Medications for opioid addiction work. Most prisons and jails don’t offer them.


To address the challenge, some startups are making chips focused on specific software tasks. Others are pushing further, finding processing and storage solutions in new materials, including synthetic DNA.
Quantum computing is the best-known of these new methods. Startups as well as tech giants including Alphabet Inc.’s Google and International Business Machines Corp. are developing quantum computers, which harness the properties of quantum physics to sort through a vast number of possibilities in nearly real time. The advent of quantum computing has paved the way for other experimental techniques, startup executives say.
The market for new computing technology comes as advancements in traditional chip making are hitting a physical limit under Moore’s Law, the idea that every two years or so, the number of transistors in a chip doubles.
At the same time, advances in artificial intelligence, easier access to huge troves of data and the continuing digitization of business processes are putting new demands on corporate and scientific computing.

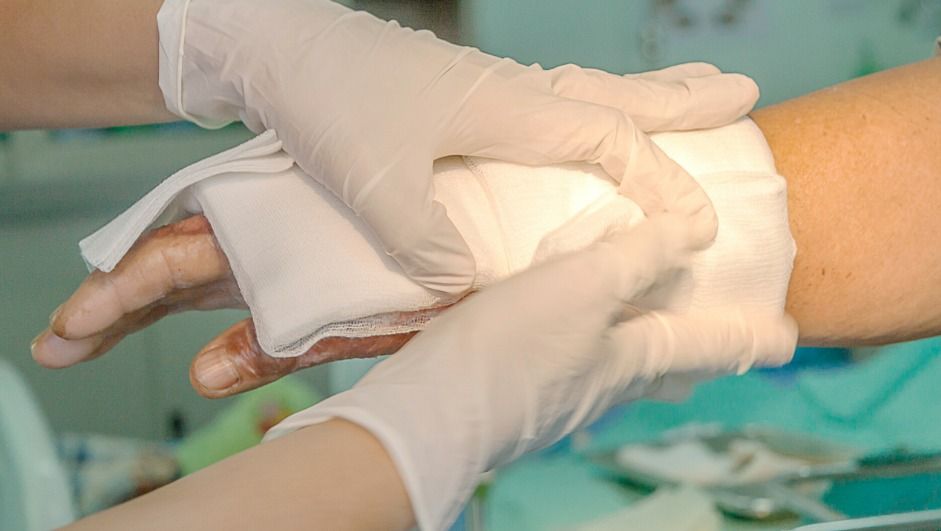
A burn that is over 25% of the human body area can be life threatening. However a burn that is only 1 percent but on a visible area of the body can be life-worsening. That is why advancements in the area of wound care and burns treatment are so important from patient perspective. Being a doctor of the future will include having a point-of-care device such as a 3D-Bioprinter that will scan the lesions in dept and width and print a gel imbued with cells and prolo-factors.
Forgive me my conservatism… we already have such clinics that are on the clinical trials for such treatments.
Read more in the article. Stay tuned for more topics through the Academy blog. Gain more knowledge in Regenerative Medicine and practical experience with biologics through the Annual Congress — Global Regenerative Congress 18–20 September 2020 in Dubai. Registrations are open: www.grc2020dubai.com
Researchers from the University of Toronto (ON, Canada) have reported success in trials of a handheld bioprinter for treating serious burns and wounds.

