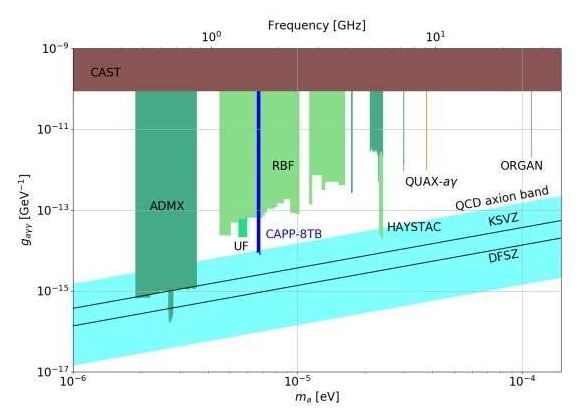
Researchers at the Center for Axion and Precision Physics Research (CAPP), within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS, South Korea), have reported the first results of their search of axions, elusive, ultra-lightweight particles that are considered dark matter candidates. IBS-CAPP is located at Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST). Published in Physical Review Letters, the analysis combines data taken over three months with a new axion-hunting apparatus developed over the last two years.
Proving the existence of axions could solve two of the biggest mysteries in modern physics at once: why galaxies orbiting within galaxy clusters are moving far faster than expected, and why two fundamental forces of nature follow different symmetry rules. The first conundrum was raised back in the 1930s, and was confirmed in the 1970s when astronomers noticed that the observed mass of the Milky Way galaxy could not explain the strong gravitational pull experienced by the stars in the galaxies. The second enigma, known as the strong CP problem, was dubbed by Forbes magazine as “the most underrated puzzle in all of physics” in 2019.
Symmetry is an important element of particle physics and CP refers to the Charge+Parity symmetry, where the laws of physics are the same if particles are interchanged with their corresponding antiparticles © in their mirror images ℗. In the case of the strong force, which is responsible for keeping nuclei together, CP violation is allowed theoretically, but has never been detected, even in the most sensitive experiments. On the other hand, CP symmetry is violated both theoretically and experimentally in the weak force, which underlies some types of radioactive decays. In 1977, theoretical physicists Roberto Peccei and Helen Quinn proposed the Peccei-Quinn symmetry as a theoretical solution to this problem, and two Nobel laureates in Physics, Frank Wilczek and Steven Weinberg, showed that the Peccei-Quinn symmetry results in a new particle: the axion. The particle was named after an American detergent, because it should clean the strong interactions mess.