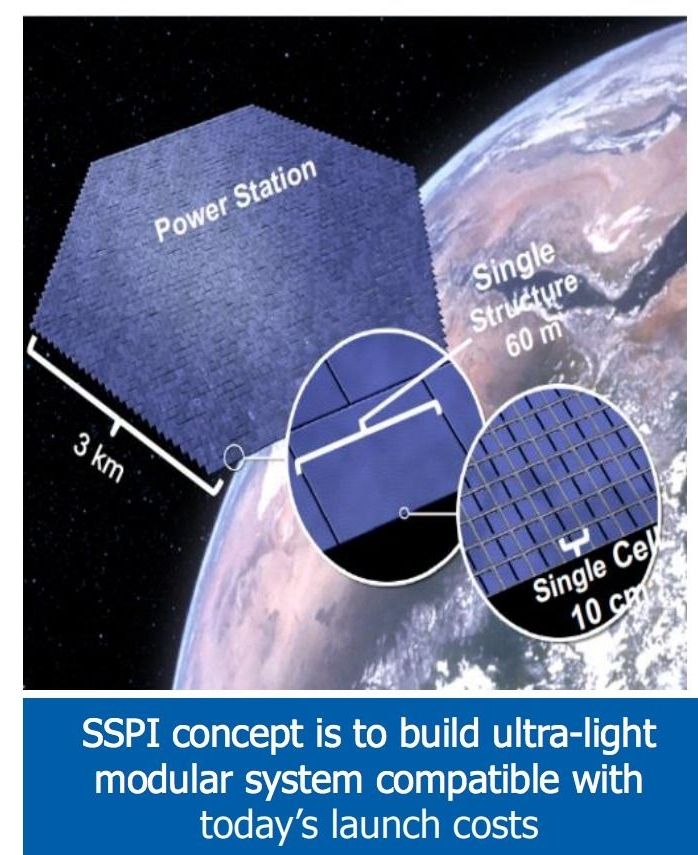
SSPI approach: • Enabling technologies developed at Caltech • Ultra-light deployable space structures • High efficiency ultra-light photovoltaic (PV) • Phased Array and Power Transmission • Integration of concentrating PV, radiators, MW power conversion and antennas in single cell unit • Localized electronics and control for system robustness, electronic beam steering • Identical spacecraft flying in formation • Target is specific power over 2000 Watts per kilogram. This would cost competitive with ground-based power.
One of the more well-known rules in physics is that light can only ever go one speed, so long as nothing stands in its way.
But new research has found there could be an interesting exception to this rule, where the mixing of light waves could bring them to a complete standstill.
The discovery hints at new ways of wrangling not just photons but nearly any kind of wave, which could be useful in technology that relies on information sent and stored using light.
