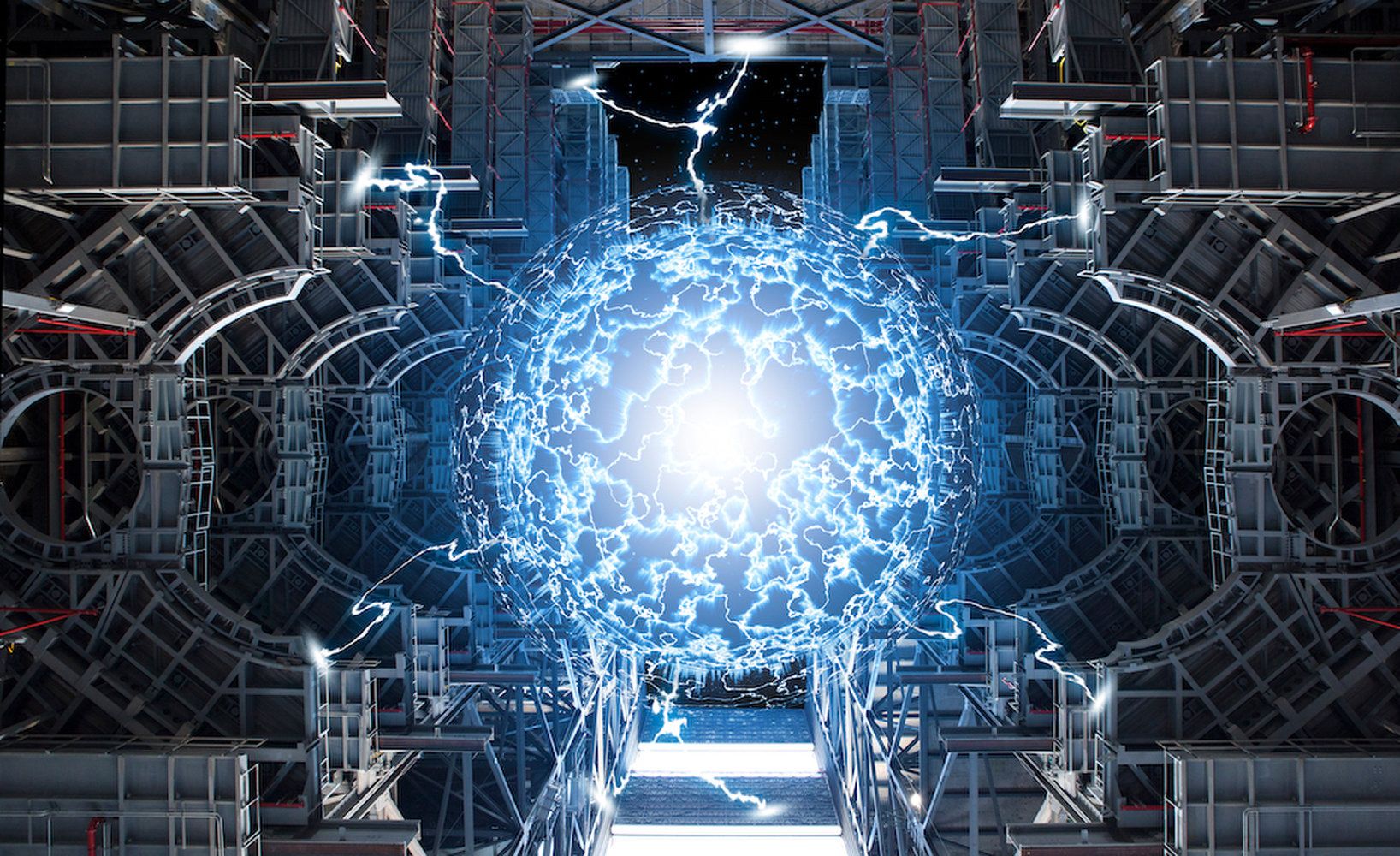
Weird waves that whisper through the ionosphere have also been discovered inside the plasma of nuclear fusion reactors. They could help stop runaway electrons.
