A research team composed of scientists from the Institute of Bioengineering and Nanotechnology (IBN) of the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) and IBM Research has produced a new synthetic molecule that can target and kill five multidrug-resistant bacteria. This synthetic polymer was found to be non-toxic and could enable entirely new classes of therapeutics to address the growing problem of antibiotic-resistant superbugs.
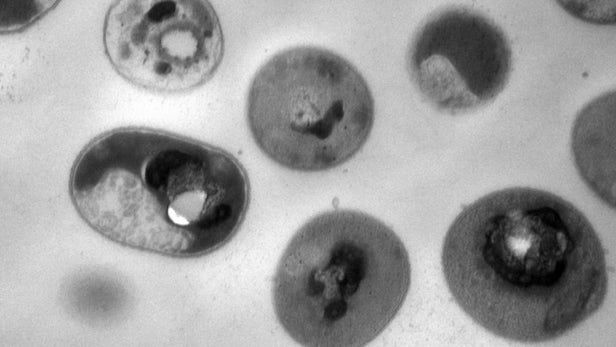
The synthetic molecules are called guanidinium-functionalized polycarbonates and were found to be both biodegradable and non-toxic to human cells. Essentially, the positively-charged synthetic polymer enters a living body and binds specifically to certain bacteria cells by homing in on a microbial membrane’s related negative charge. Once attached to the bacteria, the polymer crosses the cell membrane and triggers the solidification of proteins and DNA in the cell, killing the bacteria.