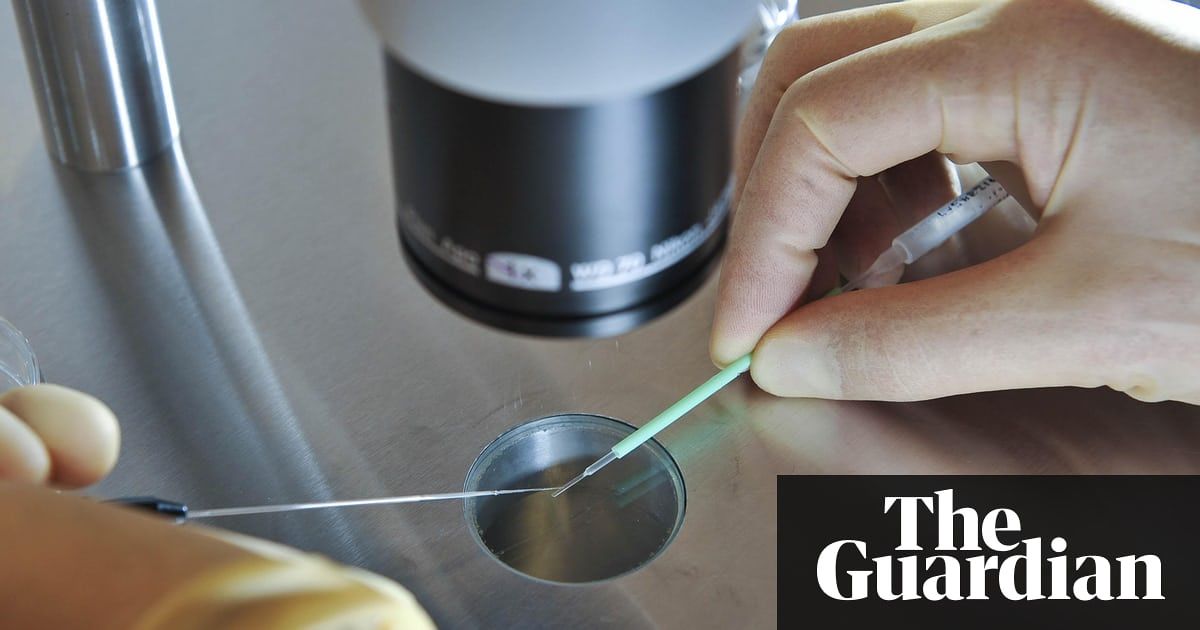
Will the benefits of making data more widely available outweigh such risks? The signs are that they will. Plenty of countries are now opening up their medical records, but few have gone as far as Sweden. It aims to give all its citizens electronic access to their medical records by 2020; over a third of Swedes have already set up accounts. Studies show that patients with such access have a better understanding of their illnesses, and that their treatment is more successful. Trials in America and Canada have produced not just happier patients but lower costs, as clinicians fielded fewer inquiries. That should be no surprise. No one has a greater interest in your health than you do. Trust in Doctor You.
NO WONDER they are called “patients”. When people enter the health-care systems of rich countries today, they know what they will get: prodding doctors, endless tests, baffling jargon, rising costs and, above all, long waits. Some stoicism will always be needed, because health care is complex and diligence matters. But frustration is boiling over. This week three of the biggest names in American business—Amazon, Berkshire Hathaway and JPMorgan Chase—announced a new venture to provide better, cheaper health care for their employees. A fundamental problem with today’s system is that patients lack knowledge and control. Access to data can bestow both.
The internet already enables patients to seek online consultations when and where it suits them. You can take over-the-counter tests to analyse your blood, sequence your genome and check on the bacteria in your gut. Yet radical change demands a shift in emphasis, from providers to patients and from doctors to data. That shift is happening. Technologies such as the smartphone allow people to monitor their own health. The possibilities multiply when you add the crucial missing ingredients—access to your own medical records and the ability easily to share information with those you trust. That allows you to reduce inefficiencies in your own treatment and also to provide data to help train medical algorithms. You can enhance your own care and everyone else’s, too.
Upgrade your inbox.
Two women with gene mutation that causes degenerative disorder will undergo therapy.
Ian Sample Science editor.