The technical skills of programmer John Carmack helped create the 3D world of Doom, the first-person shooter that took over the world 25 years ago. But it was level designers like John Romero and American McGee that made the game fun to play. Level designers that, today, might find their jobs threatened by the ever-growing capabilities of artificial intelligence.
One of the many reasons Doom became so incredibly popular was that id Software made tools available that let anyone create their own levels for the game, resulting in thousands of free ways to add to its replay value. First-person 3D games and their level design have advanced by leaps and bounds since the original Doom’s release, but the sheer volume of user-created content made it the ideal game for training an AI to create its own levels.
Researchers at the Politecnico di Milano university in Italy created a generative adversarial network for the task, which essentially uses two artificially intelligent algorithms working against each other to optimise the overall results. One algorithm was fed thousands of Doom levels which it analysed for criteria like overall size, enemy placement, and the number of rooms. It then used what it learned to generate its own original Doom levels.
Stem cells in the brain can divide and mature into neurons participating in various brain functions, including memory. In a paper scientists have discovered that the flow of cerebrospinal fluid is a key signal for neural stem cell renewal.
The ancient Greek aphorism panta rhei means “everything flows”, a phrase used by philosophers to describe the constant flux and interplay between the past and renewal. A recent paper lends this relationship a whole new meaning: a team of researchers headed by Professor Magdalena Götz and their collaborators from the LMU (Professor Benedikt Grothe, Chair of Neurobiology) and the Henrich-Heine University Düsseldorf have discovered that the flow of cerebrospinal fluid is a key signal for neural stem cell renewal.
“Neural stem cells in the brain can divide and mature into neurons and this process plays important roles in various regions of the brain – including olfactory sense and memory,” explains Magdalena Götz, Head of LMU Department of Physiological Genomics and Director of the Institute for Stem Cell Research at Helmholtz Zentrum München. “These cells are located in what is known as the neurogenic stem cell niche one of which is located at the walls of the lateral ventricles, where they are in contact with circulating cerebrospinal fluid.”
Without saying anything this device will let you talk to your computer — https://www.weforum.org/…/computer-system-transcribes-words…
MIT researchers have developed a computer interface that can transcribe words that the user concentrates on verbalizing but does not actually speak aloud.
The system consists of a wearable device and an associated computing system. Electrodes in the device pick up neuromuscular signals in the jaw and face that are triggered by internal verbalizations — saying words “in your head” — but are undetectable to the human eye. The signals are fed to a machine-learning system that has been trained to correlate particular signals with particular words.
The device also includes a pair of bone-conduction headphones, which transmit vibrations through the bones of the face to the inner ear. Because they don’t obstruct the ear canal, the headphones enable the system to convey information to the user without interrupting conversation or otherwise interfering with the user’s auditory experience.
Astronomers found a strange dwarf world that provides even more evidence that a giant planet is lurking at the edge of our solar system.
Getty Images Mark Garlick/Science Photo Library.
There might be a large planet lurking somewhere at the very edge of our solar system, and astronomers are hunting for it. While they have yet to find direct evidence of the planet, a recent discovery provides yet more indirect evidence that the planet does, in fact, exist. Astronomers found a small solar system body with a strange orbit that they say can only be explained by another, bigger planet hiding out there somewhere.
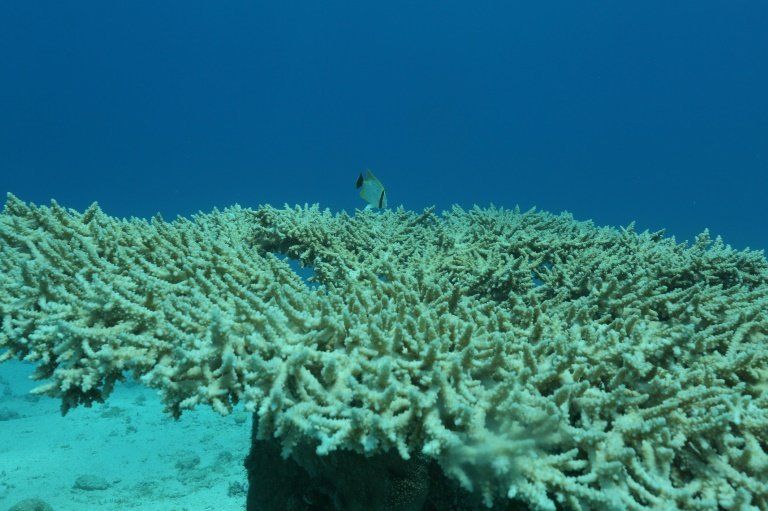
Coral reefs are the fish nurseries and so without them there will be no fish!
