By Nichols, Steve. Download it once and read it on your Kindle device, PC, phones or tablets. Use features like bookmarks, note taking and highlighting while reading THE 31st GOD: Becoming a Deity through Zenet.


We are in this together. From oxygen hoods to ventilators, our scientists and engineers across the agency are uniting to join the fight against coronavirus. Tune in to #NASAScience Live on June 25 at 3 p.m. EDT to watch this nationwide effort.
Vikki was born without her right hand and says her “life has changed forever” after receiving a Hero Arm. Vikki’s bionic arm was funded by generous donors, and there’s more funding available now for upper limb amputees from low-income families! Apply here: http://www.openbionics.com/sign-up 😍😍😍.

🤔
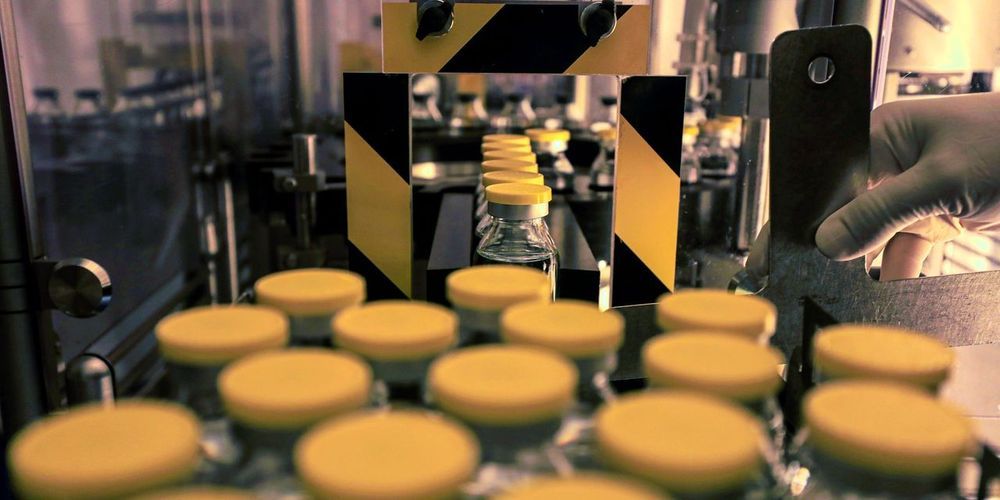
Gilead’s Covid-19 drug remdesivir will be priced at $3,120 for a typical U.S. patient with commercial insurance.
Gilead Sciences Inc. detailed its pricing plans for Covid-19 drug remdesivir, saying it will charge U.S. hospitals $3,120 for a typical patient with commercial insurance.
The drugmaker on Monday disclosed its pricing plans as it prepares to begin charging for the drug in July. The U.S. has been distributing remdesivir donated by Gilead since the drug was authorized for emergency use in May.
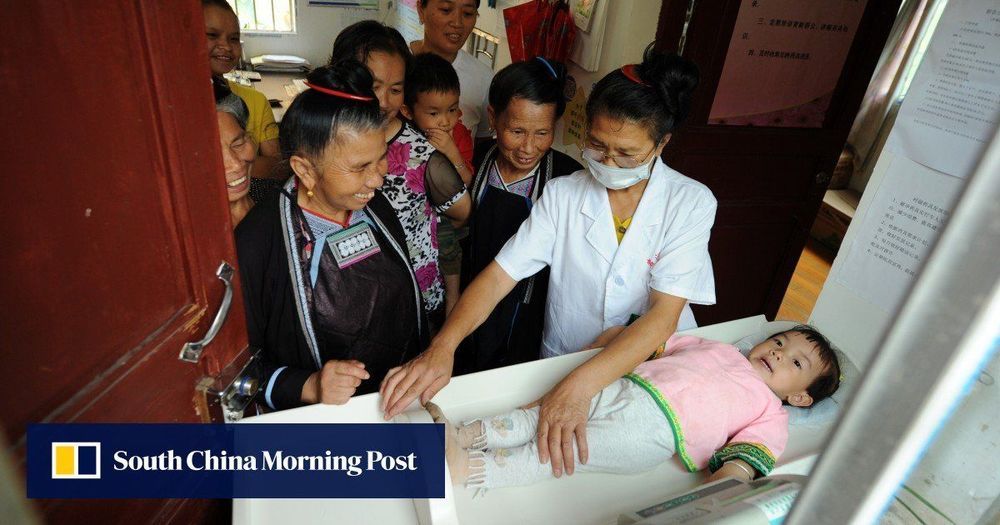

However, the situation has been improving as Chinese tech giants including e-commerce company Alibaba, search engine Baidu, on-demand delivery company Meituan Dianping, ride-hailing operator Didi Chuxing and smartphone maker Xiaomi now offer more affordable health care plans via mutual aid platforms, which operate as a collective claim-sharing mechanism.
China’s online mutual aid platforms are disrupting old school insurance companies by leveraging big data and internet finance technologies to offer low cost medical coverage.


Physicists from the University of Glasgow and the University of Arizona have experimentally verified a half-century-old theory that began as speculation about how an advanced alien civilization could use a rotating black hole to generate energy.
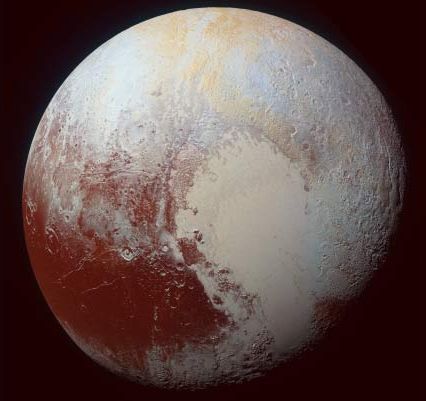

Pluto is thought to possess a subsurface ocean beneath its thick ice shell. It has generally been assumed that the dwarf planet formed out of cold material and then later developed its ocean due to warming from radioactive decay. By combining numerical simulations with geological observations by NASA’s New Horizons mission, a team of researchers from the University of California Santa Cruz and the Southwest Research Institute demonstrated that Pluto was instead relatively hot when it formed, with an early subsurface ocean.