One of the biggest problems in the sneaker resale market may now be more manageable.
Product authentication technology provider Entrupy on Wednesday released its Legit Check Tech (LCT) solution, a device that uses artificial intelligence to determine whether a sneaker is counterfeit or not — and it only takes about a minute to use.
Fake pairs of popular Nike and Adidas sneakers are rampant in the resale sector. Authorities recently busted a counterfeiting operation that shipped $470 million worth of fake Nikes to the US.
This handheld 3D printer deposits layers of skin tissue, and could one day help to heal deep wounds. Instead of waiting for skin patches to grow in a Petri dish, you apply it directly.
A team of Canadian scientists has successfully applied skin tissue to burn wounds using a handheld 3D printer. This technology may become a game-changer in the way severe burn victims are treated.
The handheld skin 3D printer, the work of scientists at the University of Toronto Engineering and Sunnybrook Hospital, was first shown back in 2018. Since then it has undergone a major redesign that improves upon the initial model’s functionality.
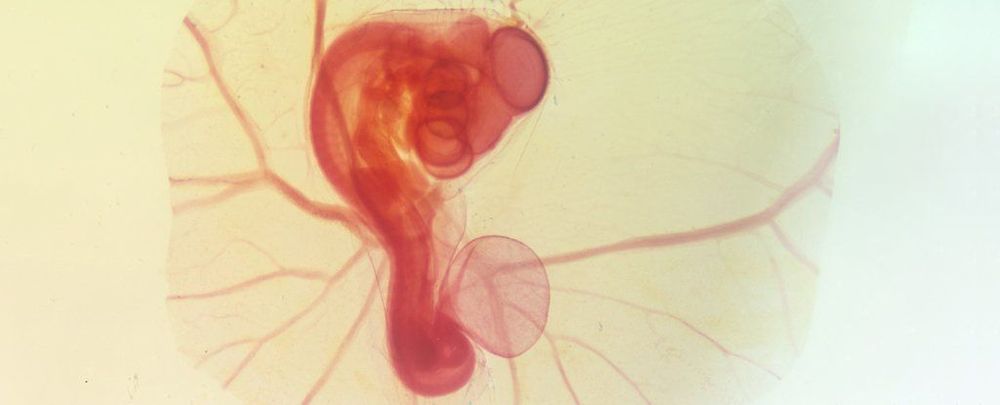
More than a year ago, the world was shocked by Chinese biophysicist He Jiankui’s attempt to use CRISPR technology to modify human embryos and make them resistant to HIV, which led to the birth of twins Lulu and Nana.
Now, crucial details have been revealed in a recent release of excerpts from the study, which have triggered a series of concerns about how Lulu and Nana’s genome was modified.
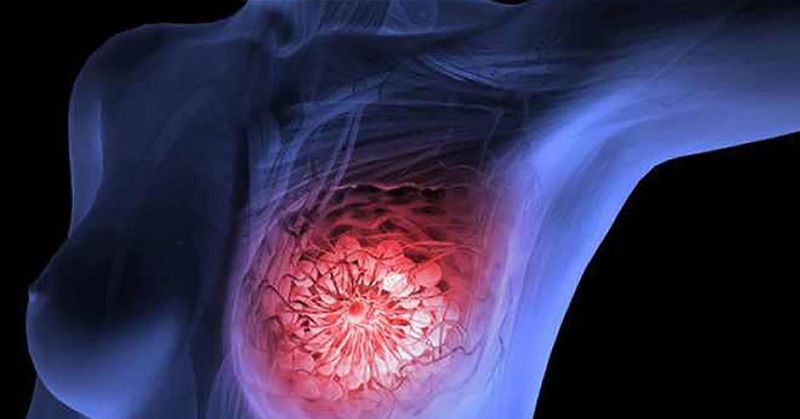
HER2-positive breast cancer is a type of aggressive cancer marked by uncontrolled production of breast cells. About 20% of women and men diagnosed with breast cancer have HER2-positive cancer, specifically.
Currently, oncologists treat HER2-positive breast cancer patients with surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or targeted treatments like Herceptin (trastuzumab), Kadcyla (Ado-trastuzumab-emtansine), Perjeta (Pertuzumab), and Tykerb (Lapatinib).
These targeted treatments work by interfering with the protein that signals breast cell production, and they’re often used in conjunction with chemotherapy, which undoubtedly, can be a very arduous treatment process.
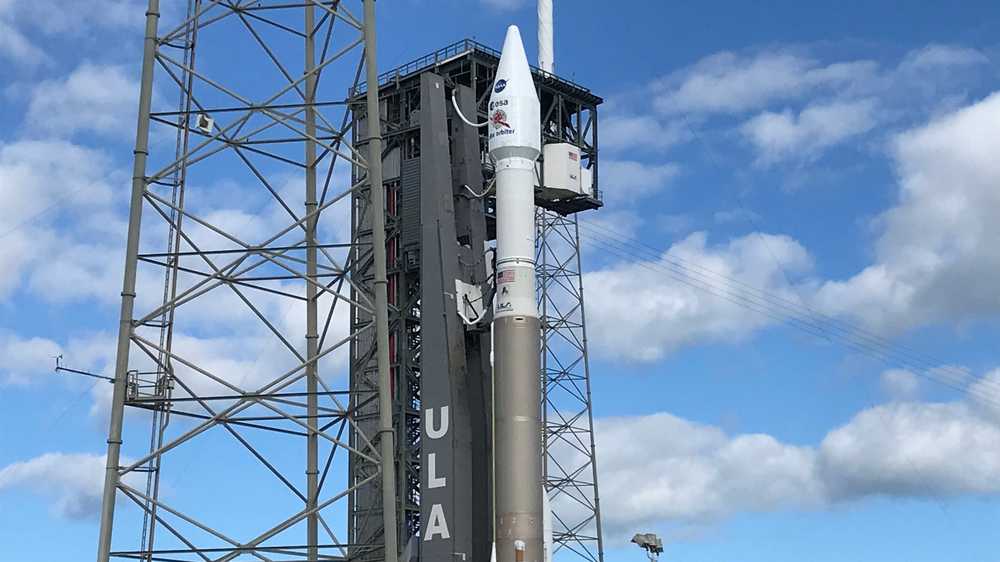

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket launches from Cape Canaveral with the Solar Orbiter probe on Sunday, Feb. 9, 2020. Florida Today.
Connect tweet linkedin comment email more
Update: LIFTOFF of Atlas V at 11:03 p.m. with Solar Orbiter!
Follow live as Solar Orbiter, a probe slated to study the sun, takes flight on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral. Liftoff is planned for 11:03 p.m. Eastern time. Teams have two hours to launch.