Japan’s biggest coral reef has not recovered from bleaching due to rising sea temperatures, with only one percent of the reef in a healthy condition, according to a government study.
The overall volume of coral in Sekisei Lagoon in southwestern Japan near Okinawa had already plunged by 80 percent since the late 1980s due to rising water temperatures and damage caused by coral-eating starfish.
Now only 1.4 percent of the lagoon, which stretches over 67.89 square kilometres, is in a healthy condition, the environment ministry said, after it was hit by mass bleaching in 1998, 2001, 2007 and most recently 2016.
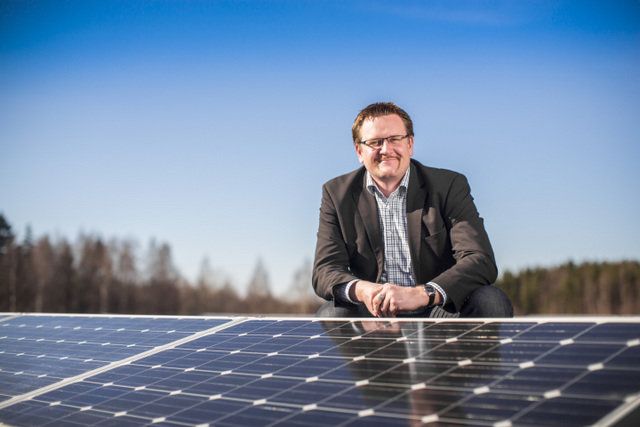
A new energy storage system developed by University of Adelaide researchers and industry partners is now successfully supporting the electricity network for the country town of Cape Jervis, South Australia.
The new, world-class system is part of a $3.65 million trial led by the University of Adelaide in collaboration with SA Power Networks and system supplier PowerTec. The project is supported by the Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA) on behalf of the Australian Government with $1.44 million in grant funding.
The mobile battery energy storage system and its specialised control system reduces peak load of the local substation, stabilises the electricity network in the area, and supports a number of nearby customers in the event of a power interruption – all without manual intervention.
Is there enough space for all the wind turbines and solar panels to provide all our energy needs? What happens when the sun doesn’t shine and the wind doesn’t blow? Won’t renewables destabilise the grid and cause blackouts?
In a review paper last year in the high-ranking journal Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, researcher Benjamin Heard and colleagues presented their case against 100 percent renewable electrical systems. They doubted the feasibility of many of the recent scenarios for high shares of renewable energy, questioning everything from whether renewables-based systems can survive extreme weather events with low sun and low wind, to the ability to keep the grid stable with so much variable generation.
Now, scientists have hit back with their response to the points raised by Heard and colleagues. The researchers from the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology and collaborators have analysed hundreds of studies to answer each of the apparent issues. They demonstrate that there are no roadblocks to a 100 percent renewable future.
Important new study to track — “The team will start recruiting the first of 1,000 low-income mothers next week…Of that 1,000, roughly half will be randomly selected to receive an unconditional $333 a month, while the others will form a control group that will receive $20. The money, which is completely unconditional, will be loaded onto a pre-paid debit card every month for 40 months, on the date of the child’s birthday. The hypothesis is that this steady stream of payments will make a positive difference in the cognitive and emotional development of the children whose mothers receive it”
___ Does growing up poor harm brain development? (The Economist): “Plenty of evidence suggests that growing up poor, living through these kinds of scrapes, has a detrimental impact on child development. Children from rich families tend to have better language and memory skills than those from poor families. More.