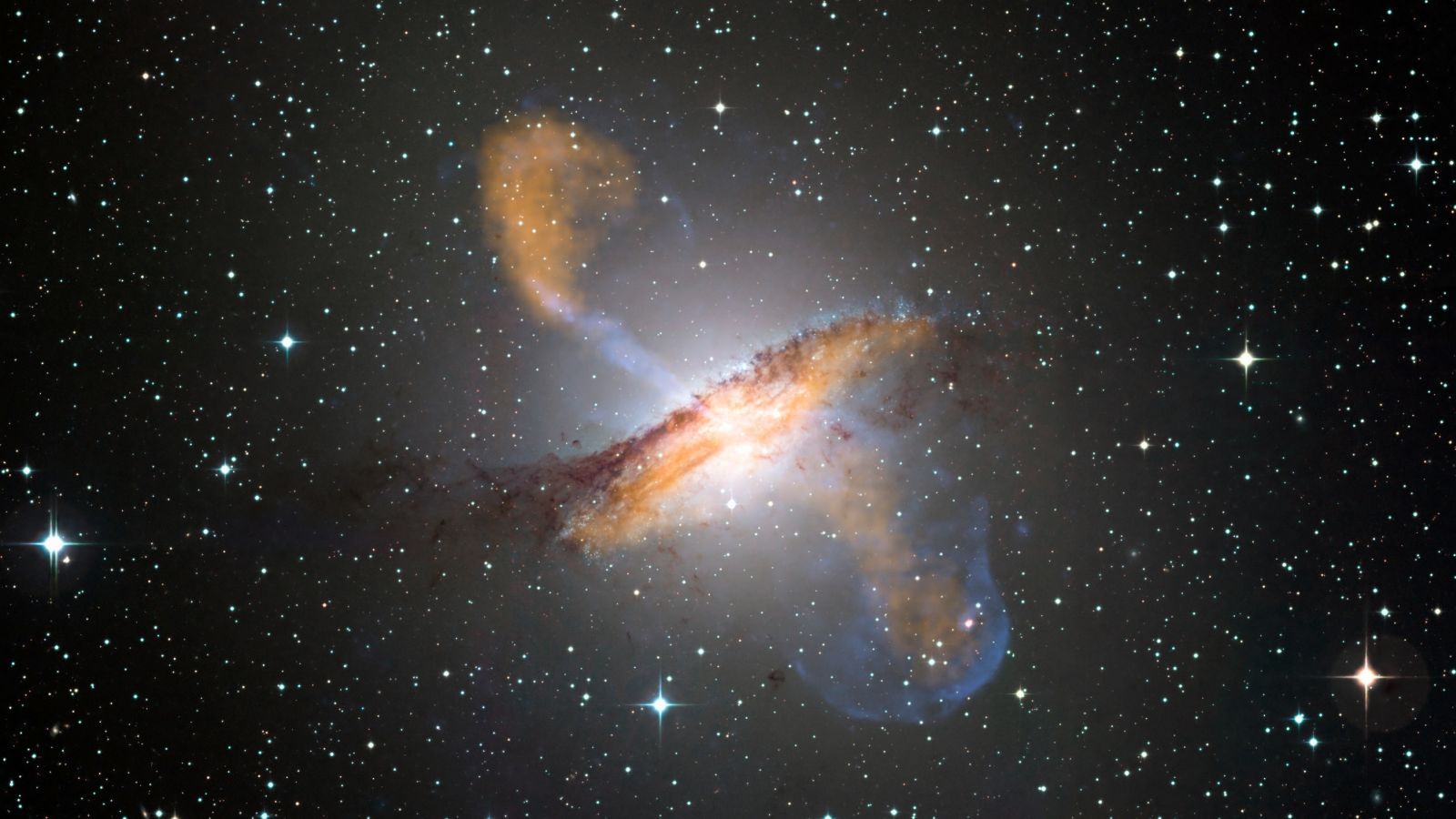
Scientists thought the Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies were unique: They’ve got rings of smaller dwarf galaxies orbiting in what seems to be a synchronized fashion. But when a team of scientists recently looked at another galaxy, they realized it also seemed to shepherd a flock of dwarfs in a strange, synchronized dance. That’s not supposed to happen.
An international team of four researchers noticed the behavior in the elliptical Centaurus A galaxy, 30 million light years away from our own Milky Way. Dwarf galaxies should travel randomly around their parent, based on the standard theory of how galaxies form. Seeing yet another galaxy with this strange behavior is highly unlikely, and calls into question the very model that scientists use to understand structure in our universe.
Sure, you would expect to find one galaxy with this behavior, study author Oliver Müller from the University of Basel in Switzerland told Gizmodo. “But two or three is startling.”